[TOC]
框架技术
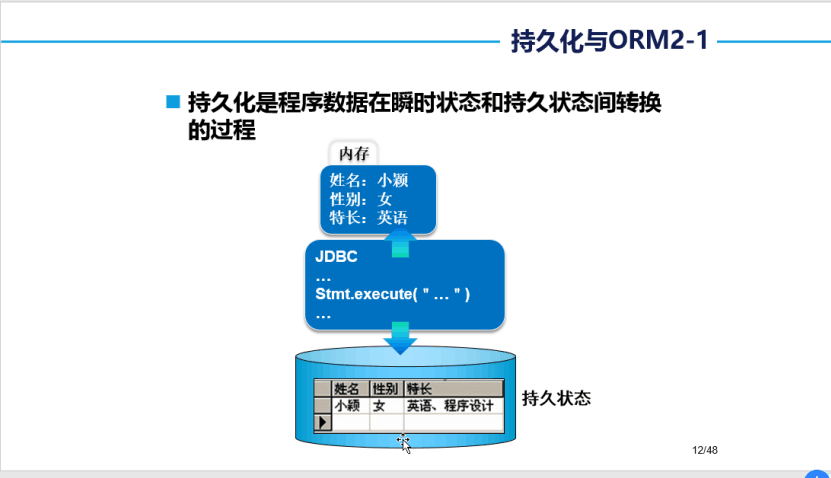
持久化
mybatis概念
概念:一个持久层框架
作用:ORM将sql语句映射成实体类
特点:巧灵活、半自动化、使用与中小型项目的开发
mybatis 入门
1、创建mybatis-config.xml文件
2、创建映射文件
3、获取xml配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
4、创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
5、获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
6、调用SqlSession的selectOne(命名空间.id名称);
Object object = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectUser");
7、关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
增删改
增
insert into user (username,password) values(#{username},#{password});
改
update user set username=#{username},password=#{password} where uid=#{uid}
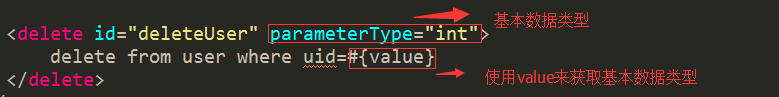
删
delete from user where uid=#{value}
Mapper接口开发
一、定义一个接口
public interface TypeMapper {
Type selectType(int typeid);
}
二、定义一个mapper.xml映射文件
mapper文件的要求:
1、namespace的值就是对象接口的全类名,并且类名和xml文件名保持一致
2、id的值就是抽象方法
3、resultType的值必须和抽象方法的返回值一致
4、parameterType的值和抽象方法的参数类型一致
注意 mapper.xml文件的约束是mapper.dtd,不是config.dtd
三、使用
将mybatis入门步骤中的步骤六改为如下代码:
TypeMapper mapper=sqlSession.getMapper(TypeMapper.class);
Type type=mapper.selectType(1);
动态sql
if
SELECT * FROM good INNER JOIN type ON good.type = type.typeid where 1=1
and gname like concat('%',#{gname},'%')
注意:
1、字符串的拼接建议使用concat来代替${}
2、判断条件中获取数据不用加#{},与el表达式不一样
where
作用where可以自动去除第一个and
and gname like concat('%',#{gname},'%')
and typename like concat('%',#{typename},'%')
choose when otherwise
作用:组合使用,相当于if else if else
set
update good
gname=#{gname},
gprice=#{gprice}
where gid=#{gid}
trim
作用:去除多余字符串
两种常见的用法
1、where and
prefix:字首 prefixOverrides:去除第一个指定的字符串
select * from good
and gname like concat('%',#{gname},'%')
and typename like concat('%',#{typename},'%')
2、set
prefix:字首 suffixOverrides:去除最后指定的字符串
update good
gname=#{gname},
gprice=#{gprice},
foreach
作用:动态循环拼接sql部分内容
1、open代表在集合前面添加的字符串
2、close代表在集合后面添加的字符串
3、separator代表集合分割使用的字符串
4、collection代表被循环的集合,值可以是list、map、array
5、常见用法,in的语句
1、如何配置多个数据库
使用environment可以配置多个数据库,通过ID来表示
2、transactionManager的type有哪些
JDBC、MANAGED
3、dataSource作用
配置数据源,有三种类型:UNPOOLED、POOLED、JNDI还可以配置四大参数(驱动。url/用户名、密码)
4、properties有什么用,如何用
加载配置文件(resource/url),
配置键值对(proprerty)
注意:如果resource和proprerty,resource优先级高
5、typeAliases有什么用,如何用
起别名
用类名(类名)
6、databaseIdProvider + databaseid
7、databaseIdProvider:给数据库起别名
8、databaseid:在statement中使用
myBatista根据url可以自动使用当前是什么数据库,然后使用哪个sql语句
9、mapper中的namespace有什么用
如果有相同的statementid的时候,使用namespace类区别
使用mapper接口开发dao时,namespace与接口全类名一致
10、增删改查
id:statement的唯一标识,或者说是调用方法名
parameterType:传入参数的数据类型 基本数据(可以不写)+引用类型(必须写)
resultType:返回数据类型
parameterType和resultType:都可以使用别名来表示数据类名
11、myBatista中的数据类型的别名
Integer Integer,int
int _int
12、#{}作用
获取传入数据
13、Mapper接口开发的四大要求
1、namespace的值就是对象接口的全类名,并且类名和xml文件名保持一致
2、id的值就是抽象方法
3、resultType的值必须和抽象方法的返回值一致
4、parameterType的值和抽象方法的参数类型一致