1. Phoenix定义
Phoenix最早是saleforce的一个开源项目,后来成为Apache基金的顶级项目。
Phoenix是构建在HBase上的一个SQL层,能让我们用标准的JDBC APIs而不是HBase客户端APIs来创建表,插入数据和对HBase数据进行查询。
put the SQL back in NoSQL
Phoenix完全使用Java编写,作为HBase内嵌的JDBC驱动。Phoenix查询引擎会将SQL查询转换为一个或多个HBase扫描,并编排执行以生成标准的JDBC结果集。直接使用HBase API、协同处理器与自定义过滤器,对于简单查询来说,其性能量级是毫秒,对于百万级别的行数来说,其性能量级是秒。
HBase的查询工具有很多,如:Hive、Tez、Impala、Spark SQL、Phoenix等。
Phoenix通过以下方式使我们可以少写代码,并且性能比我们自己写代码更好:
- 将SQL编译成原生的HBase scans。
- 确定scan关键字的最佳开始和结束
- 让scan并行执行
- ...
使用Phoenix的公司
2. 历史演进
- 3.0/4.0 release
ARRAY Type. 支持标准的JDBC数组类型
Sequences. 支持 CREATE/DROP SEQUENCE, NEXT VALUE FOR, CURRENT VALUE FOR也实现了
Multi-tenancy. 同一张HBase物理表上,不同的租户可以创建相互独立的视图
Views. 同一张HBase物理表上可以创建不同的视图
- 3.1/4.1 release
Apache Pig Loader . 通过pig来处理数据时支持pig加载器来利用Phoenix的性能
Derived Tables. 允许在一个FROM子句中使用SELECT子句来定义一张衍生表
Local Indexing. 后面介绍
Tracing. 后面介绍
- 3.2/4.2 release
Subqueries 支持在WHERE和FROM子句中的独立子查询和相关子查询
Semi/anti joins. 通过标准的[NOT] IN 和 [NOT] EXISTS关键字来支持半/反连接
Optimize foreign key joins. 通过利用跳跃扫描过滤器来优化外键连接
Statistics Collection. 通过收集表的统计信息来提高并行查询能力
- ** 3.3/4.3 release**
Many-to-many joins. 支持两边都太大以至于无法放进内存的连接
Map-reduce Integration. 支持Map-reduce集成
Functional Indexes. 后面介绍
- 4.4 release
User Defined Functions. 后面介绍
- 4.5 release
Asynchronous Index Population. 通过一个Map-reduce job,索引可以被异步创建
- 4.6 release
Time series Optimization. 优化针对时间序列数据的查询
- 4.7 release
Transaction Support. 后面介绍
- ** 4.8 release**
DISTINCT Query Optimization. 使用搜索逻辑来大幅提高 SELECT DISTINCT 和 COUNT DISTINCT的查询性能
Local Index Improvements. Reworked 后面介绍
Hive Integration. 能够在Phoenix内使用Hive来支持大表和大表之间的连接
Namespace Mapping. 将Phoenix schema映射到HBase的命名空间来增强不同schema之间的隔离性
3. 特性
3.1 Transactions (beta) 事务
该特性还处于beta版,并非正式版。通过集成Tephra,Phoenix可以支持ACID特性。Tephra也是Apache的一个项目,是事务管理器,它在像HBase这样的分布式数据存储上提供全局一致事务。HBase本身在行层次和区层次上支持强一致性,Tephra额外提供交叉区、交叉表的一致性来支持可扩展性。
要想让Phoenix支持事务特性,需要以下步骤:
- 配置客户端hbase-site.xml
phoenix.transactions.enabled
true
- 配置服务端hbase-site.xml
data.tx.snapshot.dir
/tmp/tephra/snapshots
data.tx.timeout
60
set the transaction timeout (time after which open transactions become invalid) to a reasonable value.
