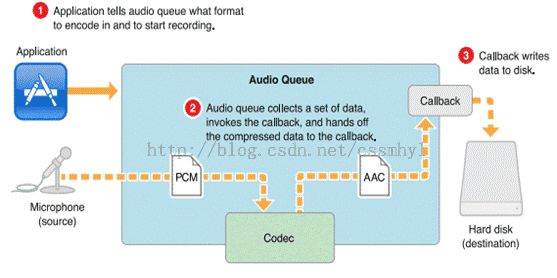
本例需求:将Mic采集的PCM转成AAC,可得到两种不同数据,本例采用AudioQueue/AudioUnit两种方式存储,即: 可采集到两种声音数据,一种为PCM,一种为转换后的AAC.
原理:由于公司需求更改为Mic采集的pcm一路提供给WebRTC使用,另一路将pcm转为aac,将aac提供给直播用的API。因此应该先让Mic采集原始pcm数据,采用AudioQueue/AudioUnit两种方式采集,然后在回调函数中将其转换为aac提供给C++API
本例中仅包含部分代码,建议下载代码详细看,在关键代码中都有注释中可以看到难理解的含义.
GitHub地址(附代码) : PCM->AAC
地址 : PCM->AAC
博客地址 : PCM->AAC
掘金地址 : PCM->AAC
实现方式:(下文两种实现方式,挑选自己适合的)
1.AudioQueue : 若对延迟要求不高,可实现录制,播放,暂停,回退,同步,转换(PCM->AAC等)等功能可采用这种方式
2.AudioUnit : 比AudioQueue更加底层,可实现高性能,低延迟,并且包括去除回声,混音等等功能。
AudioQueue为什么会出现波动的情况?解决方法?这种波动的原因是在Audio Queue的底层产生的,之前说过,Audio ToolBox是基于Audio Unit的,回调函数的波动要到底层才能解决。
一.本文需要基本知识点
C语言相关函数:
1.memset:
原型: void * memset(void * __b, int __c, size_t __len);
解释:将s中当前位置后面的n个字节(typedef unsigned int size_t) 用ch替换并返回s
作用:在一段内存块中填充某个特定的值,它是对较大的结构体或数组进行清零操作的一种最快方法。
2.memcpy:
原型: void * memcpy(void * dest, const void * src, size_t n);
解释:从源src所指的内存地址的起始位置开始拷贝n个字节到目标dest所指的内存地址的起始位置中
3.void free(void *);
解释:释放内存,需要将malloc出来的内存统统释放掉,对于结构体要先将结构体中malloc出来的释放掉最后再释放掉结构体本身。
OC 中部分知识点:
1.OSStaus:状态码,如果没有错误返回0:(即noErr)
2.AudioFormatGetPropertyInfo:
原型:
AudioFormatGetPropertyInfo(
AudioFormatPropertyID inPropertyID,
UInt32 inSpecifierSize,
const void * __nullable inSpecifier,
UInt32 * outPropertyDataSize);
* 作用:检索给定属性的信息,比如编码器目标格式的size等
3.AudioSessionGetProperty:
原型:
extern OSStatus
AudioSessionGetProperty(
AudioSessionPropertyID inID,
UInt32 *ioDataSize,
void *outData);
* 作用:获取指定AudioSession对象的inID属性的值(比如采样率,声道数等等)
4.AudioUnitSetProperty
extern OSStatus
AudioUnitSetProperty( AudioUnit inUnit,
AudioUnitPropertyID inID,
AudioUnitScope inScope,
AudioUnitElement inElement,
const void * __nullable inData,
UInt32 inDataSize)
* 作用:设置AudioUnit特定属性的值,其中scope,element不理解可参考下文audio unit概念部分,这里可以设置音频流的各种参数,比如采样频率、量化位数、通道个数、每包中帧的个数等等
音频基础知识
AVFoundation框架中的AVAudioPlayer和AVAudioRecorder类,用法简单,但是不支持流式,也就意味着在播放音频前,必须等到整个音频加载完成后,才能开始播放音频;录音时,也必须等到录音结束后才能获得录音数据。
在iOS和Mac OS X中,音频队列Audio Queues是一个用来录制和播放音频的软件对象,也就是说,可以用来录音和播放,录音能够获取实时的PCM原始音频数据。
数据介绍
(1)In CBR (constant bit rate) formats, such as linear PCM and IMA/ADPCM, all packets are the same size.
(2)In VBR (variable bit rate) formats, such as AAC, Apple Lossless, and MP3, all packets have the same number of frames but the number of bits in each sample value can vary.
(3)In VFR (variable frame rate) formats, packets have a varying number of frames. There are no commonly used formats of this type.
