以下包含SpringBoot的入门Demo和 SpringBoot+Mybatis的整合入门demo(使用IDE是IDEA)
一、简介
1、SpringBoot提供一种固定的、约定优于配置风格的框架,使开发者更快地创建基于spring的应用和程序。
2、特性:
1、高效的创建基于spring的应用服务(不是对spring功能的增强,而是提供快速使用spring的方式)
2、鼓励注解配置
3、为微服务spring cloud铺路,可整合其他框架(如dubbo thrift等)
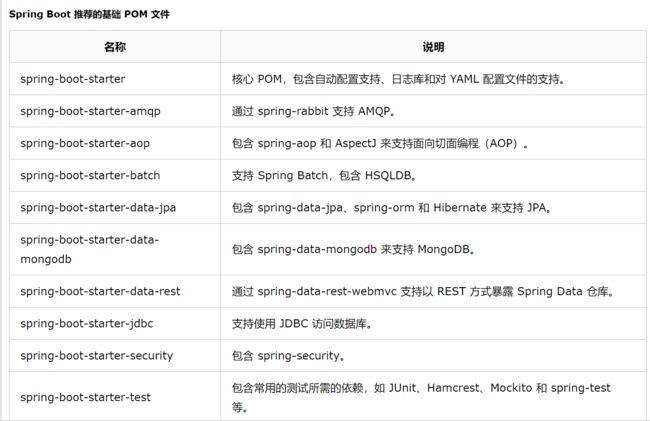
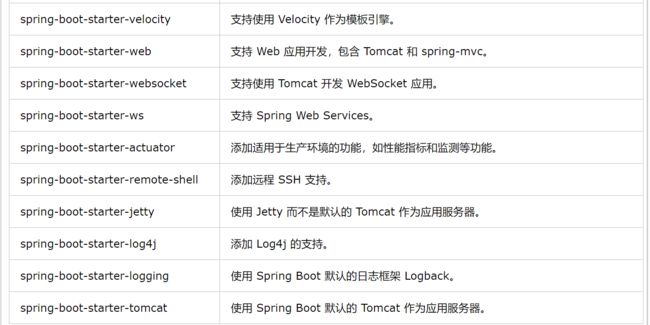
3、Spring Boot应用启动器:
首先pom.xml默认2个模块:
spring-boot-starter: Spring Boot的核心启动器,包含了自动配置支持、日志和YAML。
spring-boot-starter-test:测试模块,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito
spring-boot-starter-jdbc: 支持JDBC数据库。
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf: 支持Thymeleaf模板引擎,包括与Spring的集成。
spring-boot-starter-web: 支持全栈式开发,包括Tomcat和Spring-WebMVC。
mybatis-spring-boot-starter: 整合spring-mybatis依赖。
这些pom依赖为开发spring应用提供良好的基础,springboot的第三方库是比较适合产品开发的,其中也有些选择,如日志框架可以用 Logback 或 Log4j,应用服务器可以用 Tomcat 或 Jetty。
4、一些常用的注解:
启动类常用:
@SpringBootApplication:声明当前类为SpringBoot入口类,且项目只只能有一个
@RestController:声明当前类为控制层的类(等价于@Controller+@ResponseBody的结合,里面的方法都以json格式输出,不用再写什么jackjson配置的了)
二、下面是一个最简单的SpringBoot入门demo:
首先,生成SpringBoot web项目结构有两种办法:
1、用Spring initializer
2、用IDEA/Eclipse开放工具构建(一般springBoot推荐使用IDEA)
在创建时勾选spring initial,勾选web。
自动生成必要的DemoApplication作为启动类,对于web项目,也同样是通过启动该类,在地址栏输入映射地址达到访问目的。
HelloSpringboot.class:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloSpringboot {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String say() {
System.out.println("Hello springboot");
return "hello,this is a springboot demo!~";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password){
String result= "username:"+username+",password:"+password;
System.out.println(result);
return(result);
}
}
启动类DemoApplication.java:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试:
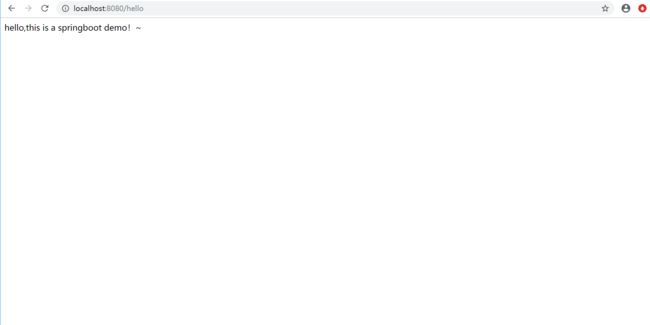
启动启动类DemoApplication.java,地址栏输入地址,若页面显示返回数据,则测试成功。
在地址栏输入:localhost:8080/hello
在地址栏输入:http://localhost:8080/login?username=tycoding&password=123
三、SpringBoot和Mybatis整合入门Demo
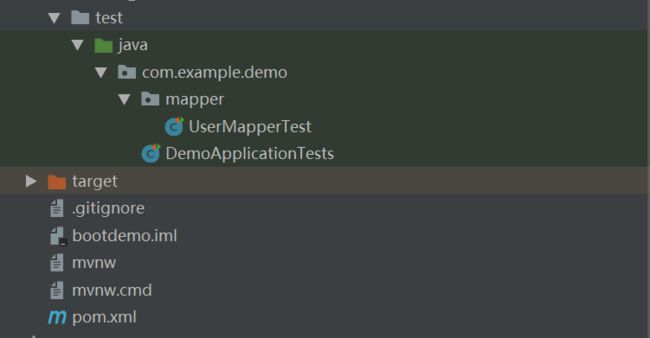
下面是项目整体目录结构:
1、创建项目,选择spring initial,选择 web,JDBC,mybatis,mysql,自动生成项目。由于后面用到了junit测试,所以pom.xml中引入junit包(版本要4.12以上)。
2、pom.xml
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.1.RELEASE
com.example
demo
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
demo
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
junit
junit
4.12
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2、使用mysql数据库,创建了表user,创建字段id(bigint) username(varchar(120)) password(varchar(20)) ,插入一些数据。
3、application.yml:配置文件,此处注意配置文件一般会自动生成在resource下,先将后缀改为yml(IDEA的自动解析要求所有的xml,yml等文件都放在resource下,且由于springBoot本身是去xml化的,所以一般会写成yml)
