UITableview缓存行高是优化UITableview性能的一个重要方面。一般情况下,造成UITableViewCell的动态行高的原因主要是UILabel的高度会随文字量的变化而变化。那么下面我们先看一下UILabel的自适应行高的实现:
UILabel自适应行高的实现
第一种 使用- (CGRect)boundingRectWithSize:(CGSize)size options:(NSStringDrawingOptions)options attributes:(nullable NSDictionary*)attributes context:(nullable NSStringDrawingContext *)context计算UILabel的size
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] init];
label.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
label.numberOfLines = 0;
label.text = @"网上聊了一个妹子,今天见面,问老妈要了二百块钱,老妈问我干嘛用,我说约会,她高高兴兴的就给了。刚出家门,老爸就把我拽到一遍说“小子,二百块给我一百,半个月不知道烟的滋味了。”";
CGSize size = CGSizeMake(200, MAXFLOAT);
CGRect rect = [label.text boundingRectWithSize:size options:NSStringDrawingUsesLineFragmentOrigin attributes:@{NSFontAttributeName: [UIFont systemFontOfSize: 17]} context:nil];
label.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, rect.size.width, rect.size.height);
[self.view addSubview:label];
第二种 使用sizeToFit
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 0)];
label.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
label.text = @"网上聊了一个妹子,今天见面,问老妈要了二百块钱,老妈问我干嘛用,我说约会,她高高兴兴的就给了。刚出家门,老爸就把我拽到一遍说“小子,二百块给我一百,半个月不知道烟的滋味了。”";
label.numberOfLines = 0;
[label sizeToFit];
[self.view addSubview:label];
以上讨论了如何实现UILabel的自适应行高,下面开始讨论UITableViewCell的自适应行高。
UITableViewCell的自适应行高分为两种,一种是使用纯代码布局Cell,另外一种是通过xib布局。
UITableView缓存行高
纯代码布局Cell
当UITableViewCell使用纯代码布局时,我们可以在从网络端拉取了数据后,就马上把每一个Cell的高度计算出来,然后缓存下来,缓存可以使用NSCache缓存,将model作为key,cell的高度作为value。具体来讲,我们创建一个
prototypeCell,这个cell是我们专门用来计算Cell的高度用的,然后我们给这个cell的model赋值,在cell的.m文件里有一个计算cell高度的方法,显然这个方法是通过model给UILabel等赋值,然后通过计算各个子控件的高度来计算出cell的最终高度。
//这是在从网络端拉取完了数据后x直接在后台计算cell高度
dispatch_async(dispatch_queue_create("mytest", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT), ^{
for (Joke *model in self.modelArray) {
self.prototypeCell.model = model;
[self.cellHeightCache setCellHeightForModel:model withTableView:self.tableView cellHeight:[self.prototypeCell getCellHeight]];
}
});
- (void)setCellHeightForModel:(id)model withTableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellHeight:(CGFloat)cellHeight
{
CGSize cacheSize = NilCacheSize;
cacheSize.height = cellHeight;
[self setOrientationSize:cacheSize forModel:model];
}
//将值设到缓存中
- (void)setOrientationSize:(CGSize)size forModel:(id)model
{
if (UIDeviceOrientationIsLandscape([UIDevice currentDevice].orientation)) {
[self.cacheLandscape setObject:[NSValue valueWithCGSize:size] forKey:[model modelID]];
}else{
[self.cacheportrait setObject:[NSValue valueWithCGSize:size] forKey:[model modelID]];
}
}
在- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath方法中:
//首先从缓存中取,缓存中取不到再通过cell的.m文件的方法去获取,然后缓存下来
return [self.cellHeightCache getCellHeightForModel:self.modelArray[indexPath.row] withTableView:tableView orCalc:^CGFloat(id model, UITableView *tableView) {
self.prototypeCell.model = model;
return [self.prototypeCell getCellHeight];
}];
当使用纯代码布局时,还有一种方式,那就是在model里面去计算cell的高度。因为cell的子控件的布局是知道的,所以在model里面可以计算那些行高动态改变的控件的高度,这样就可以计算出cell的高度。每一次调用model里面的方法去计算行高之前先去NSCache缓存里面查找有没有缓存,没有缓存才去计算,有缓存则直接取出来用。
在model的.m文件中:
- (CGFloat)getCellHeight
{
NSString *string = @"网上聊了一个妹子,今天见面,问老妈要了二百块钱,老妈问我干嘛用,我说约会,她高高兴兴的就给了。刚出家门,老爸就把我拽到一遍说“小子,二百块给我一百,半个月不知道烟的滋味了。”";
CGRect rect = [string boundingRectWithSize:CGSizeMake([UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width-60, MAXFLOAT) options:NSStringDrawingUsesLineFragmentOrigin attributes:@{NSFontAttributeName : [UIFont systemFontOfSize:20]} context:nil];
return rect.size.height + 20;
}
使用xib布局
当我们想要使用xib来布局Cell时,这里以Cell中只有一个UILabel,UILabel的高度自适应为例:
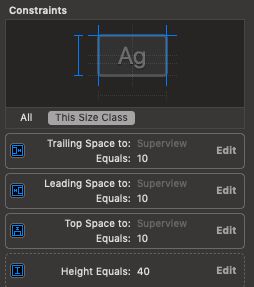
1.首先为Cell中的子控件添加约束,对于高度会改变的UILabel,同样添加四个约束,高度约束为一个指定的高度值,并且在Attributes inspector中将Lines设置为0
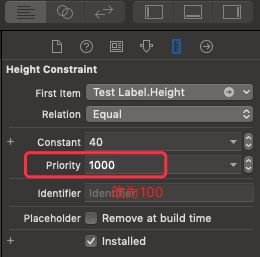
2.选中设置UILabel高度的这个约束,点击size inspector,将这个约束的propority修改为一个较小的值:
3.在- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath这个方法中,给prototypeCell的model赋值,然后调用layoutIfNeeded这个方法进行强制布局:
//这里是先尝试从缓存中去获取cell的高度,如果缓存中获取不到,那么就要自己计算
return [self.cellHeightCache getCellHeightForModel:self.modelArray[indexPath.row] withTableView:tableView orCalc:^CGFloat(id model, UITableView *tableView) {
//给cell的model赋值
self.prototypeCell.model = self.modelArray[indexPath.row];
//强制进行布局
[self.prototypeCell layoutIfNeeded];
//在布局完成后通过Label的位置来确定cell的高度
return self.prototypeCell.testLabel.frame.origin.y + self.prototypeCell.testLabel.frame.size.height + 10;
}];
one more thing
iOS11开始,UITableView默认实现了预估行高,即UITableView默认实现了下面的一行代码:
self.tableView.estimatedRowHeight = 44;
UITableView之所以可以显示超出其显示区域大小的内容,是因为其继承自UIScrollview,拥有contentSize。那么其contentSize是怎么计算出来的呢?
