本篇文章在《iOS开发之Runtime常用示例总结》基础上修改,地址是
「:」http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20170301/18804.html
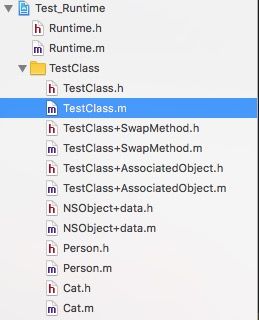
本篇文章主要创建的类如下:
首先我们先创建一个实例类TestClass
这个类实现了NSCopying和NSCoding协议,包含公共的成员属性,和实例方法以及类方法,
在.m文件中
我们有私有成员变量和成员属性,和私有方法。
下面我们来具体介绍一下runtime的常用方法
1、利用runtime来获取类名
/**
获取类名
@param class 相应类
@return NSString:类名
*/
+ (NSString *)fetchClassName:(Class)class
{
const char *className = class_getName(class);
return [NSString stringWithUTF8String:className];
}
2、利用runtime来获取成员变量
/**
获取成员变量
@param class Class
@return NSArray
*/
+(NSArray *)fetchIvarList:(Class)class
{
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList(class, &count);//获取成员变量的个数count,以及数组内容
NSMutableArray *mutableList = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:count];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
NSMutableDictionary *dic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithCapacity:2];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivarList[i]);//获取成员变量的名称
const char *ivarType = ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivarList[i]);//获取成员变量的类型
dic[@"type"] = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarType];
dic[@"ivarName"] = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
[mutableList addObject:dic];
}
free(ivarList);
return [NSArray arrayWithArray:mutableList];
}
其输出结果如下:
-
- 注意,如果用这个来获取类的成员变量,是不分私有和公有之分的,都会获取出来,意思也就是不管是成员变量,还是成员属性,都可以获取的到,并且获取到的成员属性的名称是有下划线的
3、获取类的成员属性
- 注意,如果用这个来获取类的成员变量,是不分私有和公有之分的,都会获取出来,意思也就是不管是成员变量,还是成员属性,都可以获取的到,并且获取到的成员属性的名称是有下划线的
/**
获取类的属性列表,包括私有和公有属性,以及定义再延展中的属性
@param class Class
@return 属性列表数组
*/
+(NSArray *)fetchPropertyList:(Class)class
{
unsigned int count = 0;
objc_property_t *propertyList = class_copyPropertyList(class, &count);
NSMutableArray *mutableList = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:count];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
const char *propertyName = property_getName(propertyList[i]);
[mutableList addObject:[NSString stringWithUTF8String:propertyName]];
}
free(propertyList);
return mutableList;
}
其输出结果如下:
-
- 注意,获取的成员属性名称是没有下划线的,此处也不分私有和公有
4、获取类的实例方法列表
- 注意,获取的成员属性名称是没有下划线的,此处也不分私有和公有
/**
获取类的实例方法列表:getter,setter,对象方法等。但不能获取类方法,也就是加号方法
@param class class
@return 类的实例方法列表
*/
+ (NSArray *)fetchMethodList:(Class)class
{
unsigned int count = 0;
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList(class, &count);
NSMutableArray *mutableList = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:count];
for (unsigned int i = 0 ; i < count; i ++) {
Method method = methodList[i];
SEL methodName = method_getName(method);
[mutableList addObject:NSStringFromSelector(methodName)];
}
free(methodList);
return mutableList;
}
其输出结果如下:
-
- 注意,其中类的成员属性的getter,setter方法也获取不到的,但是类方法是获取不到
5、获取类的协议列表
- 注意,其中类的成员属性的getter,setter方法也获取不到的,但是类方法是获取不到
/**
获取协议列表
@param class class
@return 协议列表
*/
+(NSArray *)fetchProtocolList:(Class)class
{
unsigned int count = 0;
__unsafe_unretained Protocol **protocolList = class_copyProtocolList(class, &count);
NSMutableArray *mutableList = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:count];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
Protocol *protocol = protocolList[i];
const char *protocolName = protocol_getName(protocol);
[mutableList addObject:[NSString stringWithUTF8String:protocolName]];
}
return mutableList;
}
其输出结果是
6、实现方法的交换
/** 方法交换 @param class 交换方法所在的类 @param method1 方法1 @param method2 方法2 */ + (void)methodSwap:(Class)class firstMethod:(SEL)method1 secondMethod:(SEL)method2 { Method firstMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, method1); Method secondMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, method2); method_exchangeImplementations(firstMethod, secondMethod); }
