ARouter 源码学习
阿里巴巴Arouter github地址如下:
ARouter gitHub 地址
ARouter我的学习注释GitHub地址:
ARouter
Arouter 组件化Demo:
Android_Modularization_Demo
强烈建议:阅读ARouter源码前,认真阅读 ARouter官方文档:Android平台页面路由框架ARouter,通过阅读该文档,会对Arouter的实现有一个大概了解,方便后边的源码阅读。
前一段时间,我们的项目中引入了Arouter,引入的目的主要是为了组件化和功能解耦。因此觉得有必要认真学习一下Arouter的源码,了解其工作原理。
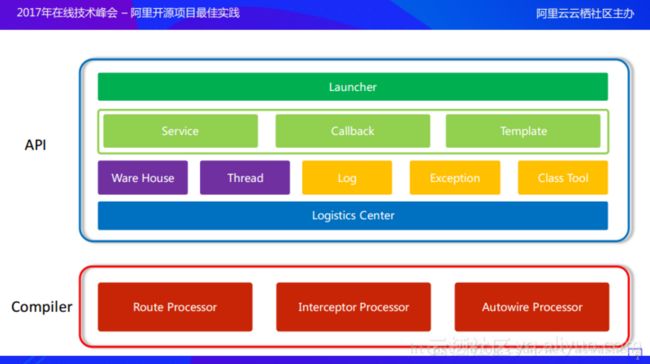
以下为官方文档中给出的架构图。
关乎Compiler部分的学习
API部分源码学习
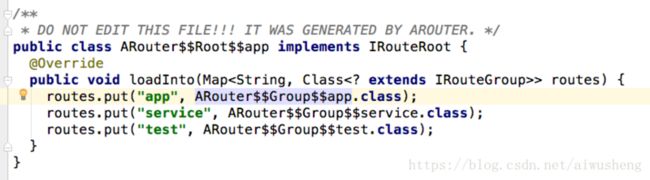
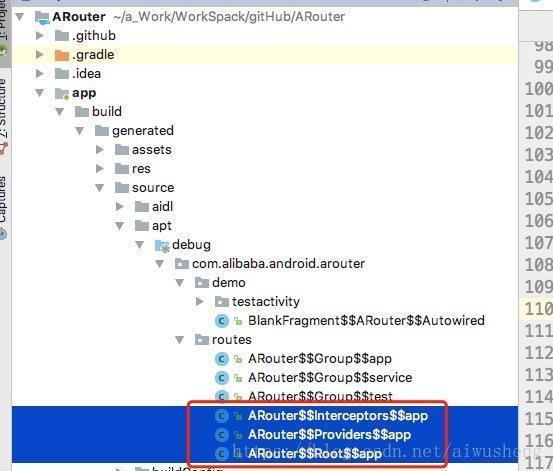
通过 ARouter 源码学习之Compiler 我们知道,Arouter工程经过build后,会在debug路径下生成以下文件:
而这些文件的加载工作,是在ARouter.init(getApplication()); 初始化时完成的。
下面跟踪源码了解这一过程:
Arouter初始化——加载编译时生成的类
sequenceDiagram
participant ARouter as clientA
participant _ARouter as clientB
participant LogisticsCenter as serverA
Note over clientA: Application中触发初始化
clientA->>clientB: ARouter.init(getApplication())
clientB->>serverA: _ARouter.init(application)
serverA-->>serverA: LogisticsCenter.init\n(mContext, executor)\n加载编辑时生成的类
Note over clientA: build下生成类加载完成ARouter.init(getApplication());
/**
* Init, it must be call before used router.
*
* 1、一般在Application中完成初始化
*/
public static void init(Application application) {
LogUtils.e("ARouter", "init");
if (!hasInit) {
// 日志
logger = _ARouter.logger;
// 加载 生成的类
hasInit = _ARouter.init(application);
// 加载 拦截器
if (hasInit) {
_ARouter.afterInit();
}
}
}
其中_ARouter.init(application);用来记载build下生成的类文件。
_ARouter.init(application);
/**
* 加载build下生成的类
*
* @param application
* @return
*/
protected static synchronized boolean init(Application application) {
mContext = application;
// 加载生成的类
LogisticsCenter.init(mContext, executor);
// 初始化完成
hasInit = true;
return true;
}这里调用到了框架的物流中心LogisticsCenter中,用LogisticsCenter.init(mContext, executor); 方法完成了生成文件类的加载。
LogisticsCenter.init
/**
* 基础物流类初始化,加载生成的类
* LogisticsCenter init, load all metas in memory. Demand initialization
*
*
*/
public synchronized static void init(Context context, ThreadPoolExecutor tpe) throws HandlerException {
mContext = context;
// 线程池
executor = tpe;
try {
long startInit = System.currentTimeMillis();
Set routerMap;
// 新版本 或者 debug包
// It will rebuild router map every times when debuggable.
if (ARouter.debuggable() || PackageUtils.isNewVersion(context)) {
// These class was generate by arouter-compiler.