- 概念:
(1)音频文件的组成:文件格式(或者音频容器)+数据格式(或者音频编码)
知识点:
- 文件格式是用于形容文件本身的格式,可以通过多种不同方法为真正的音频数据编码,例如CAF文件便是一种文件格式,它能够包含MP3格式,线性PCM以及其他数据格式音频
线性PCM:这是表示线性脉冲编码机制,主要是描写用于将模拟声音数据转换成数组格式的技术,简单地说也就是未压缩的数据。因为数据是未压缩的,所以我们便可以最快速地播放出音频,而如果空间不是问题的话这便是iPhone 音频的优先代码选择
(2).音频文件计算大小
简述:声卡对声音的处理质量可以用三个基本参数来衡量,即采样频率,采样位数和声道数。
知识点:
采样频率:单位时间内采样次数。采样频率越大,采样点之间的间隔就越小,数字化后得到的声音就越逼真,但相应的数据量就越大,声卡一般提供11.025kHz,22.05kHz和44.1kHz等不同的采样频率。
采样位数:记录每次采样值数值大小的位数。采样位数通常有8bits或16bits两种,采样位数越大,所能记录的声音变化度就越细腻,相应的数据量就越大。
声道数:处理的声音是单声道还是立体声。单声道在声音处理过程中只有单数据流,而立体声则需要左右声道的两个数据流。显然,立体声的效果要好,但相应数据量要比单声道数据量加倍。
声音数据量的计算公式:数据量(字节 / 秒)=(采样频率(Hz)* 采样位数(bit)* 声道数)/ 8
单声道的声道数为1,立体声的声道数为2. 字节B,1MB=1024KB = 1024*1024B
(3)
-
CoreAudio 介绍
(1). CoreAudio分为三层结构,如上图
1.最底层的I/O Kit, MIDI, HAL等用于直接与硬件相关操作,一般来说用不到。
2.中间层服务是对数据格式的转换,对硬盘执行读写操作,解析流,使用插件等。
- 其中AudioConverter Services 可实现不同音频格式的转码,如PCM->AAC等
- Audio File Services支持读写音频数据从硬盘
- Audio Unit Services and Audio Processing Graph Services 可实现使应用程序处理数字信号,完成一些插件功能,如均衡器和混声器等。
- Audio File Stream Services 可以使程序解析流,如播放一段来自网络的音频。
- Audio Format Services 帮助应用程序管理音频格式相关操作
3.最高层是用基于底层实现的部分功能,使用相对简单。 - Audio Queue Services 可实现录音,播放,暂停,同步音频等功能
- AVAudioPlayer 提供简单地OC接口对于音频的播放与暂停,功能较为局限。
- OpenAL 实现三维混音音频单元顶部,适合开发游戏
(2).Audio Data Formats:通过设置一组属性代码可以和操作系统支持的任何格式一起工作。(包括采样率,比特率),对于AudioQueue与AudioUnit设置略有不同。
struct AudioStreamBasicDescription
{
Float64 mSampleRate; // 采样率 :Hz
AudioFormatID mFormatID; // 采样数据的类型,PCM,AAC等
AudioFormatFlags mFormatFlags; // 每种格式特定的标志,无损编码 ,0表示没有
UInt32 mBytesPerPacket; // 一个数据包中的字节数
UInt32 mFramesPerPacket; // 一个数据包中的帧数,每个packet的帧数。如果是未压缩的音频数据,值是1。动态帧率格式,这个值是一个较大的固定数字,比如说AAC的1024。如果是动态大小帧数(比如Ogg格式)设置为0。
UInt32 mBytesPerFrame; // 每一帧中的字节数
UInt32 mChannelsPerFrame; // 每一帧数据中的通道数,单声道为1,立体声为2
UInt32 mBitsPerChannel; // 每个通道中的位数,1byte = 8bit
UInt32 mReserved; // 8字节对齐,填0
};
typedef struct AudioStreamBasicDescription AudioStreamBasicDescription;
---------------------------- Audio Queue ---------------------------
二.AudioQueue
.音频队列 — 详细请参考 Audio Queue,该文章中已有详细描述,不再重复介绍,不懂请参考。
1.简述:在iOS和Mac OS X中,音频队列是一个用来录制和播放音频的软件对象,他用AudioQueueRef这个不透明数据类型来表示,该类型在AudioQueue.h头文件中声明。
2.工作:
- 连接音频硬件
- 内存管理
- 根据需要为已压缩的音频格式引入编码器
- 媒体的录制或播放
你可以将音频队列配合其他Core Audio的接口使用,再加上相对少量的自定义代码就可以在你的应用程序中创建一套完整的数字音频录制或播放解决方案。
3.结构:
一组音频队列缓冲区(audio queue buffers),每个音频队列缓冲区都是一个存储音频数据的临时仓库
一个缓冲区队列(buffer queue),一个包含音频队列缓冲区的有序列表
一个你自己编写的音频队列回调函数(audio queue callback)
它的架构很大程度上依赖于这个音频队列是用来录制还是用来播放的。不同之处在于音频队列如何连接到它的输入和输入,还有它的回调函数所扮演的角色。
4.调用步骤,首先将项目设置为MRC,在控制器中配置audioSession基本设置(基本设置,不会谷歌),导入该头文件,直接在需要时机调用该类startRecord与stopRecord方法,另外还提供了生成录音文件的功能,具体参考github中的代码。
本例中涉及的一些宏定义,具体可以下载代码详细看
#define kBufferDurationSeconds .5
#define kXDXRecoderAudioBytesPerPacket 2
#define kXDXRecoderAACFramesPerPacket 1024
#define kXDXRecoderPCMTotalPacket 512
#define kXDXRecoderPCMFramesPerPacket 1
#define kXDXRecoderConverterEncodeBitRate 64000
#define kXDXAudioSampleRate 48000.0
(1).设置AudioStreamBasicDescription 基本信息
-(void)startRecorder {
// Reset pcm_buffer to save convert handle, 每次开始音频会话前初始化pcm_buffer, pcm_buffer用来在捕捉声音的回调中存储累加的PCM原始数据
memset(pcm_buffer, 0, pcm_buffer_size);
pcm_buffer_size = 0;
frameCount = 0;
// 是否正在录制
if (isRunning) {
// log4cplus_info("pcm", "Start recorder repeat");
return;
}
// 本例中采用log4打印log信息,若你没有可以不用,删除有关Log4的语句
// log4cplus_info("pcm", "starup PCM audio encoder");
// 设置采集的数据的类型为PCM
[self setUpRecoderWithFormatID:kAudioFormatLinearPCM];
OSStatus status = 0;
UInt32 size = sizeof(dataFormat);
// 编码器转码设置
[self convertBasicSetting];
// 这个if语句用来检测是否初始化本例对象成功,如果不成功重启三次,三次后如果失败可以进行其他处理
if (err != nil) {
NSString *error = nil;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
usleep(100*1000);
error = [self convertBasicSetting];
if (error == nil) break;
}
// if init this class failed then restart three times , if failed again,can handle at there
// [self exitWithErr:error];
}
// 新建一个队列,第二个参数注册回调函数,第三个防止内存泄露
status = AudioQueueNewInput(&dataFormat, inputBufferHandler, (__bridge void *)(self), NULL, NULL, 0, &mQueue);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","AudioQueueNewInput status:%d",(int)status);
// 获取队列属性
status = AudioQueueGetProperty(mQueue, kAudioQueueProperty_StreamDescription, &dataFormat, &size);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","AudioQueueNewInput status:%u",(unsigned int)dataFormat.mFormatID);
// 这里将头信息添加到写入文件中,若文件数据为CBR,不需要添加,为VBR需要添加
[self copyEncoderCookieToFile];
// 可以计算获得,在这里使用的是固定大小
// bufferByteSize = [self computeRecordBufferSizeFrom:&dataFormat andDuration:kBufferDurationSeconds];
// log4cplus_info("pcm","pcm raw data buff number:%d, channel number:%u",
kNumberQueueBuffers,
dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame);
// 设置三个音频队列缓冲区
for (int i = 0; i != kNumberQueueBuffers; i++) {
