1305. All Elements in Two Binary Search Trees
Hi 大家好,我是张小猪。欢迎来到『宝宝也能看懂』系列之 leetcode 题解。
这里是第 169 期的第 2 题,也是题目列表中的第 1305 题 -- 『All Elements in Two Binary Search Trees』
题目描述
Given two binary search trees root1 and root2.
Return a list containing all the integers from both trees sorted in ascending order.
Example 1:
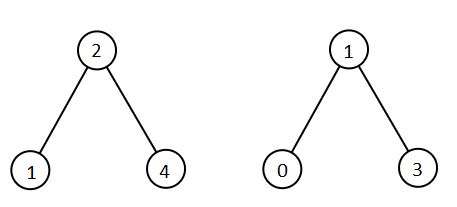
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3]
Output: [0,1,1,2,3,4]Example 2:
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
Output: [-10,0,0,1,2,5,7,10]Example 3:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
Output: [0,1,2,5,7]Example 4:
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = []
Output: [-10,0,10]Example 5:
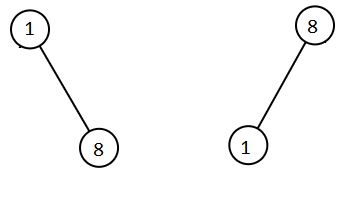
Input: root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1]
Output: [1,1,8,8]Constraints:
- Each tree has at most
5000nodes. - Each node's value is between
[-10^5, 10^5].
官方难度
MEDIUM
解决思路
题目内容很短,有两个二叉搜索树,需要把它们里面的所有值放进一个数组中,并且结果是要保持顺序递增的。
读完之后第一反应,这题还真是直白呀,没包装个什么描述性的说法,搞的我都不好写文章了,哼 >.<
关于什么是二叉搜索树,这个大家可以自行搜索,当然我之后也会写文章介绍常见的数据结构,一不小心给自己开了个新坑。
对于这道题目的要求,我们可以遍历这两个二叉搜索树,得到所有的值放进新数组中,然后再进行排序。当然,既然是非常科班的题目,自然有很套路的应对方式。毕竟一涉及到基于比较的排序,那复杂度就直接上 O(nlogn) 了。
直接方案
我们想要得到符合递增顺序的二叉搜索树内的所有值,直接进行中序遍历即可,需要的时间复杂度是 O(n)。关于什么是中序遍历,同样我会在新坑里面提到。这里先不做过多展开。
然后对于两个有序数组进行合并,我们可以这样做:
- 取得两个数组中各自的最小值,即第一个值
- 把它们进行比较,得到的小值一定是当前所有剩余的未合并元素中的最小值
- 把这个小值从数组开头剔除掉,放进最终的结果的末端
- 重复回到步骤 1,直到有一个数组空了
- 把剩下的那个数组中的值直接添加进结果的末端
这样我们只需要 O(n) 的时间复杂度即可完成合并了。
当然在实际代码中,我们还可以做一些优化,例如并不把数组开头的值剔除掉,而是使用一个索引标识当前访问的位置。因为对于数组这样的线性表,我们剃掉第一值也就意味着后续所有值的前移,代价还是很大的。
const getAllElements = (root1, root2) => {
const arr1 = [];
const arr2 = [];
traversal(root1, arr1);
traversal(root2, arr2);
const ret = [];
let idx1 = idx2 = 0;
while (idx1 < arr1.length && idx2 < arr2.length) {
arr1[idx1] < arr2[idx2] ? ret.push(arr1[idx1++]) : ret.push(arr2[idx2++]);
}
while (idx1 < arr1.length) ret.push(arr1[idx1++]);
while (idx2 < arr2.length) ret.push(arr2[idx2++]);
return ret;
function traversal(node, arr) {
if (!node) return;
traversal(node.left, arr);
arr.push(node.val);
traversal(node.right, arr);
}
};上面的代码跑到了 208ms,暂时 beats 100%。不过我跑完之后回头一看,不得不说,写的真丑。要是 code review 看到这样的代码,我肯定是不会合并的。那我们把它改的稍微好看一点吧。
const traversal = (node, arr = []) => {
if (node) {
traversal(node.left, arr);
arr.push(node.val);
traversal(node.right, arr);
}
return arr;
};
const merge = (arr1, arr2) => {
const ret = [];
let idx1 = idx2 = 0;
while (idx1 < arr1.length && idx2 < arr2.length) {
arr1[idx1] < arr2[idx2] ? ret.push(arr1[idx1++]) : ret.push(arr2[idx2++]);
}
while (idx1 < arr1.length) ret.push(arr1[idx1++]);
while (idx2 < arr2.length) ret.push(arr2[idx2++]);
return ret;
};
const getAllElements = (root1, root2) => merge(traversal(root1), traversal(root2));总结
这是一道比较套路的题,需要一点点科班知识,即二叉搜索树和中序遍历。相信大家应该很容易就能掌握这种套路了吧。
那么最后加一个小思考,上面代码中的 merge 方法是否可以改为支持不定数量的数组合并呢,即 const merge = (...list) => {}。希望小伙伴们能帮帮张小猪,么么嗒 >.<