引言
上一篇文章(nginx+springboot+redis 负载均衡Session共享的实现
) 简单的配置了负载均衡的脚手架。并且简单演示了两台服务器Session共享的解决方案,即Spring-Session。这篇文章讨论下Spring-Session底层是如何实现Session共享的。文章中代码片段均来自上一篇的DEMO GitHub地址下载地址。
第一部分:我会用循序渐进的方式来展示源码,从大家最熟悉的地方入手,而不是直接从系统启动来debug源码。直接debug源码看到后来大家都会一头雾水。 本文先从request.getSession()开始剖析源码,目标是让读者清楚的知晓Spring-session的产生过程。
第二部分:再上一部分Spring-session的产生过程的研究中如果读者清楚了整个过程的脉络,那么肯定会产生一些疑惑:Servlet容器如何从默认的Session切换到Spring-session?为什么request.getSession()会直接调用Spring的session管理方案?这一块研究结束后整个Spring-session的大体原理分析就结束了。
剩下的就是其他一些策略的问题,篇幅有限,不再展开。读者可以私下研究或者评论区域我们讨论。比如
1.CookieHttpSessionStrategy和HeaderHttpSessionStrategy的区别
2.Session创建成功后存储到session仓库的具体过程?
...
那么,先从第一部分开始
一. 提出问题假设
Spring-Session 的思路是替换Servlet容器提供的HttpSession。在web程序中通过调用方法 request.getSession() 生成session。Servlet容器里面默认的request实现是HttpServletRequestWrapper类。那么为了替换原始的HttpSession,Spring-Session有两种方案来重写getSession()方法 :
1.实现`HttpServletRequest`接口
2.继承`HttpServletRequestWrapper`类
我们从springmvc的controller进入request.getSession()方法,debug进去后发现getSession方法在这个类SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper,并且这个类继承了HttpServletRequestWrapper。很开心有木有?验证了我们上面的想法Spring-Session用第2种继承的方式来实现HttpSession的自定义。
/*IndexController.java*/
@Resource
HttpServletRequest request;
@RequestMapping({ "", "/index" })
public String index(Model model) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(); //方法debug跟踪
Object user = session.getAttribute("curuser");
if(user == null) return "redirect:login";
model.addAttribute("port", request.getLocalPort());
return "index";
}
/*SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.java*/
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession() {
return getSession(true);
}
大概的思路了然,那么getSession(true)到底是如何运作的呢?getSession()这里的业务也是最复杂的,存在各种状态的判断。开始研究getSession()。
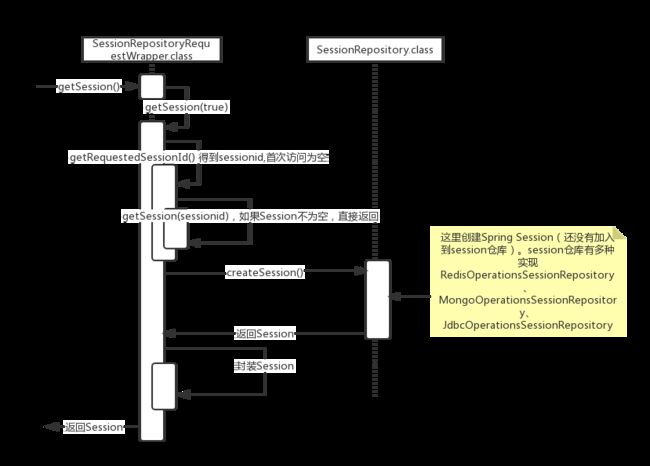
二.在Controller中获取Session
在controller中通过request.getSession()来获取Session,下图是此方法执行的过程。
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession(boolean create) {
/*
从request中获取Session,首次访问返回null
其实这里相当于request.getAttribute(key);
在Session创建成功后会调用request.setAttribute(key,session);
以便于在同一个request请求中直接获取session
*/
HttpSessionWrapper currentSession = getCurrentSession();
if (currentSession != null) {
return currentSession;
}
/*
从Cookie或者header中获取SESSIONID,如果我们用Cookie策略,这也是spring-session默认的。
可以查看浏览器cookie。存在键值对 SESSION:XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
*/
String requestedSessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if (requestedSessionId != null
&& getAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR) == null) {
/*
根据上文得到的sessionid从Session仓库中获取Session
*/
S session = getSession(requestedSessionId);
if (session != null) {//有效的Session
this.requestedSessionIdValid = true;
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
currentSession.setNew(false);
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}else {//无效的session,
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"No session found by id: Caching result for getSession(false) for this HttpServletRequest.");
}
//Session无效,在request中增加一个键值对
setAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR, "true");
}
}
if (!create) {
return null;
}
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"A new session was created. To help you troubleshoot where the session was created we provided a StackTrace (this is not an error). You can prevent this from appearing by disabling DEBUG logging for "
+ SESSION_LOGGER_NAME,
new RuntimeException(
"For debugging purposes only (not an error)"));
}
/*
首次访问,则创建Session。
*/
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.createSession();
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