// 获取com.alibaba.android.arouter.routes 路径下的生成文件
routerMap = ClassUtils.getFileNameByPackageName(mContext, ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE);
// 数据存储
if (!routerMap.isEmpty()) {
context.getSharedPreferences(AROUTER_SP_CACHE_KEY, Context.MODE_PRIVATE).edit().putStringSet(AROUTER_SP_KEY_MAP, routerMap).apply();
}
// 存储新的版本号
PackageUtils.updateVersion(context); // Save new version name when router map update finish.
} else {
// 从sp中获取数据
routerMap = new HashSet<>(context.getSharedPreferences(AROUTER_SP_CACHE_KEY, Context.MODE_PRIVATE).getStringSet(AROUTER_SP_KEY_MAP, new HashSet()));
}
startInit = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 循环com.alibaba.android.arouter.routes 路径下的所有文件
for (String className : routerMap) {
// com.alibaba.android.arouter.routes.ARouter$$Root
if (className.startsWith(ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE + DOT + SDK_NAME + SEPARATOR + SUFFIX_ROOT)) {
// 反射
// 创建 new ARouter$$Root$$app().loadInto();
//
// 将数据加载到Warehouse.groupsIndex中
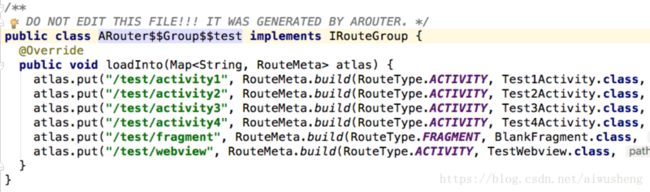
// routes.put("service", ARouter$$Group$$service.class);
// routes.put("test", ARouter$$Group$$test.class);
//
// This one of root elements, load root.
((IRouteRoot) (Class.forName(className).getConstructor().newInstance())).loadInto(Warehouse.groupsIndex);
}
// com.alibaba.android.arouter.routes.ARouter$$Interceptors
else if (className.startsWith(ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE + DOT + SDK_NAME + SEPARATOR + SUFFIX_INTERCEPTORS)) {
// 反射
// 创建 new ARouter$$Interceptors$$app().loadInto(Warehouse.interceptorsIndex)
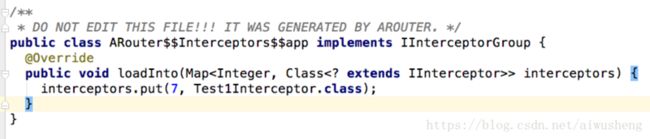
// interceptors.put(7, Test1Interceptor.class);
((IInterceptorGroup) (Class.forName(className).getConstructor().newInstance())).loadInto(Warehouse.interceptorsIndex);
}
// com.alibaba.android.arouter.routes.ARouter$$Providers
else if (className.startsWith(ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE + DOT + SDK_NAME + SEPARATOR + SUFFIX_PROVIDERS)) {
// new ARouter$$Providers$$app().loadInto();
//
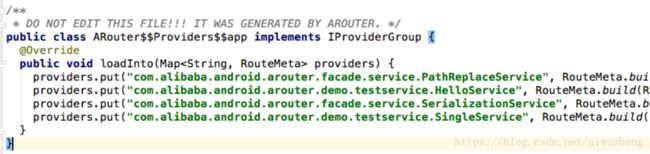
// providers.put("com.alibaba.android.arouter.demo.testservice.HelloService", RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, HelloServiceImpl.class, "/service/hello", "service", null, -1, -2147483648));
// providers.put("com.alibaba.android.arouter.facade.service.SerializationService", RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, JsonServiceImpl.class, "/service/json", "service", null, -1, -2147483648));
// providers.put("com.alibaba.android.arouter.demo.testservice.SingleService", RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, SingleService.class, "/service/single", "service", null, -1, -2147483648));
