一,概览
先简单介绍下springMVC,它是spring众多模块中的一员。
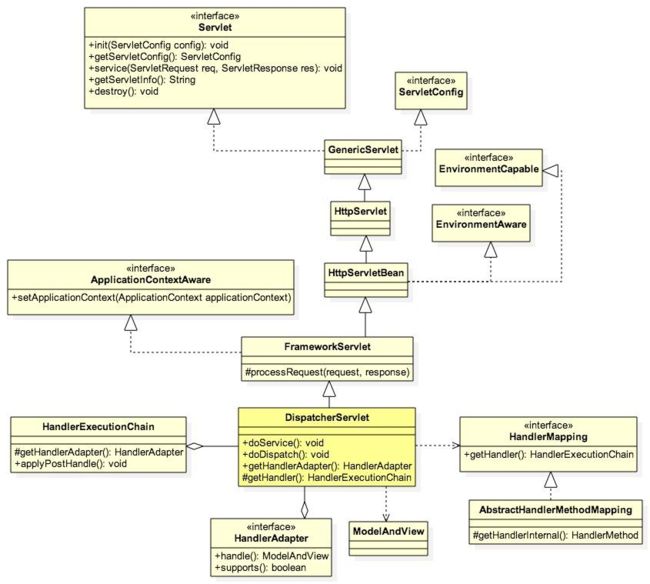
其中的核心处理类DispatcherServlet本质上是一个Servlet,是属于Java中web标准的javax包下面的一个接口,所以它是配置在web.xml下。每一个DispatcherServlet都有它自己的WebApplicationContext,继承自root WebApplicationContext,所以它可以使用root下配置的所以bean。(这里多说一句,因为这种继承关系,所以springmvc项目都存在2个WebApplicationContext,所以通常我们所有的bean都放在root中处理,否则可能出现bean无法注入等问题)
以下是DispatcherServlet结构图:
DispatcherServlet使用以下这些类来处理请求以及展示等。
| Bean type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| HandlerMapping | Maps incoming requests to handlers and a list of pre- and post-processors (handler interceptors) based on some criteria the details of which vary by HandlerMapping implementation. The most popular implementation supports annotated controllers but other implementations exists as well. |
| HandlerAdapter | Helps the DispatcherServlet to invoke a handler mapped to a request regardless of the handler is actually invoked. For example, invoking an annotated controller requires resolving various annotations. Thus the main purpose of a HandlerAdapteris to shield the DispatcherServlet from such details. |
| HandlerExceptionResolver | Maps exceptions to views also allowing for more complex exception handling code. |
| ViewResolver | Resolves logical String-based view names to actual View types. |
| LocaleResolver | Resolves the locale a client is using, in order to be able to offer internationalized views |
| ThemeResolver | Resolves themes your web application can use, for example, to offer personalized layouts |
| MultipartResolver | Parses multi-part requests for example to support processing file uploads from HTML forms. |
| FlashMapManager | Stores and retrieves the "input" and the "output" FlashMap that can be used to pass attributes from one request to another, usually across a redirect. |
二,处理流程
简单说下web项目的启动。略
1,首先标准的HTTP请求进入HttpServlet的service方法,然后根据请求方式调用具体的doGet()等方法。然后FrameworkServlet重写了service ,doGet等方法,并且再将不同类型的请求归并到processRequest()方法(有空再解释这个方法的内容)。processRequest()最核心的方法是doService(request, response),这个方法是abstract方法,这用到了well-known的模板方法模式。
//HttpServlet的service方法
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
/**
* Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome.
* The actual event handling is performed by the abstract
* {@link #doService} template method.
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
2,接下就进入到DispatcherServlet的doService方法。详解
3,doService调用了doDispatch方法。详解
抛开外部的异常处理,以及前后的Interceptor的处理,其中比较核心的是
根据request找到Handler;
根据Handler找到HandlerAdapter;
处理请求;
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//执行Interceptor PreHandle()
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
try {
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
}
applyDefaultViewName(request, mv);
//执行Interceptor PostHandle()
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Error err) {
triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
三,主要组件介绍
1,HandlerMapping ,主要是通过request找到Handler和Interceptors。
官方介绍:his maps a method to an URL, so that the DispatcherServlet will be able to invoke it when processing a request.And the DispatcherServlet uses the HandlerAdapter to actually invoke the method.
2,HandlerAdapter ,DispatcherServlet会通过Handler得到HandlerAdapter,HandlerAdapter再根据请求去定位请求的具体处理方法。
。。。。
to be continue