//将刚创建的session加入到request,以便于本次请求中再次getSession()时直接返回。
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}
至此,我们在controller中获取到了Session。可以存取数据到Session里面。在controller层response的时候把Session存储到Session仓库中(redis、mongo等)
三.spring-session与session是如何做到无缝切换的
web容器实现session共享的插件也有,比如tomcat-redis-session-manager等,缺点比较多:需要在tomcat做配置,侵入严重。
Spring-session用了一个比较聪明又简单的办法
1.自定义一个Filter ,springSessionRepositoryFilter,拦截所有请求
2.继承HttpServletRequestWrapper等类,重写getSession()等方法。
这里我们看看Spring官方文档
we can create our Spring configuration. The Spring configuration is responsible for creating a Servlet Filter that replaces the HttpSession implementation with an implementation backed by Spring Session. Add the following Spring Configuration:
(我们可以创建一个Spring 的配置,这个文件是用来创建一个Filter,这个Filter里面可以实现Spring session替换HttpSession的功能。Spring的配置如下)
XML实现方式
springSessionRepositoryFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy
springSessionRepositoryFilter
/*
REQUEST
ERROR
DelegatingFilterProxy这个类拦截每次请求,并且寻找到springSessionRepositoryFilter这个bean,并且将它转换成Filter,用这个Filter处理每个request请求。
获取springSessionRepositoryFilter这个bean。
Object obj = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(request.getServletContext()).getBean("springSessionRepositoryFilter");
debug查看对象obj ,没错这就是spring-session最核心的Filter ——SessionReponsitoryFilter
org.springframework.session.web.http.SessionRepositoryFilter@228204ee。
spring-session重写的request(SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper),response(SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper)和Session(HttpSessionWrapper)都是SessionReponsitoryFilter类的内部类。第一部分着重说的getSession(boolean)方法就是在SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper这个类里面重写的。
注解实现方式
//@EnableRedisHttpSession这个注解创建了springSessionRepositoryFilter的Bean。
//并且创建了一个操作Redis的RedisConnectionFactory工厂类
@EnableRedisHttpSession
public class Config {
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory();
}
}
上面Config创建了Filter,接下来需要将这个Config加载到Spring。以此来实现每次请求过来首先经过这个Filter。
public class Initializer extends AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer {
public Initializer() {
super(Config.class);
}
}
那么上面两种配置方式里的这个SessionReponsitoryFilter到底是啥样的?这个Filter才是Spring-session的核心。我们来看看
SessionReponsitoryFilter 源代码
@Order(SessionRepositoryFilter.DEFAULT_ORDER)
public class SessionRepositoryFilter
extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private static final String SESSION_LOGGER_NAME = SessionRepositoryFilter.class
.getName().concat(".SESSION_LOGGER");
private static final Log SESSION_LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(SESSION_LOGGER_NAME);
/**
* The session repository request attribute name.
*/
public static final String SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR = SessionRepository.class
.getName();
/**
* Invalid session id (not backed by the session repository) request attribute name.
*/
public static final String INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR = SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR
+ ".invalidSessionId";
private static final String CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR = SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR
+ ".CURRENT_SESSION";
/**
* The default filter order.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Integer.MIN_VALUE + 50;
private final SessionRepository sessionRepository;
private ServletContext servletContext;
private MultiHttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy = new CookieHttpSessionStrategy();
/**
* Creates a new instance.
*
* @param sessionRepository the SessionRepository to use. Cannot be null.
