众所周知,Angular所用的单元测试框架是Karma+Jasmine,最近在写Angular的Unit Test的时候,在Given“创建测试条件”部分会在很多地方用到Spy去模拟和监测函数调用,而jasmine为我们提供的关于Spy的函数有很多种,比如createSpyObj,createSpy,SpyOn等等,而这些方法命名相似但是用法却不相同,常常让人容易混淆而产生很多错误,下面就通过研读Jasmine关于Spy的源码来弄清楚这些Spy函数到底是干什么的,在什么场合下使用它们。
先从createSpyObj开始研究:
j$.createSpyObj = function(baseName, methodNames) {
var baseNameIsCollection = j$.isObject_(baseName) || j$.isArray_(baseName);
if (baseNameIsCollection && j$.util.isUndefined(methodNames)) {
methodNames = baseName;
baseName = 'unknown';
}
var obj = {};
var spiesWereSet = false;
if (j$.isArray_(methodNames)) {
for (var i = 0; i < methodNames.length; i++) {
obj[methodNames[i]] = j$.createSpy(baseName + '.' + methodNames[i]);
spiesWereSet = true;
//如果参数2是method的数组,则调用createSpy(base.method)
}
}else if (j$.isObject_(methodNames)) {
for (var key in methodNames) {
if (methodNames.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
obj[key] = j$.createSpy(baseName + '.' + key);
obj[key].and.returnValue(methodNames[key]);
spiesWereSet = true;
//如果参数2是method:returnValue的键值对组成的对象,则除了调用createSpy(base.method),还用“and.returnValue”来定义了方法的返回值
}
}
}
if (!spiesWereSet) {
throw 'createSpyObj requires a non-empty array or object of method names to create spies for';
}
return obj;
};
再来看SpyOn:
this.spyOn = function(obj, methodName) {
//开始是一连串的错误处理,这些错误是在写UT的时候经常出现的错误,可以对号入座
if (j$.util.isUndefined(obj) || obj === null) {
throw new Error(getErrorMsg('could not find an object to spy upon for ' + methodName + '()'));
}
if (j$.util.isUndefined(methodName) || methodName === null) {
throw new Error(getErrorMsg('No method name supplied'));
}
if (j$.util.isUndefined(obj[methodName])) {
throw new Error(getErrorMsg(methodName + '() method does not exist'));
}
if (obj[methodName] && j$.isSpy(obj[methodName]) ) {
if ( !!this.respy ){
return obj[methodName];
}else {
throw new Error(getErrorMsg(methodName + ' has already been spied upon'));
}
}
var descriptor;
try {
descriptor = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, methodName);
} catch(e) {
// IE 8 doesn't support `definePropery` on non-DOM nodes
}
if (descriptor && !(descriptor.writable || descriptor.set)) {
throw new Error(getErrorMsg(methodName + ' is not declared writable or has no setter'));
}
var originalMethod = obj[methodName],
spiedMethod = j$.createSpy(methodName, originalMethod),
//这里调用了createSpy,createSpy的param1是这个Spy的名字,意义不大;param2是要去Spy的函数
restoreStrategy;
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, methodName)) {
restoreStrategy = function() {
obj[methodName] = originalMethod;
};
} else {
restoreStrategy = function() {
if (!delete obj[methodName]) {
obj[methodName] = originalMethod;
}
};
}
currentSpies().push({
restoreObjectToOriginalState: restoreStrategy
});
obj[methodName] = spiedMethod;
return spiedMethod;
};
再来看一下createSpyObj和spyOn共同用到的方法createSpy(),也可以单独调用
j$.createSpy = function(name, originalFn) {
return j$.Spy(name, originalFn);
};
很简单,就是调用了j$.Spy这个方法,
继续看最底层的Spy():
getJasmineRequireObj().Spy = function (j$) {
var nextOrder = (function() {
var order = 0;
return function() {
return order++;
};
})();
/**
* _Note:_ Do not construct this directly, use {@link spyOn}, {@link spyOnProperty}, {@link jasmine.createSpy}, or {@link jasmine.createSpyObj}
* @constructor
* @name Spy
*/
function Spy(name, originalFn) {
var numArgs = (typeof originalFn === 'function' ? originalFn.length : 0),
wrapper = makeFunc(numArgs, function () {
//做了一个包装函数,作为虚拟调用
return spy.apply(this, Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments));
}),
spyStrategy = new j$.SpyStrategy({
//Spy策略:处理Spy的and属性:callThrough执行调用, returnValue指定返回值, callFake执行指定函数,throwError抛出异常,stub原始状态
name: name,
fn: originalFn,
getSpy: function () {
return wrapper;
}
}),
callTracker = new j$.CallTracker(),
//Spy追踪:any,count,argsFor(index),allArgs, all(调用的上下文和参数), mostRecent,first,reset
spy = function () {
/**
* @name Spy.callData
* @property {object} object - `this` context for the invocation.
* @property {number} invocationOrder - Order of the invocation.
* @property {Array} args - The arguments passed for this invocation.
*/
var callData = {
object: this,
invocationOrder: nextOrder(),
args: Array.prototype.slice.apply(arguments)
};
callTracker.track(callData);
var returnValue = spyStrategy.exec.apply(this, arguments);
callData.returnValue = returnValue;
return returnValue;
};
function makeFunc(length, fn) {
switch (length) {
case 1 : return function (a) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 2 : return function (a,b) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 3 : return function (a,b,c) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 4 : return function (a,b,c,d) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 5 : return function (a,b,c,d,e) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 6 : return function (a,b,c,d,e,f) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 7 : return function (a,b,c,d,e,f,g) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 8 : return function (a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
case 9 : return function (a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i) { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
default : return function () { return fn.apply(this, arguments); };
}
}
for (var prop in originalFn) {
if (prop === 'and' || prop === 'calls') {
throw new Error('Jasmine spies would overwrite the \'and\' and \'calls\' properties on the object being spied upon');
}
wrapper[prop] = originalFn[prop];
}
wrapper.and = spyStrategy;
wrapper.calls = callTracker;
return wrapper;
}
return Spy;
};
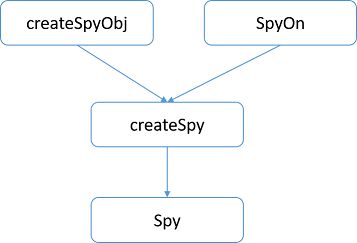
由此可以得到,createSpyObj、createSpy、SpyOn、Spy这几个方法的调用关系:
它们适用的场合如图所示:
解释:
createSpyObj:原本没有对象,无中生有地去创建一个对象,并且在对象上创建方法,然后去spy上面的方法
spyOn:原本有对象,对象上也有方法,只是纯粹地在方法上加个spy
createSpy:原本有对象,但是没有相应的方法,虚拟地创建一个方法(虚线),在虚拟的方法上去spy。如果对象上原来有方法,也可以用createSpy去spy,也就是无论有没有这个方法,createSpy都会去spy你指定的方法。
常见的出错信息:
基本上出错的信息都是在spyOn函数上,摘录出来以备查找原因:
'could not find an object to spy upon for ' + methodName + '()'
spy的对象为null或undefined
'No method name supplied’
spy的方法为null或undefined
methodName + '() method does not exist'
spy的方法不存在对象上(spyOn必须要在存在的方法上去spy)
·methodName + ' has already been spied upon'
已经有一个spy在这个方法上了,看看有没有地方已经spy了它