- 配置$HBASE_HOME并启动Tephra
./bin/tephra
通过以上配置,Phoenix已经支持了事务特性,但创建表的时候默认还是不支持的。如果想创建一个表支持事务特性,需要显示声明,如下:
CREATE TABLE my_table (k BIGINT PRIMARY KEY, v VARCHAR) TRANSACTIONAL=true;
就是在建表语句末尾增加 TRANSACTIONAL=true。
原本存在的表也可以更改成支持事务的,需要注意的是,事务表无法改回非事务的,因此更改的时候要小心。一旦改成事务的,就改不回去了。
ALTER TABLE my_other_table SET TRANSACTIONAL=true;
3.2 User-defined functions(UDFs) 用户定义函数
3.2.1 概述
Phoenix从4.4.0版本开始支持用户自定义函数。
用户可以创建临时或永久的用户自定义函数。这些用户自定义函数可以像内置的create、upsert、delete一样被调用。临时函数是针对特定的会话或连接,对其他会话或连接不可见。永久函数的元信息会被存储在一张叫做SYSTEM.FUNCTION的系统表中,对任何会话或连接均可见。
3.2.2 配置
- hive-site.xml
phoenix.functions.allowUserDefinedFunctions
true
fs.hdfs.impl
org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem
hbase.rootdir
${hbase.tmp.dir}/hbase
The directory shared by region servers and into
which HBase persists. The URL should be 'fully-qualified'
to include the filesystem scheme. For example, to specify the
HDFS directory '/hbase' where the HDFS instance's namenode is
running at namenode.example.org on port 9000, set this value to:
hdfs://namenode.example.org:9000/hbase. By default, we write
to whatever ${hbase.tmp.dir} is set too -- usually /tmp --
so change this configuration or else all data will be lost on
machine restart.
hbase.dynamic.jars.dir
${hbase.rootdir}/lib
The directory from which the custom udf jars can be loaded
dynamically by the phoenix client/region server without the need to restart. However,
an already loaded udf class would not be un-loaded. See
HBASE-1936 for more details.
后两个配置需要跟hbse服务端的配置一致。
以上配置完后,在JDBC连接时还需要执行以下语句:
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("phoenix.functions.allowUserDefinedFunctions", "true");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:phoenix:localhost", props);
以下是可选的配置,用于动态类加载的时候把jar包从hdfs拷贝到本地文件系统
hbase.local.dir
${hbase.tmp.dir}/local/
Directory on the local filesystem to be used
as a local storage.
3.3 Secondary Indexing 二级索引
在HBase中,只有一个单一的按照字典序排序的rowKey索引,当使用rowKey来进行数据查询的时候速度较快,但是如果不使用rowKey来查询的话就会使用filter来对全表进行扫描,很大程度上降低了检索性能。而Phoenix提供了二级索引技术来应对这种使用rowKey之外的条件进行检索的场景。
- Covered Indexes
只需要通过索引就能返回所要查询的数据,所以索引的列必须包含所需查询的列(SELECT的列和WHRER的列)
- Functional Indexes
从Phoeinx4.3以上就支持函数索引,其索引不局限于列,可以合适任意的表达式来创建索引,当在查询时用到了这些表达式时就直接返回表达式结果
- Global Indexes
Global indexing适用于多读少写的业务场景。
使用Global indexing的话在写数据的时候会消耗大量开销,因为所有对数据表的更新操作(DELETE, UPSERT VALUES and UPSERT SELECT),会引起索引表的更新,而索引表是分布在不同的数据节点上的,跨节点的数据传输带来了较大的性能消耗。在读数据的时候Phoenix会选择索引表来降低查询消耗的时间。在默认情况下如果想查询的字段不是索引字段的话索引表不会被使用,也就是说不会带来查询速度的提升。
- Local Indexes
Local indexing适用于写操作频繁的场景。
与Global indexing一样,Phoenix会自动判定在进行查询的时候是否使用索引。使用Local indexing时,索引数据和数据表的数据是存放在相同的服务器中的避免了在写操作的时候往不同服务器的索引表中写索引带来的额外开销。使用Local indexing的时候即使查询的字段不是索引字段索引表也会被使用,这会带来查询速度的提升,这点跟Global indexing不同。一个数据表的所有索引数据都存储在一个单一的独立的可共享的表中。
