/**
* @Description:
* @author: mengweidao
* @date: 2019-07-26 14:04
*/
public class Test001 {
/**
* A
* C
* B
* 200A
* endA
* 200C
* endC
* 200B
* endB
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //无参默认是非公平锁,有参可以配置 true代表公平锁
new Thread(()->mainLock(lock),"A").start();
new Thread(()->mainLock(lock),"B").start();
new Thread(()->mainLock(lock),"C").start();
}
public static void mainLock(ReentrantLock lock) {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(thread.getName());
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(200 + thread.getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
System.out.println("end" + thread.getName());
}
}
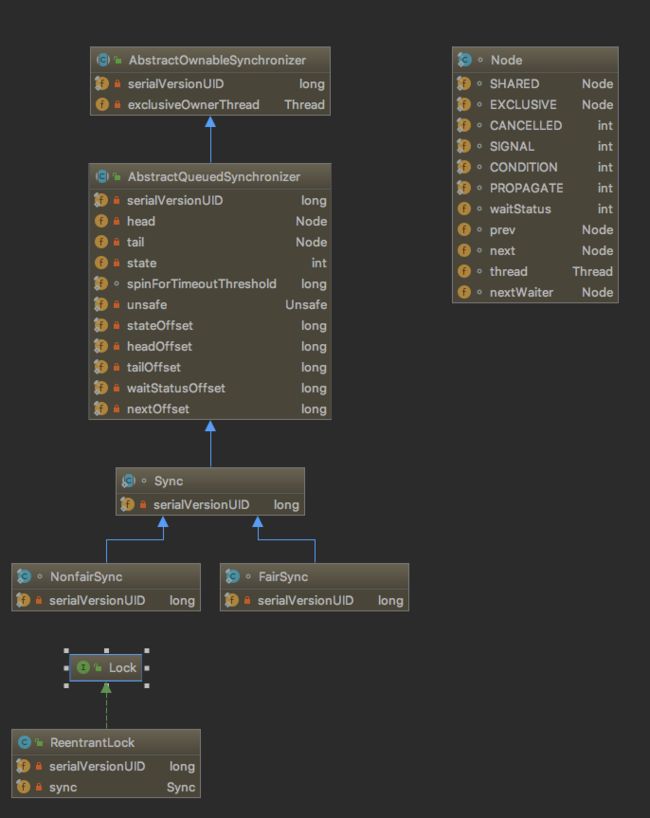
Lock.lock();方法解析(非公平锁):
ThreadA/ThreadB/ThreadC加Lock锁
1>第一个线程A进入 lock()->CAS->获得锁;
2>第二个线程B进入 lock()->CAS->拒绝->acquire(1)->tryAcquire(1)->失败->addWaiter(null)->enq->加入阻塞队列->acquireQueued->阻塞等待线程A的锁释放;
3>第三个线程C进入 lock()->CAS->拒绝->acquire(1)->tryAcquire(1)->失败->addWaiter(null)->加入阻塞队列->acquireQueued->阻塞等待线程A的锁释放;
解读:
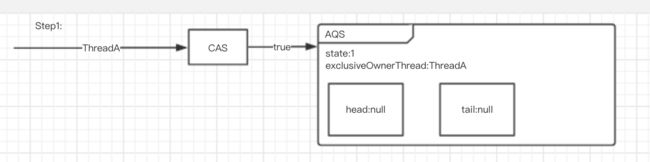
第一步:线程A/B/C竞争,线程A通过CAS:compareAndSetState(0,1)争抢到锁,BC继续尝试,线程A的操作如下:
第二步:线程B/C...竞争,CAS:compareAndSetState(0,1)都返回失败,线程B/C同时进入addWaiter的enq方法,两者竞争初始化head和tail,无论哪个线程设置成功,都会进入下次循环,通过CAS:compareAndSetTail防止并发,线程B抢到了乐观锁,设置tail成功,线程C继续循环,追加到B的后面。
第三步:acquireQueued方法让方法阻塞,通过CAS:compareAndSetWaitStatus将线程B设置为Node.SIGNAL,并继续争抢锁。注意:后置线程调用为前置线程设置为SIGNAL,C为B设置,B为虚拟节点设置。parkAndCheckInterrupt方法让线程阻塞并复位线程。复位线程的作用是检验在park阻塞过程中是否被中断过,被中断过就返回true。
thread.interrupt():中断线程
thread.interruoted:获取中断状态,复位。
selfInterrupt:如果重置过,就在此方法中进行中断
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
在此有几点注意⚠️:
1>当没有线程持有锁时,第一次竞争时通过CAS:compareAndSetState防止线程并发;当有线程持有锁时,通过CAS:compareAndSetTail防止线程并发。
下面是jdk ReentrantLock部分源码
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) //CAS尝试获取锁
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
//CAS尝试获取锁
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
//尝试获取锁
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
//尝试获取锁
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
//尝试获取锁
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//添加到阻塞队列
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
//追加阻塞队列
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { //初始化head tail
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
//追加阻塞队列
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//返回 node.prev
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}