*/
public SessionRepositoryFilter(SessionRepository sessionRepository) {
if (sessionRepository == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sessionRepository cannot be null");
}
this.sessionRepository = sessionRepository;
}
/**
* Sets the {@link HttpSessionStrategy} to be used. The default is a
* {@link CookieHttpSessionStrategy}.
*
* @param httpSessionStrategy the {@link HttpSessionStrategy} to use. Cannot be null.
设置HttpSessionStrategy的策略,默认策略是CookieHttpSessionStrategy。表示从cookie中获取sessionid。
*/
public void setHttpSessionStrategy(HttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy) {
if (httpSessionStrategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("httpSessionStrategy cannot be null");
}
this.httpSessionStrategy = new MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter(
httpSessionStrategy);
}
/**
* Sets the {@link MultiHttpSessionStrategy} to be used. The default is a
* {@link CookieHttpSessionStrategy}.
*
* @param httpSessionStrategy the {@link MultiHttpSessionStrategy} to use. Cannot be
* null.
*/
public void setHttpSessionStrategy(MultiHttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy) {
if (httpSessionStrategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("httpSessionStrategy cannot be null");
}
this.httpSessionStrategy = httpSessionStrategy;
}
/**
这个方法是典型的模板方法设计模式的运用;SessionRepositoryFilter的父类定义了抽象方法doFilterInternal,并且在doFilter中调用,具体的实现丢给子类。
*/
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute(SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR, this.sessionRepository);
//封装request和response
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper wrappedRequest = new SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(
request, response, this.servletContext);
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper wrappedResponse = new SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(
wrappedRequest, response);
//这里的作用是通过方法request.setAttribute(HttpSessionManager.class.getName(), 策略);
//把CookieHttpSessionStrategy加入到request。下面的response一样
HttpServletRequest strategyRequest = this.httpSessionStrategy
.wrapRequest(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse);
HttpServletResponse strategyResponse = this.httpSessionStrategy
.wrapResponse(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse);
try {
filterChain.doFilter(strategyRequest, strategyResponse);
}
finally {
//这里是response的时候把session加入到session仓库(redis,MongoDB等),该方法在下面的SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper类
wrappedRequest.commitSession();
}
}
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Allows ensuring that the session is saved if the response is committed.
*
* @author Rob Winch
* @since 1.0
*/
private final class SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper
extends OnCommittedResponseWrapper {
private final SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper request;
/**
* Create a new {@link SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper}.
* @param request the request to be wrapped
* @param response the response to be wrapped
*/
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
super(response);
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("request cannot be null");
}
this.request = request;
}
@Override
protected void onResponseCommitted() {
this.request.commitSession();
}
}
/**
* A {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest} that retrieves the
* {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSession} using a
* {@link org.springframework.session.SessionRepository}.
*
* @author Rob Winch
* @since 1.0
*/
private final class SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper
extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private Boolean requestedSessionIdValid;
private boolean requestedSessionInvalidated;
private final HttpServletResponse response;
private final ServletContext servletContext;
private SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(request);
this.response = response;
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Uses the HttpSessionStrategy to write the session id to the response and
* persist the Session.