((IProviderGroup) (Class.forName(className).getConstructor().newInstance())).loadInto(Warehouse.providersIndex);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HandlerException(TAG + "ARouter init logistics center exception! [" + e.getMessage() + "]");
}
}
LogisticsCenter.init(mContext, executor); 分别创建了 ARouter$$Root$$app.java 、ARouter$$Interceptors$$app.java 、ARouter$$Providers$$app.java 的对象,并分别调用了其 loadInto方法,对其内容进行了加载。
到这里_ARouter.init(application);初始化完成,完成了bulid中以下类的加载
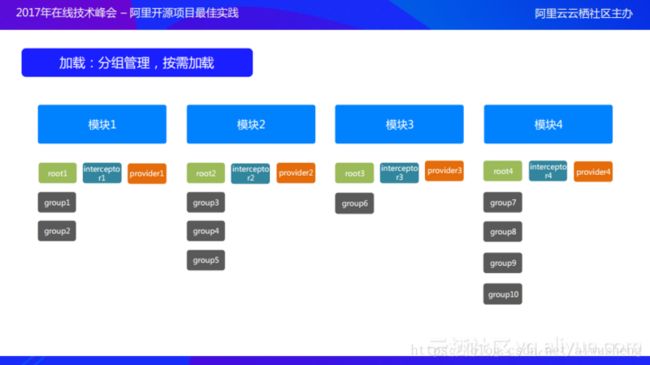
按照官方文档的说法,这里是“分组管理,按需加载”。这里加载了各个模块的Root节点,而对于Root节点下的各个页面,则暂不加载。
官方文档原话:
在运行期就需要将映射关系加载进来。而加载的时候就会遇到另一个问题,因为需要面对长久的APP的设计,所以不可能一次性把所有的页面都加载进来,当APP有一百或者几百个页面的时候,一次性将所有页面都加载到内存中本身对于内存的损耗是非常可怕的,同时对于性能的损耗也是不可忽视的。所以ARouter中提出了分组的概念,ARouter允许某一个模块下有多个分组,所有的分组最终会被一个root节点管理。如上图中所示,假设有4个模块,每个模块下面都有一个root结点,每个root结点都会管理整个模块中的group节点,每个group结点则包含了该分组下的所有页面
下边回到ARouter.init(getApplication());方法中,跟踪_ARouter.afterInit();方法的调用。
Arouter初始化——加载拦截器
build下生成类加载完成,下边加载拦截器。
_ARouter.afterInit();
/**
* afterInit
*
* 用来加载拦截器
* 完成类的加载后,由{@link ARouter.init}调用
*/
static void afterInit() {
// Trigger interceptor init, use byName.
interceptorService = (InterceptorService) ARouter.getInstance()
// 生成一个Postcard对象
.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")
// 返回一个Postcard
//这个navigation()经过多次调用之后,
//最终调用的是_ARouter.navigation(context, postcard, requestCode, navigationCallback)方法
.navigation();
}
这里继续跟踪ARouter.getInstance().build("/arouter/service/interceptor")方法。
ARouter.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")
/**
* Build the roadmap, draw a postcard.
*
* 根据path 查找对应的 Postcard
*
* @param path Where you go.
*/
public Postcard build(String path) {
return _ARouter.getInstance().build(path);
}
这里又调用到了_ARouter 中的build(path)方法。
_ARouter.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")
/**
* Build postcard by path and default group
*
* 处理PathReplaceService 并更改URL地址
*
* @param path Postcard
* @return 返回对应path地址的Postcard
*/
protected Postcard build(String path) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
throw new HandlerException(Consts.TAG + "Parameter is invalid!");
} else {
// navigation(clazz)这种方式是属于根据类型查找,而build(path)是根据名称进行查找
// 如果应用中没有实现PathReplaceService这个接口,则pService=null
PathReplaceService pService = ARouter.getInstance().navigation(PathReplaceService.class);
// 更改URL地址
if (null != pService) {
path = pService.forString(path);
}
// 返回对应URl地址的Postcard
return build(path, extractGroup(path));
}
}
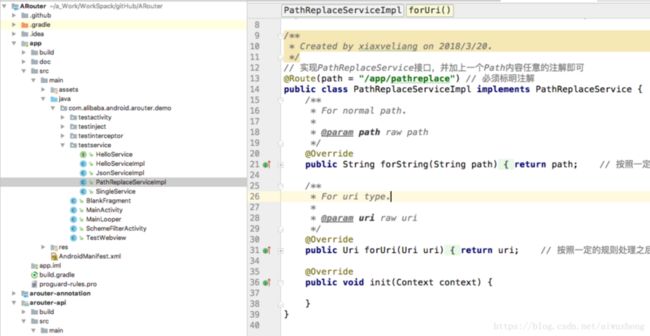
这里调用了ARouter.getInstance().navigation(PathReplaceService.class)返回了一个PathReplaceService对象,实际这里加载到了PathReplaceServiceImpl。
PathReplaceServiceImpl用于url地址替换需求:
下边继续跟踪代码,查看是如何加载到PathReplaceServiceImpl的...