3.4 Statistics Collection 统计信息收集
UPDATE STATISTICS可以更新某张表的统计信息,以提高查询性能
3.5 Row timestamp 时间戳
从4.6版本开始,Phoenix提供了一种将HBase原生的row timestamp映射到Phoenix列的方法。这样有利于充分利用HBase提供的针对存储文件的时间范围的各种优化,以及Phoenix内置的各种查询优化。
3.6 Paged Queries 分页查询
Phoenix支持分页查询:
- Row Value Constructors (RVC)
- OFFSET with limit
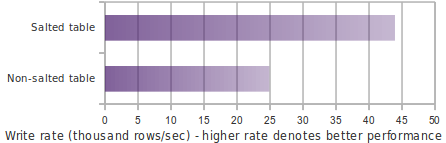
3.7 Salted Tables 散步表
如果row key是自动增长的,那么HBase的顺序写会导致region server产生数据热点的问题,Phoenix的Salted Tables技术可以解决region server的热点问题
3.8 Skip Scan 跳跃扫描
可以在范围扫描的时候提高性能
3.9 Views 视图
标准的SQL视图语法现在在Phoenix上也支持了。这使得能在同一张底层HBase物理表上创建多个虚拟表。
3.10 Multi tenancy 多租户
通过指定不同的租户连接实现数据访问的隔离
3.11 Dynamic Columns 动态列
Phoenix 1.2, specifying columns dynamically is now supported by allowing column definitions to included in parenthesis after the table in the FROM clause on a SELECT statement. Although this is not standard SQL, it is useful to surface this type of functionality to leverage the late binding ability of HBase.
3.12 Bulk CSV Data Loading 大量CSV数据加载
加载CSV数据到Phoenix表有两种方式:1. 通过psql命令以单线程的方式加载,数据量少的情况下适用。 2. 基于MapReduce的bulk load工具,适用于数据量大的情况
3.13 Query Server 查询服务器
Phoenix4.4引入的一个单独的服务器来提供thin客户端的连接
3.14 Tracing 追踪
从4.1版本开始Phoenix增加这个特性来追踪每条查询的踪迹,这使用户能够看到每一条查询或插入操作背后从客户端到HBase端执行的每一步。
3.15 Metrics 指标
Phoenix提供各种各样的指标使我们能够知道Phoenix客户端在执行不同SQL语句的时候其内部发生了什么。这些指标在客户端JVM中通过两种方式来收集:
- Request level metrics - collected at an individual SQL statement
level - Global metrics - collected at the client JVM level
4. 架构和组成
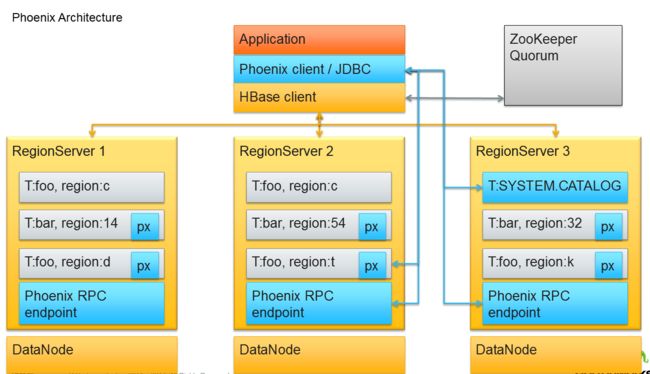
- Phoenix架构
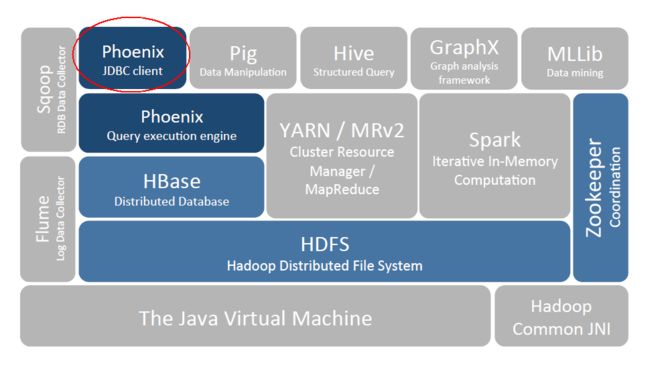
- Phoenix在Hadoop生态系统中的位置
5. 数据存储
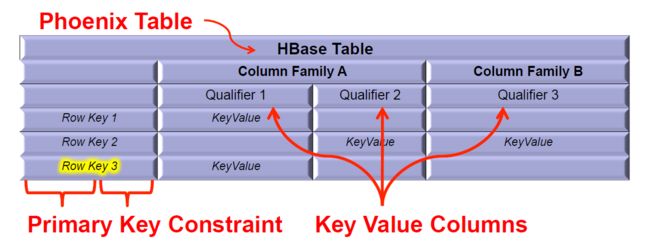
Phoenix将HBase的数据模型映射到关系型世界
6. 对QL的支持
支持的命令如下:
- SELECT
Example:
SELECT * FROM TEST LIMIT 1000;
SELECT * FROM TEST LIMIT 1000 OFFSET 100;
SELECT full_name FROM SALES_PERSON WHERE ranking >= 5.0 UNION ALL SELECT reviewer_name FROM CUSTOMER_REVIEW WHERE score >= 8.0
- UPSERT VALUES
Example:
UPSERT INTO TEST VALUES('foo','bar',3);
UPSERT INTO TEST(NAME,ID) VALUES('foo',123);
- UPSERT SELECT
Example:
UPSERT INTO test.targetTable(col1, col2) SELECT col3, col4 FROM test.sourceTable WHERE col5 < 100
UPSERT INTO foo SELECT * FROM bar;
- DELETE
Example:
DELETE FROM TEST;
DELETE FROM TEST WHERE ID=123;
DELETE FROM TEST WHERE NAME LIKE 'foo%';
- CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE my_schema.my_table ( id BIGINT not null primary key, date)
CREATE TABLE my_table ( id INTEGER not null primary key desc, date DATE not null,m.db_utilization DECIMAL, i.db_utilization) m.DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING='DIFF'
CREATE TABLE stats.prod_metrics ( host char(50) not null, created_date date not null,txn_count bigint CONSTRAINT pk PRIMARY KEY (host, created_date) )
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "my_case_sensitive_table"