// 注意:为每个缓冲区分配大小,可根据具体需求进行修改,但是一定要注意必须满足转换器的需求,转换器只有每次给1024帧数据才会完成一次转换,如果需求为采集数据量较少则用本例提供的pcm_buffer对数据进行累加后再处理
status = AudioQueueAllocateBuffer(mQueue, kXDXRecoderPCMTotalPacket*kXDXRecoderAudioBytesPerPacket*dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame, &mBuffers[i]);
// 入队
status = AudioQueueEnqueueBuffer(mQueue, mBuffers[i], 0, NULL);
}
isRunning = YES;
hostTime = 0;
status = AudioQueueStart(mQueue, NULL);
log4cplus_info("pcm","AudioQueueStart status:%d",(int)status);
}
初始化输出流的结构体描述
struct AudioStreamBasicDescription
{
Float64 mSampleRate; // 采样率 :Hz
AudioFormatID mFormatID; // 采样数据的类型,PCM,AAC等
AudioFormatFlags mFormatFlags; // 每种格式特定的标志,无损编码 ,0表示没有
UInt32 mBytesPerPacket; // 一个数据包中的字节数
UInt32 mFramesPerPacket; // 一个数据包中的帧数,每个packet的帧数。如果是未压缩的音频数据,值是1。动态帧率格式,这个值是一个较大的固定数字,比如说AAC的1024。如果是动态大小帧数(比如Ogg格式)设置为0。
UInt32 mBytesPerFrame; // 每一帧中的字节数
UInt32 mChannelsPerFrame; // 每一帧数据中的通道数,单声道为1,立体声为2
UInt32 mBitsPerChannel; // 每个通道中的位数,1byte = 8bit
UInt32 mReserved; // 8字节对齐,填0
};
typedef struct AudioStreamBasicDescription AudioStreamBasicDescription;
注意: kNumberQueueBuffers,音频队列可以使用任意数量的缓冲区。你的应用程序制定它的数量。一般情况下这个数字是3。这样就可以让给一个忙于将数据写入磁盘,同时另一个在填充新的音频数据,第三个缓冲区在需要做磁盘I/O延迟补偿的时候可用
如何使用AudioQueue:
- 创建输入队列AudioQueueNewInput
- 分配buffers
- 入队:AudioQueueEnqueueBuffer
- 回调函数采集音频数据
- 出队
AudioQueueNewInput
// 作用:创建一个音频队列为了录制音频数据
原型:extern OSStatus
AudioQueueNewInput( const AudioStreamBasicDescription *inFormat, 同上
AudioQueueInputCallback inCallbackProc, // 注册回调函数
void * __nullable inUserData,
CFRunLoopRef __nullable inCallbackRunLoop,
CFStringRef __nullable inCallbackRunLoopMode,
UInt32 inFlags,
AudioQueueRef __nullable * __nonnull outAQ);
// 这个函数的第四个和第五个参数是有关于线程的,我设置成null,代表它默认使用内部线程去录音,而且还是异步的
(2).设置采集数据的格式,采集PCM必须按照如下设置,参考苹果官方文档,不同需求自己另行修改
-(void)setUpRecoderWithFormatID:(UInt32)formatID {
// Notice : The settings here are official recommended settings,can be changed according to specific requirements. 此处的设置为官方推荐设置,可根据具体需求修改部分设置
//setup auido sample rate, channel number, and format ID
memset(&dataFormat, 0, sizeof(dataFormat));
UInt32 size = sizeof(dataFormat.mSampleRate);
AudioSessionGetProperty(kAudioSessionProperty_CurrentHardwareSampleRate,
&size,
&dataFormat.mSampleRate);
dataFormat.mSampleRate = kXDXAudioSampleRate; // 设置采样率
size = sizeof(dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame);
AudioSessionGetProperty(kAudioSessionProperty_CurrentHardwareInputNumberChannels,
&size,
&dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame);
dataFormat.mFormatID = formatID;
// 关于采集PCM数据是根据苹果官方文档给出的Demo设置,至于为什么这么设置可能与采集回调函数内部实现有关,修改的话请谨慎
if (formatID == kAudioFormatLinearPCM)
{
/*
为保存音频数据的方式的说明,如可以根据大端字节序或小端字节序,
浮点数或整数以及不同体位去保存数据
例如对PCM格式通常我们如下设置:kAudioFormatFlagIsSignedInteger | kAudioFormatFlagIsPacked等
*/
dataFormat.mFormatFlags = kLinearPCMFormatFlagIsSignedInteger | kLinearPCMFormatFlagIsPacked;
// 每个通道里,一帧采集的bit数目
dataFormat.mBitsPerChannel = 16;
// 8bit为1byte,即为1个通道里1帧需要采集2byte数据,再*通道数,即为所有通道采集的byte数目
dataFormat.mBytesPerPacket = dataFormat.mBytesPerFrame = (dataFormat.mBitsPerChannel / 8) * dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame;
// 每个包中的帧数,采集PCM数据需要将dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket设置为1,否则回调不成功
dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket = kXDXRecoderPCMFramesPerPacket;
}
}
(3).将PCM转成AAC一些基本设置
-(NSString *)convertBasicSetting {
// 此处目标格式其他参数均为默认,系统会自动计算,否则无法进入encodeConverterComplexInputDataProc回调
AudioStreamBasicDescription sourceDes = dataFormat; // 原始格式
AudioStreamBasicDescription targetDes; // 转码后格式
// 设置目标格式及基本信息
memset(&targetDes, 0, sizeof(targetDes));
targetDes.mFormatID = kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC;
targetDes.mSampleRate = kXDXAudioSampleRate;
targetDes.mChannelsPerFrame = dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame;
targetDes.mFramesPerPacket = kXDXRecoderAACFramesPerPacket; // 采集的为AAC需要将targetDes.mFramesPerPacket设置为1024,AAC软编码需要喂给转换器1024个样点才开始编码,这与回调函数中inNumPackets有关,不可随意更改
OSStatus status = 0;
UInt32 targetSize = sizeof(targetDes);
status = AudioFormatGetProperty(kAudioFormatProperty_FormatInfo, 0, NULL, &targetSize, &targetDes);
// log4cplus_info("pcm", "create target data format status:%d",(int)status);
memset(&_targetDes, 0, sizeof(_targetDes));
// 赋给全局变量
memcpy(&_targetDes, &targetDes, targetSize);
// 选择软件编码
AudioClassDescription audioClassDes;
status = AudioFormatGetPropertyInfo(kAudioFormatProperty_Encoders,
sizeof(targetDes.mFormatID),
&targetDes.mFormatID,
&targetSize);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","get kAudioFormatProperty_Encoders status:%d",(int)status);
// 计算编码器容量
UInt32 numEncoders = targetSize/sizeof(AudioClassDescription);
// 用数组存放编码器内容
AudioClassDescription audioClassArr[numEncoders];
// 将编码器属性赋给数组
AudioFormatGetProperty(kAudioFormatProperty_Encoders,
