ansible简介
ansible是一款新出的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,可实现对多台服务器进行批量配置、程序的部署及指令的运行。大大减少了在运维工程中的工作量。
常见的运维工具的工作模式有两种agent和agentless。ansible属于后者,即在被控制端没有代理运行。ansible基于ssh实现信息的传输,且在运行过程中具有幂等性(同一个操作执行多次,结果相同,不会重复执行)
ansible的安装
rpm包安装
在epel源中就有,添加epel源,直接使用yum下载即可。
[root@www ~]# yum install ansible
源码安装
源码的安装包可去https://github.com上下载,各个版本的都有。
[root@www ~]# yum -y install python-jinja2 PyYAML python-paramiko python-babel python-crypto [root@www ~]# tar xf ansible-1.9.2.tar.gz [root@www ~]# cd ansible-1.9.2 [root@www ~]# python setup.py build [root@www ~]# python setup.py install [root@www ~]# mkdir /etc/ansible [root@www ~]# cp -r examples/* /etc/ansible/
ansible的简单应用
正真实现批量部署的是ansible中的模块,常用的模块有command,user,copy,cron,file,ping,yum,service,shell,script......
命令格式:ansible
host-pattern # 目标主机的地址,一般是配置文件中的组名
-m module # 指定应用的模块
-a args # 指定模块的参数
ansible-doc -l # 查看所有可用的模块
ansible-doc moduleName # 查看指定模块的帮助信息
定义Host Inventory
/etc/ansible/hosts该文件中定义了目标主机的地址,往往以组的形式定义。
[root@www ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [myhosts] 192.168.1.118 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=passwd 192.168.1.119 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=passwd 192.168.1.120 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=passwd
在命令行中module指定为myhosts,即可同时操纵这3台主机。在主机地址后面指定主机的用户名和密码,则在命令行可直接进行连接。常见参数还有有:
ansible_ssh_host # 指定连接的主机名
ansible_ssh_port # 指定ssh连接的端口
ansible_sudo_pass # sudo的密码
ansible_connection # 指定连接方式(local,ssh,paramiko)
上面的认证方式不是很安全(密码直接写在了配置文件上),可基于密钥实现认证:
[root@vm1 ansible]# ssh-keygen -t rsa -P '' [root@vm1 ansible]# ansible myhosts -m copy -a 'src=/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub dest=/root/.ssh/authorized_keys owner=root group=root mode=600'
以下是几个简单的应用:
使用ping模块测试所有主机是否在线:
[root@www ansible-1.9.2]# ansible myhosts -m ping
user模块,为每台主机添加用户:
[root@CentOS-6 ~]# openssl passwd -1 -salt `openssl rand -hex 8` Password: $1$a787e6a4$ySdBzC2krv/EbZQBDJSYl1 [root@CentOS-6 ~]# ansible myhosts -m user -a 'name=fedora password=$1$a787e6a4$ySdBzC2krv/EbZQBDJSYl1'
copy模块,复制文件至每一台主机:
[root@CentOS-6 ~]# ansible myhosts -m copy -a 'src=/root/hellodb.sql dest=/tmp owner=fedora group=root mode=440'
file模块,创建文件和链接:
[root@www ansible-1.9.2]# ansible myhosts -m file -a 'path=/tmp/test.txt state=touch' [root@www ansible-1.9.2]# ansible myhosts -m file -a 'src=/tmp/test.txt path=/tmp/ptTest state=link'
yum模块,使用yum在所有主机上安装、删除软件:
[root@www ~]# ansible myhosts -m yum -a 'name=zsh state=present' [root@www ~]# ansible myhosts -m yum -a 'name=zsh state=absent'
service模块,在所有主机上启动、关闭相应的服务。
[root@www ~]# ansible myhosts -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes' [root@www ~]# ansible myhosts -m service -a 'name=httpd state=stopped enabled=no'
setup模块,这个模块比较特殊,它可以用来获取目标主机上的一些关于系统环境的变量,例如:
ansible_os_family # 目标主机的操作系统
ansible_pkg_mgr # 目标主机的软件包管理器
ansible_machine # 计算机架构
........