( "id" char(10) not null primary key, "value" integer)
DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING='NONE',VERSIONS=5,MAX_FILESIZE=2000000 split on (?, ?, ?)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_schema.my_table (org_id CHAR(15), entity_id CHAR(15), payload binary(1000),CONSTRAINT pk PRIMARY KEY (org_id, entity_id) )TTL=86400
- DROP TABLE
Example:
DROP TABLE my_schema.my_table;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS my_table;
DROP TABLE my_schema.my_table CASCADE;
- CREATE FUNCTION
Example:
CREATE FUNCTION my_reverse(varchar) returns varchar as 'com.mypackage.MyReverseFunction' using jar 'hdfs:/localhost:8080/hbase/lib/myjar.jar'
CREATE FUNCTION my_reverse(varchar) returns varchar as 'com.mypackage.MyReverseFunction'
CREATE FUNCTION my_increment(integer, integer constant defaultvalue='10') returns integer as 'com.mypackage.MyIncrementFunction' using jar '/hbase/lib/myincrement.jar'
CREATE TEMPORARY FUNCTION my_reverse(varchar) returns varchar as 'com.mypackage.MyReverseFunction' using jar 'hdfs:/localhost:8080/hbase/lib/myjar.jar'
- DROP FUNCTION
Example:
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS my_reverse
DROP FUNCTION my_reverse
- CREATE VIEW
Example:
CREATE VIEW "my_hbase_table"( k VARCHAR primary key, "v" UNSIGNED_LONG) default_column_family='a';
CREATE VIEW my_view ( new_col SMALLINT ) AS SELECT * FROM my_table WHERE k = 100;
CREATE VIEW my_view_on_view AS SELECT * FROM my_view WHERE new_col > 70;
- DROP VIEW
Example:
DROP VIEW my_view
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS my_schema.my_view
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS my_schema.my_view CASCADE
- CREATE SEQUENCE
Example:
CREATE SEQUENCE my_sequence;
CREATE SEQUENCE my_sequence START WITH -1000
CREATE SEQUENCE my_sequence INCREMENT BY 10
CREATE SEQUENCE my_schema.my_sequence START 0 CACHE 10
- DROP SEQUENCE
Example:
DROP SEQUENCE my_sequence
DROP SEQUENCE IF EXISTS my_schema.my_sequence
- ALTER
Example:
ALTER TABLE my_schema.my_table ADD d.dept_id char(10) VERSIONS=10
ALTER TABLE my_table ADD dept_name char(50), parent_id char(15) null primary key
ALTER TABLE my_table DROP COLUMN d.dept_id, parent_id;
ALTER VIEW my_view DROP COLUMN new_col;
ALTER TABLE my_table SET IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true,DISABLE_WAL=true;
- CREATE INDEX
Example:
CREATE INDEX my_idx ON sales.opportunity(last_updated_date DESC)
CREATE INDEX my_idx ON log.event(created_date DESC) INCLUDE (name, payload) SALT_BUCKETS=10
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS my_comp_idx ON server_metrics ( gc_time DESC, created_date DESC ) DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING='NONE',VERSIONS=?,MAX_FILESIZE=2000000 split on (?, ?, ?)