例如我们在TestClass(SwapMethod)类别中,写如下代码:
#import "TestClass+SwapMethod.h"
#import "Runtime.h"
@implementation TestClass(SwapMethod)
+ (void)load
{
[Runtime methodSwap:[self class] firstMethod:@selector(method1) secondMethod:@selector(method2)];
}
- (void)method2
{
NSLog(@"这里实际上调用的是method1的实现");
}
@end
然后我们去调用method2,会发现调用的方法实际上是method1的方法,调用method1方法,实际上调用的是method2的方法
7、给类添加新的方法与实现
/**
给类上添加新的方法与实现
@param class 相应的类
@param methodSel 方法的名
@param methodSelImpl 对应方法实现的方法名
*/
+ (void)addMethod:(Class)class method:(SEL)methodSel method:(SEL)methodSelImpl
{
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(class, methodSelImpl);
IMP methodIMP = method_getImplementation(method);
const char *types = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
class_addMethod(class, methodSel, methodIMP, types);
}
- *注意,此方法添加的是实例方法,而非类方法
当我们访问一个方法时,如果找不到此方法的实现,iOS提供了两个方法去访问,
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel;//针对访问不到类方法时,访问的方法
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel;//针对访问不到实例方法时,访问的方法
我们以实例方法未准,假如我们在TestClass中添加一个方法,然后不去实现
此时,如果访问此方法,则系统会找不到此方法的实现,此时我们重写resolveInstanceMethod方法,你会发现系统会访问此方法,如果我们在此方法中给未实现的方法添加实现,则系统会去访问我们提供的实现方法的,例如:
void addnewMethodIMP(id self,SEL _cmd,NSString *temp)
{
NSLog(@"动态添加实现");
}
- (void)addMethodComplete:(NSString *)value
{
NSLog(@"oc替换的方法:%@",value);
}
//此方法时针对对象方法的
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
{
#warning mark-- 以下是两种添加形式
//第一种
//其中“v@:”代表的是针对谁添加的方法,如果后面带有参数,则写在:后面,例如下面的 "v@:@"
// if (sel == @selector(missMethod:)) {
// class_addMethod([self class], sel, (IMP)addnewMethodIMP, "v@:@");
// return YES;
// }
//第二种 此种方法就是我们上面写的
// [Runtime addMethod:[self class] method:sel method:@selector(addMethodComplete:)];
// return YES;
// return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
return NO;
}
8、属性关联
在类目中动态的为我们的类添加相应的属性。
下方就是在TestClass的类目中通过objc_getAssociatedObject()和objc_setAssociatedObject()两个方法为TestClass类添加了一个addNewProperty属性
#import "TestClass+AssociatedObject.h"
@interface TestClass (AssociatedObject)
@property (nonatomic,strong)NSString *addNewProperty;
@end
@implementation TestClass(AssociatedObject)
#pragma mark-- 动态属性关联
static char addNewProperty;
/**
getter方法
@return 返回关联属性的值
*/
- (NSString *)addNewProperty
{
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &addNewProperty);
}
/**
setter方法
@param addNewProperty 设置关联属性的值
*/
- (void)setAddNewProperty:(NSString *)addNewProperty
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &addNewProperty, addNewProperty, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
@end
此时如果我们再去获取TestClass的属性,其输出结果就是
其中包含了我们动态添加的addNewProperty属性
9、下面我们用runtime来做一些数据解析的应用
首先我们创建一个NSObject(data)的类别,注意,运用runtime一定要导入头文件#import
- 1 将对象转化为字典
- (NSDictionary *)objectToDic
{
unsigned int count = 0;
objc_property_t *propertyList = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
NSMutableDictionary *propertyDic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithCapacity:count];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
objc_property_t property = propertyList[i];
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:property_getName(property)];
id value = [self valueForKey:key];
if (value == nil) {
value = [NSNull null];
}
else
{
value = [self getObjectInternal:value];
}
[propertyDic setObject:value forKey:key];
}
return propertyDic;
}
//此方法是针对,当如果我们的对象中含有其他对象时,我们可以将其对象也转换为字典的形式
- (id)getObjectInternal:(id)obj
{
if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]||[obj isKindOfClass:[NSNumber class]]||[obj isKindOfClass:[NSNull class]]) {
return obj;