sizeof(targetDes.mFormatID),
&targetDes.mFormatID,
&targetSize,
audioClassArr);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","wrirte audioClassArr status:%d",(int)status);
// 遍历数组,设置软编
for (int i = 0; i < numEncoders; i++) {
if (audioClassArr[i].mSubType == kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC && audioClassArr[i].mManufacturer == kAppleSoftwareAudioCodecManufacturer) {
memcpy(&audioClassDes, &audioClassArr[i], sizeof(AudioClassDescription));
break;
}
}
// 防止内存泄露
if (_encodeConvertRef == NULL) {
// 新建一个编码对象,设置原,目标格式
status = AudioConverterNewSpecific(&sourceDes, &targetDes, 1,
&audioClassDes, &_encodeConvertRef);
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder","new convertRef failed status:%d \n",(int)status);
return @"Error : New convertRef failed \n";
}
}
// 获取原始格式大小
targetSize = sizeof(sourceDes);
status = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCurrentInputStreamDescription, &targetSize, &sourceDes);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","get sourceDes status:%d",(int)status);
// 获取目标格式大小
targetSize = sizeof(targetDes);
status = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCurrentOutputStreamDescription, &targetSize, &targetDes);;
// log4cplus_info("pcm","get targetDes status:%d",(int)status);
// 设置码率,需要和采样率对应
UInt32 bitRate = kXDXRecoderConverterEncodeBitRate;
targetSize = sizeof(bitRate);
status = AudioConverterSetProperty(_encodeConvertRef,
kAudioConverterEncodeBitRate,
targetSize, &bitRate);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","set covert property bit rate status:%d",(int)status);
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder","set covert property bit rate status:%d",(int)status);
return @"Error : Set covert property bit rate failed";
}
return nil;
}
AudioFormatGetProperty:
原型:
extern OSStatus
AudioFormatGetProperty( AudioFormatPropertyID inPropertyID,
UInt32 inSpecifierSize,
const void * __nullable inSpecifier,
UInt32 * __nullable ioPropertyDataSize,
void * __nullabl outPropertyData);
作用:检索某个属性的值
AudioClassDescription:
指的是一个能够对一个信号或者一个数据流进行变换的设备或者程序。这里指的变换既包括将 信号或者数据流进行编码(通常是为了传输、存储或者加密)或者提取得到一个编码流的操作,也包括为了观察或者处理从这个编码流中恢复适合观察或操作的形式的操作。编解码器经常用在视频会议和流媒体等应用中。
默认情况下,Apple会创建一个硬件编码器,如果硬件不可用,会创建软件编码器。
经过我的测试,硬件AAC编码器的编码时延很高,需要buffer大约2秒的数据才会开始编码。而软件编码器的编码时延就是正常的,只要喂给1024个样点,就会开始编码。
AudioConverterNewSpecific:
原型: extern OSStatus
AudioConverterNewSpecific( const AudioStreamBasicDescription * inSourceFormat,
const AudioStreamBasicDescription * inDestinationFormat,
UInt32 inNumberClassDescriptions,
const AudioClassDescription * inClassDescriptions,
AudioConverterRef __nullable * __nonnull outAudioConverter);
解释:创建一个转换器
作用:设置一些转码基本信息
AudioConverterSetProperty:
原型:extern OSStatus
AudioConverterSetProperty( AudioConverterRef inAudioConverter,
AudioConverterPropertyID inPropertyID,
UInt32 inPropertyDataSize,
const void * inPropertyData);
作用:设置码率,需要注意,AAC并不是随便的码率都可以支持。比如如果PCM采样率是44100KHz,那么码率可以设置64000bps,如果是16K,可以设置为32000bps。
(4).设置最终音频文件的头部信息(此类写法为将pcm转为AAC的写法)
-(void)copyEncoderCookieToFile
{
// Grab the cookie from the converter and write it to the destination file.
UInt32 cookieSize = 0;
OSStatus error = AudioConverterGetPropertyInfo(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCompressionMagicCookie, &cookieSize, NULL);
// If there is an error here, then the format doesn't have a cookie - this is perfectly fine as som formats do not.
// log4cplus_info("cookie","cookie status:%d %d",(int)error, cookieSize);
if (error == noErr && cookieSize != 0) {
char *cookie = (char *)malloc(cookieSize * sizeof(char));
// UInt32 *cookie = (UInt32 *)malloc(cookieSize * sizeof(UInt32));
error = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCompressionMagicCookie, &cookieSize, cookie);
// log4cplus_info("cookie","cookie size status:%d",(int)error);
if (error == noErr) {
error = AudioFileSetProperty(mRecordFile, kAudioFilePropertyMagicCookieData, cookieSize, cookie);
// log4cplus_info("cookie","set cookie status:%d ",(int)error);
if (error == noErr) {
UInt32 willEatTheCookie = false;
error = AudioFileGetPropertyInfo(mRecordFile, kAudioFilePropertyMagicCookieData, NULL, &willEatTheCookie);
printf("Writing magic cookie to destination file: %u\n cookie:%d \n", (unsigned int)cookieSize, willEatTheCookie);
} else {
printf("Even though some formats have cookies, some files don't take them and that's OK\n");
}
} else {
printf("Could not Get kAudioConverterCompressionMagicCookie from Audio Converter!\n");
}
free(cookie);
}
}
Magic cookie 是一种不透明的数据格式,它和压缩数据文件与流联系密切,如果文件数据为CBR格式(无损),则不需要添加头部信息,如果为VBR需要添加,// if collect CBR needn't set magic cookie , if collect VBR should set magic cookie, if needn't to convert format that can be setting by audio queue directly.