CREATE INDEX my_idx ON sales.opportunity(UPPER(contact_name))
- DROP INDEX
Example:
DROP INDEX my_idx ON sales.opportunity
DROP INDEX IF EXISTS my_idx ON server_metrics
- ALTER INDEX
Example:
ALTER INDEX my_idx ON sales.opportunity DISABLE
ALTER INDEX IF EXISTS my_idx ON server_metrics REBUILD
- EXPLAIN
Example:
EXPLAIN SELECT NAME, COUNT(*) FROM TEST GROUP BY NAME HAVING COUNT(*) > 2;
EXPLAIN SELECT entity_id FROM CORE.CUSTOM_ENTITY_DATA WHERE organization_id='00D300000000XHP' AND SUBSTR(entity_id,1,3) = '002' AND created_date < CURRENT_DATE()-1;
- UPDATE STATISTICS
Example:
UPDATE STATISTICS my_table
UPDATE STATISTICS my_schema.my_table INDEX
UPDATE STATISTICS my_index
UPDATE STATISTICS my_table COLUMNS
UPDATE STATISTICS my_table SET phoenix.stats.guidepost.width=50000000
- CREATE SCHEMA
Example:
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS my_schema
CREATE SCHEMA my_schema
- USE
Example:
USE my_schema
USE DEFAULT
- DROP SCHEMA
Example:
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS my_schema
DROP SCHEMA my_schema
7. 安装部署
7.1 安装预编译的Phoenix
下载并解压最新版的phoenix-[version]-bin.tar包
将phoenix-[version]-server.jar放入服务端和master节点的HBase的lib目录下
重启HBase
将phoenix-[version]-client.jar添加到所有Phoenix客户端的classpath
7.2 使用Phoenix
7.2.1 命令行
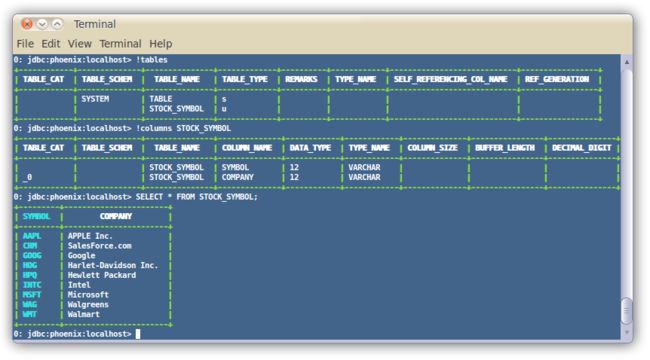
若要在命令行执行交互式SQL语句:
1.切换到bin目录
2.执行以下语句
$ sqlline.py localhost
若要在命令行执行SQL脚本
$ sqlline.py localhost ../examples/stock_symbol.sql
7.2.2 客户端
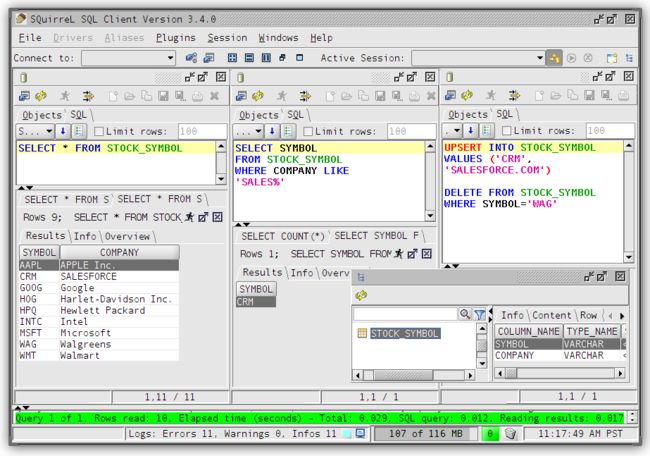
SQuirrel是用来连接Phoenix的客户端。
SQuirrel安装步骤如下:
1. Remove prior phoenix-[*oldversion*]-client.jar from the lib directory of SQuirrel, copy phoenix-[*newversion*]-client.jar to the lib directory (*newversion* should be compatible with the version of the phoenix server jar used with your HBase installation)