ARouter.navigation(PathReplaceService.class);
public T navigation(Class service) {
return _ARouter.getInstance().navigation(service);
} 继续跟踪_ARouter.getInstance().navigation(service)
_ARouter.navigation(PathReplaceService.class);
protected T navigation(Class service) {
LogUtils.e("_ARouter", "navigation: " + service.getSimpleName());
Log.e("xiaxve_ARouter", "navigation: " + service.getName());
try {
// serviceName 为 PathReplaceService 时,通过 Warehouse.providersIndex 找到 PathReplaceServiceImpl
Postcard postcard = LogisticsCenter.buildProvider(service.getName());
// Compatible 1.0.5 compiler sdk.
if (null == postcard) { // No service, or this service in old version.
postcard = LogisticsCenter.buildProvider(service.getSimpleName());
}
LogisticsCenter.completion(postcard);
return (T) postcard.getProvider();
} catch (NoRouteFoundException ex) {
logger.warning(Consts.TAG, ex.getMessage());
return null;
}
} 终于找到PathReplaceServiceImpl
这里 LogisticsCenter.buildProvider(service.getName())
通过 Warehouse.providersIndex
找到 RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, PathReplaceServiceImpl.class, "/app/pathreplace", "app", null, -1, -2147483648)
最后返回一个new Postcard("/app/pathreplace", "app")
下边继续跟踪LogisticsCenter.completion(postcard);
LogisticsCenter.completion(new Postcard("/app/pathreplace", "app"));
public synchronized static void completion(Postcard postcard) {
if (null == postcard) {
throw new NoRouteFoundException(TAG + "No postcard!");
}
// 第一次走到这里 Warehouse.routes 还没有赋值
// 因此返回的数据为null
RouteMeta routeMeta = Warehouse.routes.get(postcard.getPath());
if (null == routeMeta) {
/**
* 加载对应的组内数据
*/
// 通过"app"找到 routes.put("app", ARouter$$Group$$app.class);
Class groupMeta = Warehouse.groupsIndex.get(postcard.getGroup()); // Load route meta.
if (null == groupMeta) {
throw new NoRouteFoundException(TAG + "There is no route match the path [" + postcard.getPath() + "], in group [" + postcard.getGroup() + "]");
} else {
// Load route and cache it into memory, then delete from metas.
try {
if (ARouter.debuggable()) {
logger.debug(TAG, String.format(Locale.getDefault(), "The group [%s] starts loading, trigger by [%s]", postcard.getGroup(), postcard.getPath()));
}
// new ARouter$$Group$$app();
IRouteGroup iGroupInstance = groupMeta.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 加载"app"组内内容
// 这里加载的是
// atlas.put("/app/pathreplace",
// RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, PathReplaceServiceImpl.class, "/app/pathreplace", "app", null, -1, -2147483648));
iGroupInstance.loadInto(Warehouse.routes);
// 将已经加载过的组从Warehouse.groupsIndex中移除,避免重复添加进Warehouse.routes
Warehouse.groupsIndex.remove(postcard.getGroup());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HandlerException(TAG + "Fatal exception when loading group meta. [" + e.getMessage() + "]");
}
// 递归调用
completion(postcard); // Reload
}
}
// 第二次加载时,已经找到
// RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, PathReplaceServiceImpl.class, "/app/pathreplace", "app", null, -1, -2147483648))
else {
// 给postcard赋值
postcard.setDestination(routeMeta.getDestination());
postcard.setType(routeMeta.getType());
postcard.setPriority(routeMeta.getPriority());
postcard.setExtra(routeMeta.getExtra());
Uri rawUri = postcard.getUri();
if (null != rawUri) { // Try to set params into bundle.