(5).AudioQueue中注册的回调函数
// AudioQueue中注册的回调函数
static void inputBufferHandler(void * inUserData,
AudioQueueRef inAQ,
AudioQueueBufferRef inBuffer,
const AudioTimeStamp * inStartTime,
UInt32 inNumPackets,
const AudioStreamPacketDescription* inPacketDesc) {
// 相当于本类对象实例
TVURecorder *recoder = (TVURecorder *)inUserData;
/*
inNumPackets 总包数:音频队列缓冲区大小 (在先前估算缓存区大小为kXDXRecoderAACFramesPerPacket*2)/ (dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket (采集数据每个包中有多少帧,此处在初始化设置中为1) * dataFormat.mBytesPerFrame(每一帧中有多少个字节,此处在初始化设置中为每一帧中两个字节)),所以可以根据该公式计算捕捉PCM数据时inNumPackets。
注意:如果采集的数据是PCM需要将dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket设置为1,而本例中最终要的数据为AAC,因为本例中使用的转换器只有每次传入1024帧才能开始工作,所以在AAC格式下需要将mFramesPerPacket设置为1024.也就是采集到的inNumPackets为1,在转换器中传入的inNumPackets应该为AAC格式下默认的1,在此后写入文件中也应该传的是转换好的inNumPackets,如果有特殊需求需要将采集的数据量小于1024,那么需要将每次捕捉到的数据先预先存储在一个buffer中,等到攒够1024帧再进行转换。
*/
// collect pcm data,可以在此存储
// First case : collect data not is 1024 frame, if collect data not is 1024 frame, we need to save data to pcm_buffer untill 1024 frame
memcpy(pcm_buffer+pcm_buffer_size, inBuffer->mAudioData, inBuffer->mAudioDataByteSize);
pcm_buffer_size = pcm_buffer_size + inBuffer->mAudioDataByteSize;
if(inBuffer->mAudioDataByteSize != kXDXRecoderAACFramesPerPacket*2)
NSLog(@"write pcm buffer size:%d, totoal buff size:%d", inBuffer->mAudioDataByteSize, pcm_buffer_size);
frameCount++;
// Second case : If the size of the data collection is not required, we can let mic collect 1024 frame so that don't need to write firtst case, but it is recommended to write the above code because of agility
// if collect data is added to 1024 frame
if(frameCount == totalFrames) {
AudioBufferList *bufferList = convertPCMToAAC(recoder);
pcm_buffer_size = 0;
frameCount = 0;
// free memory
free(bufferList->mBuffers[0].mData);
free(bufferList);
// begin write audio data for record audio only
// 出队
AudioQueueRef queue = recoder.mQueue;
if (recoder.isRunning) {
AudioQueueEnqueueBuffer(queue, inBuffer, 0, NULL);
}
}
}
解析回调函数:相当于中断服务函数,每次录取到音频数据就进入这个函数
注意:inNumPackets 总包数:音频队列缓冲区大小 (在先前估算缓存区大小为2048)/ (dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket (采集数据每个包中有多少帧,此处在初始化设置中为1) * dataFormat.mBytesPerFrame(每一帧中有多少个字节,此处在初始化设置中为每一帧中两个字节))
- inAQ 是调用回调函数的音频队列
- inBuffer 是一个被音频队列填充新的音频数据的音频队列缓冲区,它包含了回调函数写入文件所需要的新数据
- inStartTime 是缓冲区中的一采样的参考时间,对于基本的录制,你的毁掉函数不会使用这个参数
- inNumPackets是inPacketDescs参数中包描述符(packet descriptions)的数量,如果你正在录制一个VBR(可变比特率(variable bitrate))格式, 音频队列将会提供这个参数给你的回调函数,这个参数可以让你传递给AudioFileWritePackets函数. CBR (常量比特率(constant bitrate)) 格式不使用包描述符。对于CBR录制,音频队列会设置这个参数并且将inPacketDescs这个参数设置为NULL,官方解释为The number of packets of audio data sent to the callback in the inBuffer parameter.
// PCM -> AAC
AudioBufferList* convertPCMToAAC (AudioQueueBufferRef inBuffer, XDXRecorder *recoder) {
UInt32 maxPacketSize = 0;
UInt32 size = sizeof(maxPacketSize);
OSStatus status;
status = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef,
kAudioConverterPropertyMaximumOutputPacketSize,
&size,
&maxPacketSize);
// log4cplus_info("AudioConverter","kAudioConverterPropertyMaximumOutputPacketSize status:%d \n",(int)status);
// 初始化一个bufferList存储数据
AudioBufferList *bufferList = (AudioBufferList *)malloc(sizeof(AudioBufferList));
bufferList->mNumberBuffers = 1;
bufferList->mBuffers[0].mNumberChannels = _targetDes.mChannelsPerFrame;
bufferList->mBuffers[0].mData = malloc(maxPacketSize);
bufferList->mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize = pcm_buffer_size;
AudioStreamPacketDescription outputPacketDescriptions;
/*
inNumPackets设置为1表示编码产生1帧数据即返回,官方:On entry, the capacity of outOutputData expressed in packets in the converter's output format. On exit, the number of packets of converted data that were written to outOutputData. 在输入表示输出数据的最大容纳能力 在转换器的输出格式上,在转换完成时表示多少个包被写入
*/
UInt32 inNumPackets = 1;
status = AudioConverterFillComplexBuffer(_encodeConvertRef,
encodeConverterComplexInputDataProc, // 填充数据的回调函数
pcm_buffer, // 音频队列缓冲区中数据
&inNumPackets,
bufferList, // 成功后将值赋给bufferList
&outputPacketDescriptions); // 输出包包含的一些信息
log4cplus_info("AudioConverter","set AudioConverterFillComplexBuffer status:%d",(int)status);
if (recoder.needsVoiceDemo) {
// if inNumPackets set not correct, file will not normally play. 将转换器转换出来的包写入文件中,inNumPackets表示写入文件的起始位置
OSStatus status = AudioFileWritePackets(recoder.mRecordFile,
FALSE,
bufferList->mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize,
&outputPacketDescriptions,
recoder.mRecordPacket,
&inNumPackets,
bufferList->mBuffers[0].mData);
// log4cplus_info("write file","write file status = %d",(int)status);
recoder.mRecordPacket += inNumPackets; // Used to record the location of the write file,用于记录写入文件的位置
}
return bufferList;
}
解析
outputPacketDescriptions数组是每次转换的AAC编码后各个包的描述,但这里每次只转换一包数据(由传入的packetSize决定)。调用AudioConverterFillComplexBuffer触发转码,他的第二个参数是填充原始音频数据的回调。转码完成后,会将转码的数据存放在它的第五个参数中(bufferList).
// 录制声音功能
-(void)startVoiceDemo
{
NSArray *searchPaths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [[searchPaths objectAtIndex:0] stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"VoiceDemo"];
OSStatus status;
// Get the full path to our file.