[root@www ~]# ansible 192.168.1.108 -m setup
playbook简介
playbook使用YAML语法结构,可读性高。简单的说,playbook就是将需要对多台服务器的操纵过程以一定的格式写在一个配置文件中。然后在执行过程中,目标服务器就会按照实现定义好的机制一个接着一个完成任务。下面是一段playbook内容:
- name: web service remote_user: root hosts: web #以上是全局配置 tasks: - name: install httpd yum: name=httpd state=present - name: configuration copy: src=httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf - name: start service service: name=httpd state=started enabled=no
hosts # 用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,往往是/etc/ansible/hosts中定义的组
remote_user # 用于指定远程主机上的执行任务的用户,也可用于各task中
task格式(每个横线“-”代表一个任务):
name:任务名称 # (用于playbook的执行结果输出)
模块名称: 参数1=value 参数2=value
task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后再开始第二个。在运行自下而下某playbook时,如果中途发生错误,不会回滚,更正playbook后重新执行一次即可,因为模块执行是幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,结果均一致。
如果某个任务执行出现失败,就立即结束,后面的任务将不会被运行。这是可以用如下方式解决:
tasks: - name: ***** shell: /usr/bin/somecommand || /bin/true
或者使用ignore_errors来忽略错误信息:
tasks: - name: run this command and ignore the result shell: /usr/bin/somecommand ignore_errors: True #若上面的命令执行错误则把它忽略
roles简介
roles用于层次性、结构化地组织playbook,能够根据层次型结构自动装载变量文件、tasks以及handlers等。roles将变量,任务,文件等放置在不同的目录中,然后直接调用某个roles即可完成某些特定的任务。
roles的目录结构:
site.yml # 用来描述当前目录是用来做什么的
webservers.yml
roles/
common/ #第一个角色
files/ # 存放由copy或script等模块调用的文件
tasks/ # 定义了此角色的任务列表
handlers/ # 用于定义此角色用到的各handler
vars/ #用于定义此角色用到的变量
meta/ # 用于定义此角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系
webservers/ #第二个角色
........
........
使用ansible批量部署LAMP
实验环境:使用ansible实现在192.168.1.118,192.168.1.119两台服务器上部署httpd,php服务,在192.168.1.120上部署mysql服务。
配置inventory文件(以实现密钥认证)
[root@www ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [myhosts] 192.168.1.118 192.168.1.119 192.168.1.120 [web] 192.168.1.118 192.168.1.119 [mysql] 192.168.1.120
创建roles的相关目录(以下是我的roles目录结构):