* 将session加入到session仓库(redis,MongoDB等
*/
private void commitSession() {
HttpSessionWrapper wrappedSession = getCurrentSession();
if (wrappedSession == null) {
if (isInvalidateClientSession()) {
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionStrategy
.onInvalidateSession(this, this.response);
}
}
else {
S session = wrappedSession.getSession();
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.save(session);
if (!isRequestedSessionIdValid()
|| !session.getId().equals(getRequestedSessionId())) {
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionStrategy.onNewSession(session,
this, this.response);
}
}
}
//从当前request中获取session
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private HttpSessionWrapper getCurrentSession() {
return (HttpSessionWrapper) getAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR);
}
//将session存储到当前request请求中
private void setCurrentSession(HttpSessionWrapper currentSession) {
if (currentSession == null) {
removeAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR);
}
else {
setAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR, currentSession);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public String changeSessionId() {
HttpSession session = getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot change session ID. There is no session associated with this request.");
}
// eagerly get session attributes in case implementation lazily loads them
Map attrs = new HashMap();
Enumeration iAttrNames = session.getAttributeNames();
while (iAttrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = iAttrNames.nextElement();
Object value = session.getAttribute(attrName);
attrs.put(attrName, value);
}
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.delete(session.getId());
HttpSessionWrapper original = getCurrentSession();
setCurrentSession(null);
HttpSessionWrapper newSession = getSession();
original.setSession(newSession.getSession());
newSession.setMaxInactiveInterval(session.getMaxInactiveInterval());
for (Map.Entry attr : attrs.entrySet()) {
String attrName = attr.getKey();
Object attrValue = attr.getValue();
newSession.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue);
}
return newSession.getId();
}
@Override
public boolean isRequestedSessionIdValid() {
if (this.requestedSessionIdValid == null) {
String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
S session = sessionId == null ? null : getSession(sessionId);
return isRequestedSessionIdValid(session);
}
return this.requestedSessionIdValid;
}
private boolean isRequestedSessionIdValid(S session) {
if (this.requestedSessionIdValid == null) {
this.requestedSessionIdValid = session != null;
}
return this.requestedSessionIdValid;
}
private boolean isInvalidateClientSession() {
return getCurrentSession() == null && this.requestedSessionInvalidated;
}
private S getSession(String sessionId) {
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository
.getSession(sessionId);
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
return session;
}
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession(boolean create) {
HttpSessionWrapper currentSession = getCurrentSession();
if (currentSession != null) {
return currentSession;
}
String requestedSessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if (requestedSessionId != null
&& getAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR) == null) {
S session = getSession(requestedSessionId);
if (session != null) {
this.requestedSessionIdValid = true;
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
currentSession.setNew(false);
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}
else {
// This is an invalid session id. No need to ask again if
// request.getSession is invoked for the duration of this request
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"No session found by id: Caching result for getSession(false) for this HttpServletRequest.");
}
setAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR, "true");
}
}
if (!create) {
return null;
}
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"A new session was created. To help you troubleshoot where the session was created we provided a StackTrace (this is not an error). You can prevent this from appearing by disabling DEBUG logging for "
+ SESSION_LOGGER_NAME,
new RuntimeException(
"For debugging purposes only (not an error)"));
}
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.createSession();
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
if (this.servletContext != null) {
return this.servletContext;
}
// Servlet 3.0+
return super.getServletContext();
}
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession() {
return getSession(true);
}
//从session策略中获取sessionid
@Override
public String getRequestedSessionId() {
return SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionStrategy
.getRequestedSessionId(this);
}
/**
* Allows creating an HttpSession from a Session instance.
*
* @author Rob Winch
* @since 1.0
*/
private final class HttpSessionWrapper extends ExpiringSessionHttpSession {
HttpSessionWrapper(S session, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(session, servletContext);
}
@Override
public void invalidate() {
super.invalidate();
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.this.requestedSessionInvalidated = true;
setCurrentSession(null);
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.delete(getId());
}
}
}
/**
* A delegating implementation of {@link MultiHttpSessionStrategy}.
*/
static class MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter implements MultiHttpSessionStrategy {
private HttpSessionStrategy delegate;
/**
* Create a new {@link MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter} instance.
* @param delegate the delegate HTTP session strategy
*/
MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter(HttpSessionStrategy delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public String getRequestedSessionId(HttpServletRequest request) {
return this.delegate.getRequestedSessionId(request);
}
public void onNewSession(Session session, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
this.delegate.onNewSession(session, request, response);
}
public void onInvalidateSession(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
this.delegate.onInvalidateSession(request, response);
}
public HttpServletRequest wrapRequest(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
return request;
}
public HttpServletResponse wrapResponse(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
return response;
}
}
}
结语
spring-session源码的解读就这么粗糙的结束了,一些状态判断性的源码没有解读。我相信只要读者把主线业务整理明白了,其他方法小菜一碟。
文末分享一些解读源码的经验:其实解读源码的窍门和难点就是梳理各个类、各个方法之间的关系。紧抓业务主线,把次要的类和方法首先剔除掉,以免扰乱视线。如果会画一些流程图、序列图那就更好了,是非常有效的方法。不会UML也没事,只要你能用自己的方式把类与类、方法和方法之间的关系理清楚也是ok的。比如spring-session的源码解读,首先我从官网了解到设计者的大体思路
自定义Filter拦截所有请求→Filter中自定义request、response、session
是的,就是这么简单的一个思路。落实到代码实处,逻辑不要特么的太费劲。