2. Start SQuirrel and add new driver to SQuirrel (Drivers -> New Driver)
3. In Add Driver dialog box, set Name to Phoenix, and set the Example URL to jdbc:phoenix:localhost.
4. Type “org.apache.phoenix.jdbc.PhoenixDriver” into the Class Name textbox and click OK to close this dialog.
5. Switch to Alias tab and create the new Alias (Aliases -> New Aliases)
6. In the dialog box, Name: *any name*, Driver: Phoenix, User Name: *anything*, Password: *anything*
7. Construct URL as follows: jdbc:phoenix: *zookeeper quorum server*. For example, to connect to a local HBase use: jdbc:phoenix:localhost
8. Press Test (which should succeed if everything is setup correctly) and press OK to close.
9. Now double click on your newly created Phoenix alias and click Connect. Now you are ready to run SQL queries against Phoenix.
8. 测试
8.1 Pherf
Pherf是可以通过Phoenix来进行性能和功能测试的工具。Pherf可以用来生成高度定制的数据集,并且测试SQL在这些数据集上的性能。
8.1.1 构建Pherf
Pherf是在用maven构建Phoenix的过程中同时构建的。可以用两种不同的配置来构建:
- 集群(默认)
This profile builds Pherf such that it can run along side an existing cluster. The dependencies are pulled from the HBase classpath.
- 独立
This profile builds all of Pherf’s dependencies into a single standalone jar. The deps will be pulled from the versions specified in Phoenix’s pom.
- 构建全部的Phoenix。包含Pherf的默认配置。
mvn clean package -DskipTests
- 用Pherf的独立配置来构建Phoenix。
mvn clean package -P standalone -DskipTests
8.1.2 安装
用以上的Maven命令构建完Pherf后,会在该模块的目标目录下生成一个zip文件。
- 将该zip文件解压到合适的目录
- 配置
env.sh文件 - ./pherf.sh -h
- 想要在一个真正的集群上测试,运行如下命令:
./pherf.sh -drop all -l -q -z localhost -schemaFile .*user_defined_schema.sql -scenarioFile .*user_defined_scenario.xml
8.1.3 命令示例
- 列出所有可运行的场景文件
$./pherf.sh -listFiles
- 删掉全部场景文件中存在的特定的表、加载和查询数据
$./pherf.sh -drop all -l -q -z localhost
8.1.4 参数
-h Help
-l Apply schema and load data
-q Executes Multi-threaded query sets and write results
-z [quorum] Zookeeper quorum
-m Enable monitor for statistics
-monitorFrequency [frequency in Ms] _Frequency at which the monitor will snopshot stats to log file.
-drop [pattern] Regex drop all tables with schema name as PHERF. Example drop Event tables: -drop .(EVENT). Drop all: -drop .* or -drop all*
-scenarioFile Regex or file name of a specific scenario file to run.
-schemaFile Regex or file name of a specific schema file to run.