NSString *fullFileName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@.%@",[[XDXDateTool shareXDXDateTool] getDateWithFormat_yyyy_MM_dd_HH_mm_ss],@"caf"];
NSString *filePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:fullFileName];
[mRecordFilePath release];
mRecordFilePath = [filePath copy];;
CFURLRef url = CFURLCreateWithString(kCFAllocatorDefault, (CFStringRef)filePath, NULL);
// create the audio file
status = AudioFileCreateWithURL(url, kAudioFileMPEG4Type, &_targetDes, kAudioFileFlags_EraseFile, &mRecordFile);
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder","AudioFileCreateWithURL Failed, status:%d",(int)status);
}
CFRelease(url);
// add magic cookie contain header file info for VBR data
[self copyEncoderCookieToFile];
mNeedsVoiceDemo = YES;
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
--------------------------- Audio Unit -----------------------------
1. What is Audio Unit ? AudioUnit官方文档, 优秀博客1
1). AudioUnit是 iOS提供的为了支持混音,均衡,格式转换,实时输入输出用于录制,回放,离线渲染和实时回话(VOIP),这让我们可以动态加载和使用,即从iOS应用程序中接收这些强大而灵活的插件。它是iOS音频中最低层,所以除非你需要合成声音的实时播放,低延迟的I/O,或特定声音的特定特点。
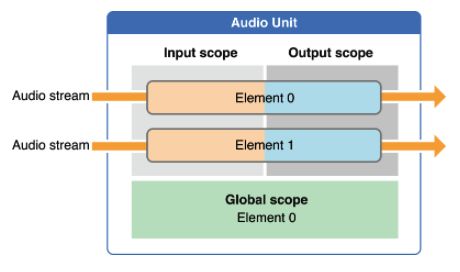
Audio unit scopes and elements :
-
上图是一个AudioUnit的组成结构,A scope 主要使用到的输入kAudioUnitScope_Input和输出kAudioUnitScope_Output。Element 是嵌套在audio unit scope的编程上下文。
- AudioUnit 的Remote IO有2个element,大部分代码和文献都用bus代替element,两者同义,bus0就是输出,bus 1代表输入,播放音频文件就是在bus 0传送数据,bus 1输入在Remote IO 默认是关闭的,在录音的状态下 需要把bus 1设置成开启状态。
- 我们能使用(kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO)属性独立地开启或禁用每个element,Element 1 直接与音频输入硬件相连(麦克风),Element 1 的input scope对我们是不透明的,来自输入硬件的音频数据只能在Element 1的output scope中访问。
- 同样的element 0直接和输出硬件相连(扬声器),我们可以将audio数据传输到element 0的input scope中,但是output scope对我们是不透明的。
- 注意:每个element本身都有一个输入范围和输出范围,因此在代码中如果不理解可能会比较懵逼,比如你从input element的 output scope 中受到音频,并将音频发送到output element的intput scope中,如果代码中不理解,可以再看看上图。
2.相关概念解析
2 - 1. I/O Units : iOS提供了3种I/O Units.
- The Remote I/O unit 是最常用的,它连接音频硬件的输入和输出并且提供单个传入和传出音频样本值得低延迟访问。还支持硬件音频格式和应用程序音频格式的转换,通过包含Format Converter unit来实现。
- The Voice-Processing I/O unit 继承了the Remote I/O unit 并且增加回声消除用于VOIP或语音聊天应用。它还提供了自动增益校正,语音处理的质量调整和静音的功能。(本例中用此完成回声消除)
- The Generic Output unit 不连接音频硬件,而是一共一种将处理链的输出发送到应用程序的机制。通常用来进行脱机音频处理。
3. 使用步骤:
1). 导入所需动态库与头文件(At runtime, obtain a reference to the dynamically-linkable library that defines an audio unit you want to use.)
2). 实例化audio unit(Instantiate the audio unit.)
3). 配置audioUnit的类型去完成特定的需求(Configure the audio unit as required for its type and to accomodate the intent of your app.)
4). 初始化uandio unit(Initialize the audio unit to prepare it to handle audio.
)
5). 开始audio flow(Start audio flow.)
6). 控制audio unit(Control the audio unit.)
7). 结束后回收audio unit(When finished, deallocate the audio unit.)
4.代码解析
- 1). init.
- (void)initAudioComponent {
OSStatus status;
// 配置AudioUnit基本信息
AudioComponentDescription audioDesc;
audioDesc.componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output;
// 如果你的应用程序需要去除回声将componentSubType设置为kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO,否则根据需求设置为其他,在博客中有介绍
audioDesc.componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO;//kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO;
// 苹果自己的标志
audioDesc.componentManufacturer = kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple;
audioDesc.componentFlags = 0;
audioDesc.componentFlagsMask = 0;
AudioComponent inputComponent = AudioComponentFindNext(NULL, &audioDesc);
// 新建一个AudioComponent对象,只有这步完成才能进行后续步骤,所以顺序不可颠倒
status = AudioComponentInstanceNew(inputComponent, &_audioUnit);
if (status != noErr) {
_audioUnit = NULL;
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "couldn't create a new instance of AURemoteIO, status : %d \n",status);
}
}
解析
- To find an audio unit at runtime, start by specifying its type, subtype, and manufacturer keys in an audio component description data structure. You do this whether using the audio unit or audio processing graph API.
- 要在运行时找到AudioUnit,首先要在AudioComponentDescription中指定它的类型,子类型和制作商,AudioComponentFindNext参数inComponent一般设置为NULL,从系统中找到第一个符合inDesc描述的Component,如果为其赋值,则从其之后进行寻找。AudioUnit实际上就是一个AudioComponentInstance实例对象
- componentSubType一般可设置为kAudioUnitSubType_RemoteIO,如果有特别需求,如本例中要去除回声,则使用kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO,每种类型作用在2-1中均有描述,不再重复。
- (void)initBuffer {
// 禁用AudioUnit默认的buffer而使用我们自己写的全局BUFFER,用来接收每次采集的PCM数据,Disable AU buffer allocation for the recorder, we allocate our own.