// ... 这次未调用到,暂时省略
}
switch (routeMeta.getType()) {
case PROVIDER: // if the route is provider, should find its instance
// Its provider, so it must be implememt IProvider
Class providerMeta = (Class) routeMeta.getDestination();
// 第一次被调用时,Warehouse.providers还没有赋值,因此instance==null
// 参数 PathReplaceServiceImpl.class
IProvider instance = Warehouse.providers.get(providerMeta);
if (null == instance) { // There's no instance of this provider
IProvider provider;
try {
// new PathReplaceServiceImpl();
provider = providerMeta.getConstructor().newInstance();
// new PathReplaceServiceImpl().init(mContext);
provider.init(mContext);
// 添加到Warehouse.providers中
Warehouse.providers.put(providerMeta, provider);
//
instance = provider;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HandlerException("Init provider failed! " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 将new PathReplaceServiceImpl()保存在postcard中,
// 因此可以从postcard获取IProvider的实例对象;
postcard.setProvider(instance);
// greenChannel()会忽略拦截器
postcard.greenChannel(); // Provider should skip all of interceptors
break;
case FRAGMENT:
// greenChannel()会忽略拦截器
postcard.greenChannel(); // Fragment needn't interceptors
default:
break;
}
}
}关键代码
该方法又体现了分组加载的思想,通过加载“app”节点下的"/app/pathreplace",完善了new Postcard("/app/pathreplace", "app")对象,通过反射创建了PathReplaceServiceImpl对象,并添加到了new Postcard("/app/pathreplace", "app")中
- 1、通过“app”分组找到
routes.put("app", ARouter$$Group$$app.class); - 2、通过反射创建
new ARouter$$Group$$app()对象,并加载ARouter$$Group$$app()分组内的全部数据,其中就包含RouteMeta.build(RouteType.PROVIDER, PathReplaceServiceImpl.class, "/app/pathreplace", "app", null, -1, -2147483648)) - 3、递归调用,创建
new PathReplaceServiceImpl();并添加到Warehouse.providers与new Postcard("/app/pathreplace", "app")中
到这里PathReplaceService的加载完成了,下边我们回到_ARouter.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")继续拦截器的加载。
_ARouter.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")
这里我们回到_ARouter.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")方法,
protected Postcard build(String path) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
throw new HandlerException(Consts.TAG + "Parameter is invalid!");
} else {
// navigation(clazz)这种方式是属于根据类型查找,而build(path)是根据名称进行查找
// 如果应用中没有实现PathReplaceService这个接口,则pService=null
PathReplaceService pService = ARouter.getInstance().navigation(PathReplaceService.class);
// 这里通过PathReplaceService,进行URL地址的更换
if (null != pService) {
path = pService.forString(path);
}
// 返回对应URl地址的Postcard
return build(path, extractGroup(path));
}
}这里最终返回new Postcard("/arouter/service/interceptor", "group")
下边回到_ARouter.afterInit()方法
_ARouter.afterInit() 方法结束
/**
* afterInit
*
* 用来加载拦截器
*
* 完成类的加载后,由{@link ARouter.init}调用
*/
static void afterInit() {
// Trigger interceptor init, use byName.
interceptorService = (InterceptorService) ARouter.getInstance()
// 生成一个Postcard对象
.build("/arouter/service/interceptor")
// 返回一个Postcard
//这个navigation()经过多次调用之后,
//最终调用的是_ARouter.navigation(context, postcard, requestCode, navigationCallback)方法
.navigation();
}
到这里,下边我们要跟踪的方法变为new Postcard("/arouter/service/interceptor", "group").navigation();
而该调用,最终会调用到_ARouter中
public Object navigation(Context mContext, Postcard postcard, int requestCode, NavigationCallback callback) {
return _ARouter.getInstance().navigation(mContext, postcard, requestCode, callback);
}最终会返回InterceptorServiceImpl拦截器对象,并赋值给InterceptorService interceptorService
可能因为InterceptorServiceImpl类的存在,所以在官方文档中,才会说Arouter是自举的吧
后边的不想说了,如果看到了这里,后边的东西,也不用我再说了,就到这吧。