对springboot和jdbc、mybatis等都进行了简单的配置(此处尤其注意一些配置不能写错,在这也出现了不少bug导致研究了很长时间,这是debug的记录 SpringBoot+Mybatis web项目常见bug)
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
datasource:
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smtest?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
server:
port: 8080
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath*:mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.example.demo.entity
4、entity层:
User.class:
package com.example.demo.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
public User(Long id, String username, String password) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
5、Mapper层:注意不同于eclipse,IDEA的mapper.xml必须放在resource/mapper下。
UserMapper.java(接口,放在java.com.example.demo.mapper下):
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
public interface UserMapper {
User findById( Long id);
}
UserMapper.xml:(在resource/mapper下):
6、Service层:访问mapper
一些注解:
@Service:声明该类为Service类
@Resource:常常与@Autowired注解替换,声明为一个bean,@Autowire注解在IDEA中常会引起一些不必要的错误,IDEA会无法识别这是一个bean而报警告,此时可用@Resource
package com.example.demo.service;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
UserMapper userMapper;
public User findById(Long id){
return userMapper.findById(id);
}
}
7、Contoller控制层:
@RestController:声明该类为控制类。
@RequestMapping:该类/方法的映射地址
@Autowired:声明bean
UserController:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/boot")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/getUser/{id}")
public String GetUser(@PathVariable Long id){
return userService.findById(id).toString();
}
@RequestMapping("/find")
public String findUser(){
Long id=1000l;
return userService.findById(id).toString();
}
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
8、测试类:
自动生成测试类,用junit测试,idea对着要进行测试的类/方法光标覆盖 ctrl+shift+t 选择create test class,勾选要测试的方法。
UserMapper的测试类UserMapperTest:
注意一些注解:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@WebAppConfiguration
@Resource
@Test
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
//web项目,junit需要模拟servletContext,所以要加@webAppConfiguration
@WebAppConfiguration
//告诉Junit Spring配置文件
public class UserMapperTest {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void findById() throws Exception{
Long id=1000l;
User user=userMapper.findById(id);
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
}
测试时,只允许测试类的该方法。
以上,是本人初学springboot的基本入门demo,相信只要学过spring以及其他框架的,对于springboot都会比较容易上手,目前,我通过这两个demo,掌握了一些基本的应用。
对于springboot的学习,不少人都说并没有必要去买工具书,做demo就会容易上手,对我来说确实如此,但也因此学得不够系统化,因此之后会不断巩固和学习,并记录下来。
纯洁的微笑-SpringBoot,博主写的挺好的,我本人就是特别不喜欢技术文章太冗长的,这个还蛮简明扼要的。但是初学看的时候有一丢丢看不下去,先上手demo之后再尝试去看就好得多。
此外,在入手过程中,也遇到了不少bug,尝试了不少解决方案,并记录了这些bug。
详阅——SpringBoot+Mybatis web项目常见bug