UInt32 flag = 0;
OSStatus status = AudioUnitSetProperty(_audioUnit,
kAudioUnitProperty_ShouldAllocateBuffer,
kAudioUnitScope_Output,
INPUT_BUS,
&flag,
sizeof(flag));
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "couldn't AllocateBuffer of AudioUnitCallBack, status : %d \n",status);
}
_buffList = (AudioBufferList*)malloc(sizeof(AudioBufferList));
_buffList->mNumberBuffers = 1;
_buffList->mBuffers[0].mNumberChannels = dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame;
_buffList->mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize = kTVURecoderPCMMaxBuffSize * sizeof(short);
_buffList->mBuffers[0].mData = (short *)malloc(sizeof(short) * kTVURecoderPCMMaxBuffSize);
}
解析
本例通过禁用AudioUnit默认的buffer而使用我们自己写的全局BUFFER,用来接收每次采集的PCM数据,Disable AU buffer allocation for the recorder, we allocate our own.还有一种写法是可以使用回调中提供的ioData存储采集的数据,这里使用全局的buff是为了供其他地方使用,可根据需要自行决定采用哪种方式,若不采用全局buffer则不可采用上述禁用操作。
// 因为本例只做录音功能,未实现播放功能,所以没有设置播放相关设置。
- (void)setAudioUnitPropertyAndFormat {
OSStatus status;
[self setUpRecoderWithFormatID:kAudioFormatLinearPCM];
// 应用audioUnit设置的格式
status = AudioUnitSetProperty(_audioUnit,
kAudioUnitProperty_StreamFormat,
kAudioUnitScope_Output,
INPUT_BUS,
&dataFormat,
sizeof(dataFormat));
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "couldn't set the input client format on AURemoteIO, status : %d \n",status);
}
// 去除回声开关
UInt32 echoCancellation;
AudioUnitSetProperty(_audioUnit,
kAUVoiceIOProperty_BypassVoiceProcessing,
kAudioUnitScope_Global,
0,
&echoCancellation,
sizeof(echoCancellation));
// AudioUnit输入端默认是关闭,需要将他打开
UInt32 flag = 1;
status = AudioUnitSetProperty(_audioUnit,
kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO,
kAudioUnitScope_Input,
INPUT_BUS,
&flag,
sizeof(flag));
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "could not enable input on AURemoteIO, status : %d \n",status);
}
}
-(void)setUpRecoderWithFormatID:(UInt32)formatID {
// Notice : The settings here are official recommended settings,can be changed according to specific requirements. 此处的设置为官方推荐设置,可根据具体需求修改部分设置
//setup auido sample rate, channel number, and format ID
memset(&dataFormat, 0, sizeof(dataFormat));
UInt32 size = sizeof(dataFormat.mSampleRate);
AudioSessionGetProperty(kAudioSessionProperty_CurrentHardwareSampleRate,
&size,
&dataFormat.mSampleRate);
dataFormat.mSampleRate = kXDXAudioSampleRate;
size = sizeof(dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame);
AudioSessionGetProperty(kAudioSessionProperty_CurrentHardwareInputNumberChannels,
&size,
&dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame);
dataFormat.mFormatID = formatID;
dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame = 1;
if (formatID == kAudioFormatLinearPCM) {
if (self.releaseMethod == XDXRecorderReleaseMethodAudioQueue) {
dataFormat.mFormatFlags = kLinearPCMFormatFlagIsSignedInteger | kLinearPCMFormatFlagIsPacked;
}else if (self.releaseMethod == XDXRecorderReleaseMethodAudioQueue) {
dataFormat.mFormatFlags = kAudioFormatFlagIsSignedInteger | kAudioFormatFlagIsPacked;
}
dataFormat.mBitsPerChannel = 16;
dataFormat.mBytesPerPacket = dataFormat.mBytesPerFrame = (dataFormat.mBitsPerChannel / 8) * dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame;
dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket = kXDXRecoderPCMFramesPerPacket; // 用AudioQueue采集pcm需要这么设置
}
}
解析
上述操作针对录音功能需要对Audio Unit做出对应设置,首先设置ASBD采集数据为PCM的格式,需要注意的是如果是使用AudioQueue与AudioUnit的dataFormat.mFormatFlags设置略有不同,经测试必须这样设置,原因暂不详,设置完后使用AudioUnitSetProperty应用设置,这里只做录音,所以对kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO 的 kAudioUnitScope_Input 开启,而对kAudioUnitScope_Output 输入端输出的音频格式进行设置,如果不理解可参照1中概念解析进行理解,kAUVoiceIOProperty_BypassVoiceProcessing则是回声的开关。
-(NSString *)convertBasicSetting {
// 此处目标格式其他参数均为默认,系统会自动计算,否则无法进入encodeConverterComplexInputDataProc回调
AudioStreamBasicDescription sourceDes = dataFormat; // 原始格式
AudioStreamBasicDescription targetDes; // 转码后格式
// 设置目标格式及基本信息
memset(&targetDes, 0, sizeof(targetDes));
targetDes.mFormatID = kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC;
targetDes.mSampleRate = kXDXAudioSampleRate;
targetDes.mChannelsPerFrame = dataFormat.mChannelsPerFrame;
targetDes.mFramesPerPacket = kXDXRecoderAACFramesPerPacket; // 采集的为AAC需要将targetDes.mFramesPerPacket设置为1024,AAC软编码需要喂给转换器1024个样点才开始编码,这与回调函数中inNumPackets有关,不可随意更改
OSStatus status = 0;
UInt32 targetSize = sizeof(targetDes);
status = AudioFormatGetProperty(kAudioFormatProperty_FormatInfo, 0, NULL, &targetSize, &targetDes);
// log4cplus_info("pcm", "create target data format status:%d",(int)status);
memset(&_targetDes, 0, sizeof(_targetDes));
// 赋给全局变量
memcpy(&_targetDes, &targetDes, targetSize);
// 选择软件编码
AudioClassDescription audioClassDes;
status = AudioFormatGetPropertyInfo(kAudioFormatProperty_Encoders,
sizeof(targetDes.mFormatID),
&targetDes.mFormatID,
&targetSize);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","get kAudioFormatProperty_Encoders status:%d",(int)status);
// 计算编码器容量
UInt32 numEncoders = targetSize/sizeof(AudioClassDescription);
// 用数组存放编码器内容
AudioClassDescription audioClassArr[numEncoders];
// 将编码器属性赋给数组
AudioFormatGetProperty(kAudioFormatProperty_Encoders,
sizeof(targetDes.mFormatID),