}
if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
NSArray *objArr = obj;
NSMutableArray *arr = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:objArr.count];
for (int i = 0 ; i < objArr.count; i ++) {
[arr setObject:[self getObjectInternal:[objArr objectAtIndex:i]] atIndexedSubscript:i];
}
return arr;
}
if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
NSDictionary *objDic = obj;
NSMutableDictionary *dic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithCapacity:[objDic count]];
for (NSString *key in objDic.allKeys) {
[dic setValue:[self getObjectInternal:[objDic objectForKey:key]] forKey:key];
}
return dic;
}
return [obj objectToDic];
}
其中 - (id)getObjectInternal:(id)obj这个方法,是当我们的对象中含有其他对象时,我们也可以将其转换为字典的形式,例如:
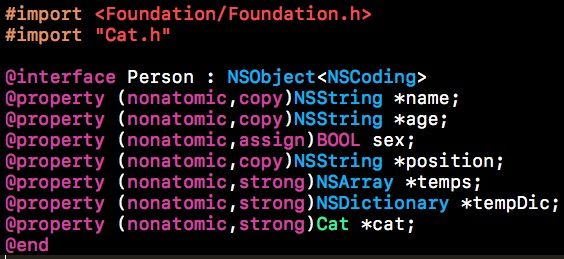
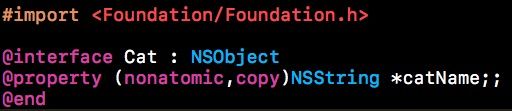
Person类中含有Cat类,
当我们用Person对象调用转换为字典的方法时,Person对象中含有的Cat对象也会被转换为字典的形式,例如:
其输出结果是:
然后我们将其转化为json字符串
//将字典转化为json
- (NSString *)dicToJson
{
NSError *error;
NSData *jsonData = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:self options:NSJSONWritingPrettyPrinted error:&error];
NSString *jsonString;
if (!jsonData) {
NSLog(@"%@",error);
}else{
jsonString = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:jsonData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
}
NSMutableString *mutStr = [NSMutableString stringWithString:jsonString];
NSRange range = {0,jsonString.length};
//去掉字符串中的空格
[mutStr replaceOccurrencesOfString:@" " withString:@"" options:NSLiteralSearch range:range];
NSRange range2 = {0,mutStr.length};
//去掉字符串中的换行符
[mutStr replaceOccurrencesOfString:@"\n" withString:@"" options:NSLiteralSearch range:range2];
return mutStr;
}
如果要将json转化为字典则调用下面的方法
//json转化为字典
- (NSDictionary *)jsonToDic
{
if (self == nil) {
return nil;
}
NSData *jsonData = [(NSString *)self dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSError *err;
NSDictionary *dic = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:jsonData options:NSJSONReadingMutableContainers error:&err];
if (err) {
return nil;
}
return dic;
}
- 2 字典转化为对象
/**
字典转对象
@param dic 字典
@return 属性已经有值的对象实例
*/
- (id)dicToObject:(NSDictionary *)dic
{
unsigned int count = 0;
objc_property_t *propertyList = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
for (unsigned int i = 0 ; i < count; i ++) {
objc_property_t property = propertyList[i];
NSString *propertyName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:property_getName(property)];
NSString *propertyType = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:property_getAttributes(property)];
if ([[dic allKeys] containsObject:propertyName])
{
id value = [dic valueForKey:propertyName];
if (![value isKindOfClass:[NSNull class]]&&value!=nil) {
if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
id pro = [self cretateInstanceByClassName:[self getClassName:propertyType]];
[pro dicToObject:value];
[self setValue:pro forKey:propertyName];
}
else
{
[self setValue:value forKey:propertyName];
}
}
else
{
value = [NSNull null];
[self setValue:value forKey:propertyName];
}
}
}
return self;
}
//获取属性类型名字
- (NSString *)getClassName:(NSString *)typeString
{
NSArray * attributes = [typeString componentsSeparatedByString:@","];
// T@"NSDictionary",&,N,V_tempDic
if (attributes.count>0) {
NSString * typeAttribute = [attributes objectAtIndex:0];
if ([typeAttribute hasPrefix:@"T@"] && [typeAttribute length] > 1) {
NSString * typeClassName = [typeAttribute substringWithRange:NSMakeRange(3, [typeAttribute length]-4)]; return typeClassName;
}
}
return typeString;
}
//下面的方法是我们针对当对象中含有某个类时,做的处理
//根据类名称,创建一个实例对象
- (id)cretateInstanceByClassName:(NSString *)className
{
