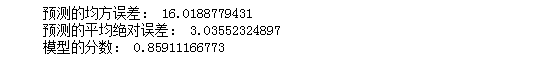一、boston房价预测
1. 读取数据集
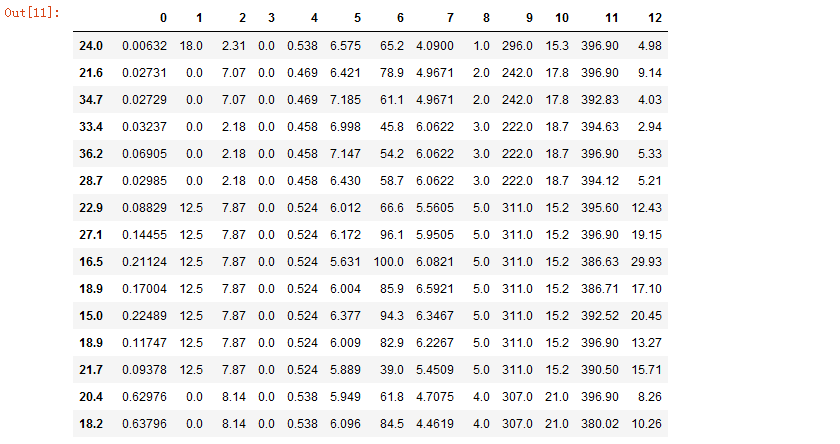
#boston房价预测 #1.读取boston房价数据集 import pandas as pd from sklearn.datasets import load_boston boston = load_boston() x=boston.data y=boston.target pd.DataFrame(x,y)
运行结果如下:
2. 训练集与测试集划分
#2.训练集与测试集划分 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.3)#训练集是0.7,测试集是0.3
3. 线性回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
#3.线性回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。 #多元线性回归模型 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression lineR=LinearRegression() lineR.fit(x_train,y_train) w=lineR.coef_ b=lineR.intercept_ print(w,b) #检测模型好坏 from sklearn.metrics import regression y_pred=lineR.predict(x_test) print("预测的均方误差:", regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred)) print("预测的平均绝对误差:", regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred)) # 输出模型的分数 print("模型的分数:",lineR.score(x_test, y_test))
运行结果如下:
4. 多项式回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
#4.多项式回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。 #多项式回归模型 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures poly=PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) x_train_poly=poly.fit_transform(x_train) x_test_poly=poly.transform(x_test) lrp=LinearRegression() lrp.fit(x_train_poly,y_train) #检测模型好坏 y_pred_plot=lrp.predict(x_test_poly) print("预测的均方误差:", regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred_plot)) print("预测的平均绝对误差:", regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred_plot)) # 输出模型的分数 print("模型的分数:",lrp.score(x_test_poly, y_test))
运行结果如下:
5. 比较线性模型与非线性模型的性能,并说明原因。
同过比较线性模型与非线性模型运行结果,可以知道非线性模型更加贴合样本点的分布,而且比线性模型的误差小,所以非线性模型的性能比线性模型的性能更好。
二、中文文本分类
import os import jieba import numpy as np import sys from datetime import datetime import gc path = 'F:\\0369' with open(r'F:\\stopsCN.txt',encoding='utf-8') as f: stopwords = f.read().split('\n') def processing(text): text = "".join([char for char in text if char.isalpha()]) text = [token for token in jieba.cut(text,cut_all=True) if len(token) >=3] text = " ".join([token for token in text if token not in stopwords]) return text data=[] target=[] for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path): for f in files: file = os.path.join(root,f) with open(file, encoding='utf-8') as f: datafile = f.read() targets = file.split('\\')[-2] target.append(targets) data.append(processing(datafile))
运行结果如下:
#2.训练集与测试集划分 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(data,target,test_size=0.3)#训练集是0.7,测试集是0.3
#TF-IDF from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer vectorizer=TfidfVectorizer(min_df=2,ngram_range=(1,2),stop_words='english',strip_accents='unicode',norm='l2')#构建一个计算TF-IDF X_train=vectorizer.fit_transform(x_train)#vectorizer.fit_transform(TFIDF_train)将文本TFIDF_train输入,得到词频矩阵 X_test=vectorizer.transform(x_test)#将这个矩阵作为输入,用transformer.fit_transform(词频矩阵)得到TF-IDF权重矩阵 X_train
运行结果如下:
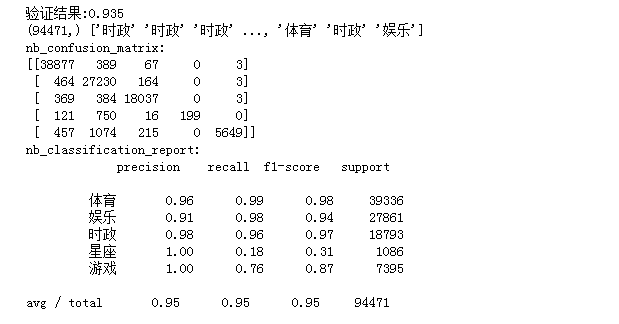
#将其向量化 #多项式朴素贝叶斯 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB mul=MultinomialNB() clf= mul.fit(X_train,y_train) y_nb_pred=clf.predict(X_test) #模型精确度 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score scores = cross_val_score(mul, X_test, y_test, cv=5) print("验证结果:%.3f" % scores.mean()) #分类结果显示 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix from sklearn.metrics import classification_report #x_test预测结果 print(y_nb_pred.shape,y_nb_pred) print('nb_confusion_matrix:') #混淆矩阵 cm=confusion_matrix(y_test,y_nb_pred) print(cm) print('nb_classification_report:') cr=classification_report(y_test,y_nb_pred)#主要分类指标的文本报告 print(cr)
运行结果如下: