CSS 选择器
1、CSS 元素选择器
如果设置 HTML 的样式,选择器通常将是某个 HTML 元素,比如 p、h1、em、a,甚至可以是 html 本身。
这是 heading 1
这是 heading 2
这是一段普通的段落。
2、CSS 选择器分组
这是 heading 1
这是 heading 2
这是 heading 3
这是 heading 4
这是一段普通的段落文本。
通配选择器(universal selector),显示为一个星号(*)。该选择器可以与任何元素匹配,就像是一个通配符。
例如,下面的规则可以使文档中的每个元素都为红色:
这是 heading 1
这是 heading 2
这是 heading 3
这是 heading 4
这是一段普通的段落文本。
3、CSS 类选择器
类选择器允许以一种独立于文档元素的方式来指定样式。
该选择器可以单独使用,也可以与其他元素结合使用。
This heading is very important.
This paragraph is very important.
This is a paragraph.
This is a paragraph.
This is a paragraph.
...
4、CSS ID 选择器
ID 选择器前面有一个 # 号 - 也称为棋盘号或井号。
类选择器和ID选择器的区别
- 区别 1:只能在文档中使用一次
与类不同,在一个 HTML 文档中,ID 选择器会使用一次,而且仅一次。 - 区别 2:不能使用 ID 词列表
不同于类选择器,ID 选择器不能结合使用,因为 ID 属性不允许有以空格分隔的词列表。 - 区别 3:ID 能包含更多含义
类似于类,可以独立于元素来选择 ID。
5、CSS 属性选择器
属性选择器可以根据元素的属性及属性值来选择元素。
[title]
{
color:red;
}
a[href]
{
color:red;
}
6、CSS 后代选择器
注:两个元素之间的层次间隔可以是无限的。
例如,如果写作 ul em,这个语法就会选择从 ul 元素继承的所有 em 元素,而不论 em 的嵌套层次多深。
7、CSS 子元素选择器
与后代选择器相比,子元素选择器(Child selectors)只能选择作为某元素子元素的元素。
从右向左读,选择器 h1 > strong 可以解释为“选择作为 h1 元素子元素的所有 strong 元素”。
This is very very important.
This is really very important.
8、CSS 相邻兄弟选择器
相邻兄弟选择器(Adjacent sibling selector)可选择紧接在另一元素后的元素,且二者有相同父元素。
h1 + p {margin-top:50px;}
这个选择器读作:“选择紧接在 h1 元素后出现的段落,h1 和 p 元素拥有共同的父元素”。
html > body table + ul {margin-top:20px;}
这个选择器解释为:选择紧接在 table 元素后出现的所有兄弟 ul 元素,该 table 元素包含在一个 body 元素中,body 元素本身是 html 元素的子元素。
用一个结合符只能选择两个相邻兄弟中的第二个元素。
li + li {font-weight:bold;}
上面这个选择器只会把列表中的第二个和第三个列表项变为粗体。第一个列表项不受影响。
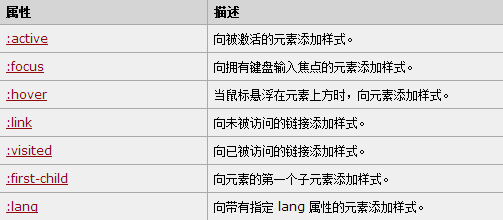
9、CSS伪类
伪类的语法:
selector:pseudo-class {property:value;}
CSS类也可以使用伪类:
selector.class:pseudo-class {property:value;}
CSS - :first - child伪类选择元素的第一个子元素
These are the necessary steps:
- Intert Key
- Turn key clockwise
- Push accelerator
Do not push the brake at the same time as the accelerator.
作为第一个元素的元素包括第一个 p、第一个 li 和 strong 和 em 元素。


p:first-child {font-weight: bold;}
li:first-child {text-transform:uppercase;}
第一个规则将作为某元素第一个子元素的所有 p 元素设置为粗体。第二个规则将作为某个元素(在 HTML 中,这肯定是 ol 或 ul 元素)第一个子元素的所有 li 元素变成大写。
- 例子 1 - 匹配第一个 < p > 元素
some text
some text
- 例子 2 - 匹配所有 < p > 元素中的第一个 < i > 元素
some text. some text.
some text. some text.
- 例子 3 - 匹配所有作为第一个子元素的 < p > 元素中的所有 < i > 元素
some text. some text.
some text. some text.
CSS - :lang 伪类使你有能力为不同的语言定义特殊的规则
Some text A quote in a paragraph
Some text.
在这个例子中,:lang定义了q元素的值为lang =“no”
10、CSS 伪元素
CSS 伪元素用于向某些选择器设置特殊效果。
伪元素的语法:
selector:pseudo-element {property:value;}
CSS 类也可以与伪元素配合使用:
selector.class:pseudo-element {property:value;}
:first-line 伪元素用于向文本的首行设置特殊样式。只能用于块级元素。
下面的属性可应用于 "first-line" 伪元素:
- font properties
- color properties
- background properties
- word-spacing
- letter-spacing
- text-decoration
- vertical-align
- text-transform
- line-height
- clear
this is a demo
:first-letter 伪元素用于向文本的首字母设置特殊样式。用于块级元素。
你可以使用 "first-letter" 伪元素向文本的首字母设置特殊样式:
注意: 下面的属性可应用于 "first-letter" 伪元素:
- font properties
- color properties
- background properties
- margin properties
- padding properties
- border properties
- text-decoration
- vertical-align (only if "float" is "none")
- text-transform
- line-height
- float
- clear