[root@www ansible]# ls mysql.yml remove.yml roles site.yml web.yml [root@www ansible]# tree . ├── mysql.yml ├── remove.yml ├── roles │ ├── mysql │ │ ├── files │ │ │ └── my.cnf │ │ ├── handlers │ │ │ └── main.yml │ │ ├── tasks │ │ │ └── main.yml │ │ ├── templates │ │ └── vars │ ├── php │ │ ├── files │ │ │ └── php.ini │ │ ├── handlers │ │ ├── tasks │ │ │ └── main.yml │ │ ├── templates │ │ └── vars │ └── web │ ├── files │ │ └── httpd.conf │ ├── handlers │ │ └── main.yml │ ├── tasks │ │ └── main.yml │ ├── templates │ └── vars ├── site.yml └── web.yml
编辑web与php的playbook,php是以模块的形式添加至httpd中,所以两个服务在同一台服务器上:
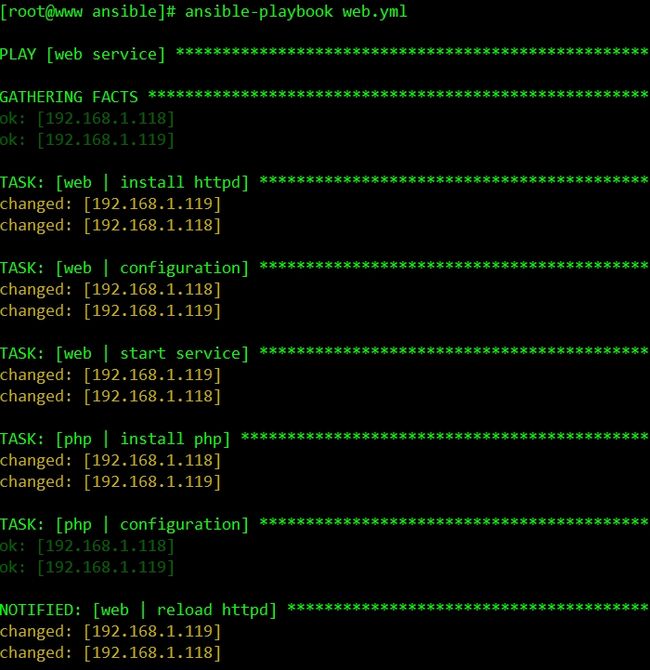
[root@www ansible]# cat web.yml - name: web service remote_user: root hosts: web roles: - web - php #########web########## [root@www ansible]# cat roles/web/tasks/main.yml - name: install httpd yum: name=httpd state=present tags: install - name: configuration copy: src=httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf #src指定的文件会自动去上一层的files目录中寻找 tags: conf notify: #当配置文件发生更改时会触发下面的动作 - reload httpd #会去handlers目录下寻找任务文件,然后执行 - name: start service service: name=httpd state=started enabled=no [root@www ansible]# cat roles/web/handlers/main.yml - name: reload httpd service: name=httpd state=reloaded #########php########## [root@www ansible]# cat roles/php/tasks/main.yml - name: install php yum: name=php state=present tags: install - name: configuration copy: src=php.ini dest=/etc/php.ini tags: conf
编辑mysql的playbook:
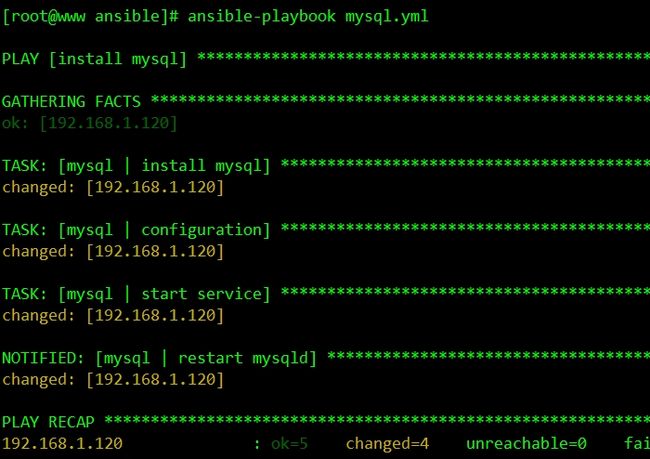
[root@www ansible]# cat mysql.yml - name: install mysql remote_user: root hosts: mysql roles: - mysql ####################### [root@www ansible]# cat roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml - name: install mysql yum: name=mysql-server state=present tags: install - name: configuration copy: src=my.cnf dest=/etc/my.cnf tags: conf notify: - restart mysqld - name: start service service: name=mysqld state=started enabled=no [root@www ansible]# cat roles/mysql/handlers/main.yml - name: restart mysqld service: name=mysqld state=restarted
三者的配置文件均存放在各自的file目录下。
开始批量安装,配置,启动httpd,php服务:
mysql的安装,配置,启动
检查服务器端的宽口监听状况:
![]{2R%3WB4DT5(A]@MG72FM5.png 自动化运维工具ansible_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info3/1176c25a24084ddbbc89b53e6f214cb6.jpg) 服务已安装完成,并启动。.................^_^
服务已安装完成,并启动。.................^_^