当没有设置预估行高时,会通过调用- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath这个方法来计算出contentSize,如果总共有n个cell,那么为了计算contentSize,会调用3n次上述方法,为什么会调用3n次我至今没有搞明白。
所以没有预估行高时,UITableView的方法的调用过程大概如下:
- 1.为了计算contentSize,调用3n次
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath方法 - 2.然后再布局每一个cell,在布局每一个cell时,会先调用
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath方法,然后调用- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath方法。
当设置了预估行高时,则不会去通过调用- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath这个方法去计算contentSize,而是简单的通过estimatedRowHeight*n来计算contentSize,显然这样计算是要快很多。预估行高的产生也就是为了更快的计算出contentSize。
但是预估行高当预估行高和真实行高之间的差距较大时,会出现闪屏的现象
那么我们如何关闭自动打开的预估行高设置呢?只需要将预估行高设置为0即可:
self.tableView.estimatedRowHeight = 44;
UITableView的性能优化
UITableView的性能优化主要分为以下几个方面:
- 1.cell的重用
- 2.缓存行高
- 3.按需加载内容
有些情况下我们可能会快速滑动列表,这时候其实会有大量的cell被创建,被重用,但是其实我们只是去浏览列表停止的那一页的上下一定范围内的信息,前面快速划过的信息对我来说都是无用的,此时我们可以通过scrollview的代理方法:
scrollViewWillEndDragging: withVelocity: targetContentoffset:
// 按需加载 - 如果目标行与当前行相差超过指定行数,只在目标滚动范围的前后指定3行加载。
- (void)scrollViewWillEndDragging:(UIScrollView *)scrollView withVelocity:(CGPoint)velocity targetContentOffset:(inout CGPoint *)targetContentOffset {
[self.needLoadArray removeAllObjects];
NSIndexPath *ip = [self.tableView indexPathForRowAtPoint:CGPointMake(0, targetContentOffset->y)]; // 停止拖拽后,预计滑动停止后到的偏移量
NSIndexPath *cip = [[self.tableView indexPathsForVisibleRows] firstObject]; // 当前可视区域内 cell 组
NSInteger skipCount = 8;
NSLog(@"targetContentOffset = %f",targetContentOffset->y);
NSLog(@"indexPathForRowAtPoint = %@",ip);
NSLog(@"visibleRows = %@",[self.tableView indexPathsForVisibleRows]);
if (labs(cip.row - ip.row) > skipCount) { // labs-返回 x 的绝对值,进入该方法,说明滑动太厉害了,预计停留位置与当前可视区域范围内差 8 个cell 以上了.
// 拖拽停止滑动停止后,即将显示的 cell 索引组
NSArray *temp = [self.tableView indexPathsForRowsInRect:CGRectMake(0, targetContentOffset->y, self.tableView.width, self.tableView.height)];
NSMutableArray *arrM = [NSMutableArray arrayWithArray:temp];
NSLog(@"temp = %@",temp);
if (velocity.y < 0) { // 向上滑动-即加载更多数据
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [temp lastObject];
if (indexPath.row + 3 < self.dataSource.count) { // 滑动停止后出现的 cell 索引仍在数据源范围之内
[arrM addObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:indexPath.row + 1 inSection:0]];
[arrM addObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:indexPath.row + 2 inSection:0]];
[arrM addObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:indexPath.row + 3 inSection:0]];
}
} else { // 向下滑动-加载之前的数据
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [temp firstObject];
if (indexPath.row > 3) {
[arrM addObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:indexPath.row - 3 inSection:0]];
[arrM addObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:indexPath.row - 2 inSection:0]];
[arrM addObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:indexPath.row - 1 inSection:0]];
}
}
[self.needLoadArray addObjectsFromArray:arrM];
}
}
然后在- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath中,进行判断:
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
if(self.needLoadArray.count > 0 && [self.needLoadArray indexOfObject:indexPath] == NSNotFound) {
[cell clear];
return;
}
- 4.加载网络数据,下载图片,使用异步加载,并缓存
- 5.不给cell动态添加subview,而是使用hidden属性
- 6.UIKit优化