-export Exports query results to CSV files in CSV_EXPORT directory
-diff Compares results with previously exported results
-hint Executes all queries with specified hint. Example SMALL
-rowCountOverride
-rowCountOverride [number of rows] Specify number of rows to be upserted rather than using row count specified in schema
8.1.5 为数据生成增加规则
8.1.6 定义场景
8.1.7 结果
结果实时写入结果目录中。可以打开.jpg格式文件来实时可视化。
8.1.8 测试
Run unit tests: mvn test -DZK_QUORUM=localhost
Run a specific method: mvn -Dtest=ClassName#methodName test
More to come...
8.2 性能
Phoenix通过以下方法来奉行把计算带到离数据近的地方的哲学:
协处理器
在服务端执行操作来最小化服务端和客户端的数据传输定制的过滤器
为了删减数据使之尽可能地靠近源数据并最小化启动代价,Phoenix使用原生的HBase APIs而不是使用Map/Reduce框架
8.2.1 Phoenix对比相近产品
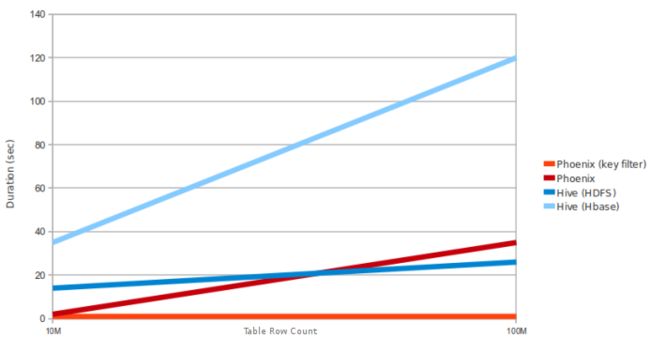
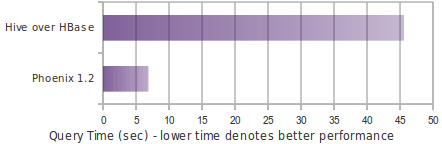
8.2.1.1 Phoenix vs Hive (running over HDFS and HBase)
Query: select count(1) from table over 10M and 100M rows. Data is 5 narrow columns. Number of Region Servers: 4 (HBase heap: 10GB, Processor: 6 cores @ 3.3GHz Xeon)
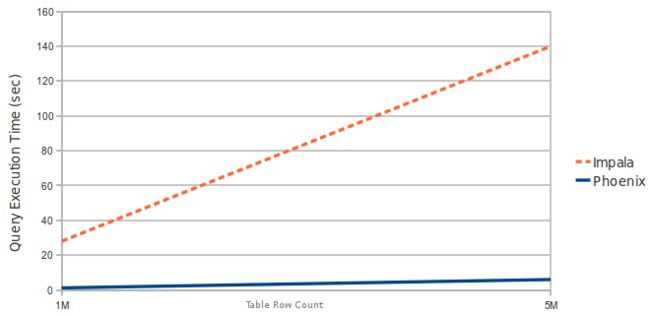
8.2.1.2 Phoenix vs Impala (running over HBase)
Query: select count(1) from table over 1M and 5M rows. Data is 3 narrow columns. Number of Region Server: 1 (Virtual Machine, HBase heap: 2GB, Processor: 2 cores @ 3.3GHz Xeon)
8.2.2 Latest Automated Performance Run
Latest Automated Performance Run | Automated Performance Runs History
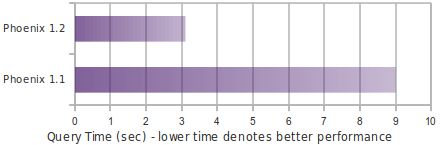
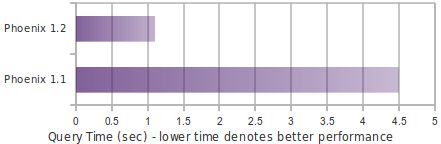
8.2.3 Phoenix1.2性能提升
- Essential Column Family
- Skip Scan
- Salting
- Top-N
9. 参考资料
- http://phoenix.apache.org
- http://phoenix.apache.org/Phoenix-in-15-minutes-or-less.html
- http://hadooptutorial.info/apache-phoenix-hbase-an-sql-layer-on-hbase/
- http://www.phoenixframework.org/docs/resources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apache_Phoenix
可进入我的博客查看原文
欢迎关注公众号: FullStackPlan 获取更多干货哦~