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
Class aclass = [bundle classNamed:className];
id anInstance = [[aclass alloc] init];
return anInstance;
}
例如,当我们用上面的对象转字典输出的字典,经过这个字典转对象的方法,
其输出的结果是我们赋给的catName的名称@“bb”
- 3 利用runtime对象序列化,当然我们要实现NSCoding协议
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)decoder
{
if (self = [super init]) {
unsigned int count = 0;
//获取类中所有成员变量名
Ivar *ivar = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i- 4 利用runtime实现UIAlertView的Block回调
平时我们用UIAlertView需要使用其代理方法来确定我们的点击事件,使用起来不够方便,新的sdk中UIAlertViewController是使用block来访问其点击事件的,那我们就将UIAlertView也封装成可以利用block来访问点击事件的类别
首先我们需要一个block属性值
@interface UIAlertView ()
@property (copy, nonatomic) void (^block)(UIAlertView *UIAlertView, NSInteger buttonIndex);
@end
利用数组来添加按钮
- (instancetype)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title message:(NSString *)message
cancelButtonTitle:(NSString *)cancelButtonTitle
otherButtonTitles:(NSArray *)otherButtonTitles
{
self = [self initWithTitle:title message:message
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:cancelButtonTitle otherButtonTitles:nil];
if (self) {
for (NSString *otherButtonTitle in otherButtonTitles) {
[self addButtonWithTitle:otherButtonTitle];
}
}
return self;
}
将alertView与block关联起来(通过runtime)注意:要导入头文件
import
这里也就是动态给alertView添加了block属性
- (void)setBlock:(void (^)(UIAlertView *, NSInteger))block
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(block), block, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
- (void (^)(UIAlertView *, NSInteger))block
{
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @selector(block));
}
当点击alertview 的按钮时
- (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex
{
if (self.block) {
self.block(alertView, buttonIndex);
}
}
下面的方法就是block回调
- (void)showUsingBlock:(void (^)(UIAlertView *, NSInteger))block
{
self.delegate = self;
self.block = block;
[self show];
}
通过调用此方法,得到的block回调值来判断当前点击的按钮
UIAlertView *alert = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"" message:@"" delegate:nil cancelButtonTitle:@"cancel" otherButtonTitles:@"ok", nil];
[alert showUsingBlock:^(UIAlertView *alertView, NSInteger buttonIndex) {
}];
当我们需要针对ios8之前和之后的版本做适配时,我们可以写出一个公共的方法来调用alertView,代码如下:
+ (void)alertTitle:(NSString *)title message:(NSString *)message cancelButtonTitle: (NSString *)cancelButtonTitle otherButtonTitles:(NSArray *)otherButtonTitles showInVC: (UIViewController *)vc index:(void (^)(NSInteger))block
{
if (IsIOS8Early) {
UIAlertView *alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:title message:message cancelButtonTitle:cancelButtonTitle otherButtonTitles:otherButtonTitles];
[alert showUsingBlock:^(UIAlertView *alertView, NSInteger buttonIndex) {
block(buttonIndex);
}];
}
else
{
UIAlertController *alertVC = [UIAlertController alertControllerWithTitle:title message:message preferredStyle:UIAlertControllerStyleAlert];
UIAlertAction *cancelAction = [UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:cancelButtonTitle style:UIAlertActionStyleCancel handler:^(UIAlertAction * _Nonnull action) {
block(0);
}];
[alertVC addAction:cancelAction];
if (otherButtonTitles&&otherButtonTitles.count>0) {
for (int i = 0; i < otherButtonTitles.count; i ++)
{
UIAlertAction *okAction = [UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:otherButtonTitles[i] style:UIAlertActionStyleDefault handler:^(UIAlertAction * _Nonnull action) {
block(i +1);
}];
[alertVC addAction:okAction];
}
}
[vc presentViewController:alertVC animated:YES completion:nil];
}
}
如果我们需要对UIActionSheet做出这样的适配,也可以用上述方法来解决
以上就是runtime的常用示例的介绍,此文转自
「:」http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20170301/18804.html
若有不理解的,请跳转至此链接