&targetDes.mFormatID,
&targetSize,
audioClassArr);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","wrirte audioClassArr status:%d",(int)status);
// 遍历数组,设置软编
for (int i = 0; i < numEncoders; i++) {
if (audioClassArr[i].mSubType == kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC && audioClassArr[i].mManufacturer == kAppleSoftwareAudioCodecManufacturer) {
memcpy(&audioClassDes, &audioClassArr[i], sizeof(AudioClassDescription));
break;
}
}
// 防止内存泄露
if (_encodeConvertRef == NULL) {
// 新建一个编码对象,设置原,目标格式
status = AudioConverterNewSpecific(&sourceDes, &targetDes, 1,
&audioClassDes, &_encodeConvertRef);
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder","new convertRef failed status:%d \n",(int)status);
return @"Error : New convertRef failed \n";
}
}
// 获取原始格式大小
targetSize = sizeof(sourceDes);
status = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCurrentInputStreamDescription, &targetSize, &sourceDes);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","get sourceDes status:%d",(int)status);
// 获取目标格式大小
targetSize = sizeof(targetDes);
status = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCurrentOutputStreamDescription, &targetSize, &targetDes);;
// log4cplus_info("pcm","get targetDes status:%d",(int)status);
// 设置码率,需要和采样率对应
UInt32 bitRate = kXDXRecoderConverterEncodeBitRate;
targetSize = sizeof(bitRate);
status = AudioConverterSetProperty(_encodeConvertRef,
kAudioConverterEncodeBitRate,
targetSize, &bitRate);
// log4cplus_info("pcm","set covert property bit rate status:%d",(int)status);
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder","set covert property bit rate status:%d",(int)status);
return @"Error : Set covert property bit rate failed";
}
return nil;
}
解析
设置原格式与转码格式并创建_encodeConvertRef转码器对象完成相关初始化操作,值得注意的是targetDes.mFramesPerPacket设置为1024,AAC软编码需要喂给转换器1024个样点才开始编码,不可随意更改,原因如下图,由AAC编码器决定。
- (void)initRecordeCallback {
// 设置回调,有两种方式,一种是采集pcm的BUFFER使用系统回调中的参数,另一种是使用我们自己的,本例中使用的是自己的,所以回调中的ioData为空。
// 方法1:
AURenderCallbackStruct recordCallback;
recordCallback.inputProc = RecordCallback;
recordCallback.inputProcRefCon = (__bridge void *)self;
OSStatus status = AudioUnitSetProperty(_audioUnit,
kAudioOutputUnitProperty_SetInputCallback,
kAudioUnitScope_Global,
INPUT_BUS,
&recordCallback,
sizeof(recordCallback));
// 方法2:
AURenderCallbackStruct renderCallback;
renderCallback.inputProc = RecordCallback;
renderCallback.inputProcRefCon = (__bridge void *)self;
AudioUnitSetProperty(_rioUnit, kAudioUnitProperty_SetRenderCallback, kAudioUnitScope_Input, 0, & RecordCallback, sizeof(RecordCallback));
if (status != noErr) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "Audio Unit set record Callback failed, status : %d \n",status);
}
}
解析
以上为设置采集回调,有两种方式,1种为使用我们自己的buffer,这样需要先在上述initBuffer中禁用系统的buffer,则回调函数中每次渲染的为我们自己的buffer,另一种则是使用系统的buffer,对应需要在回调函数中将ioData放进渲染的函数中。
static OSStatus RecordCallback(void *inRefCon,
AudioUnitRenderActionFlags *ioActionFlags,
const AudioTimeStamp *inTimeStamp,
UInt32 inBusNumber,
UInt32 inNumberFrames,
AudioBufferList *ioData) {
/*
注意:如果采集的数据是PCM需要将dataFormat.mFramesPerPacket设置为1,而本例中最终要的数据为AAC,因为本例中使用的转换器只有每次传入1024帧才能开始工作,所以在AAC格式下需要将mFramesPerPacket设置为1024.也就是采集到的inNumPackets为1,在转换器中传入的inNumPackets应该为AAC格式下默认的1,在此后写入文件中也应该传的是转换好的inNumPackets,如果有特殊需求需要将采集的数据量小于1024,那么需要将每次捕捉到的数据先预先存储在一个buffer中,等到攒够1024帧再进行转换。
*/
XDXRecorder *recorder = (XDXRecorder *)inRefCon;
// 将回调数据传给_buffList
AudioUnitRender(recorder->_audioUnit, ioActionFlags, inTimeStamp, inBusNumber, inNumberFrames, recorder->_buffList);
void *bufferData = recorder->_buffList->mBuffers[0].mData;
UInt32 bufferSize = recorder->_buffList->mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize;
// printf("Audio Recoder Render dataSize : %d \n",bufferSize);
// 由于PCM转成AAC的转换器每次需要有1024个采样点(每一帧2个字节)才能完成一次转换,所以每次需要2048大小的数据,这里定义的pcm_buffer用来累加每次存储的bufferData
memcpy(pcm_buffer+pcm_buffer_size, bufferData, bufferSize);
pcm_buffer_size = pcm_buffer_size + bufferSize;
if(pcm_buffer_size >= kTVURecoderPCMMaxBuffSize) {
AudioBufferList *bufferList = convertPCMToAAC(recorder);
// 因为采样不可能每次都精准的采集到1024个样点,所以如果大于2048大小就先填满2048,剩下的跟着下一次采集一起送给转换器
memcpy(pcm_buffer, pcm_buffer + kTVURecoderPCMMaxBuffSize, pcm_buffer_size - kTVURecoderPCMMaxBuffSize);
pcm_buffer_size = pcm_buffer_size - kTVURecoderPCMMaxBuffSize;
// free memory
if(bufferList) {
free(bufferList->mBuffers[0].mData);
free(bufferList);
}
}
return noErr;
}
解析
在该回调中如果采用我们自己定义的全局buffer,则回调函数参数中的ioData为NULL,不再使用,如果想使用ioData按照上述设置并将其放入AudioUnitRender函数中进行渲染,回调函数中采用pcm_buffer存储满2048个字节的数组传给转换器,这是编码器的特性,所以如果采集的数据小于2048先取pcm_buffer的前2048个字节,后面的数据与下次采集的PCM数据累加在一起。上述转换过程在AudioQueue中已经有介绍,逻辑完全相同,可在上文中阅读。
-(void)copyEncoderCookieToFile
{
// Grab the cookie from the converter and write it to the destination file.
UInt32 cookieSize = 0;
OSStatus error = AudioConverterGetPropertyInfo(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCompressionMagicCookie, &cookieSize, NULL);
// If there is an error here, then the format doesn't have a cookie - this is perfectly fine as som formats do not.
// log4cplus_info("cookie","cookie status:%d %d",(int)error, cookieSize);
if (error == noErr && cookieSize != 0) {
char *cookie = (char *)malloc(cookieSize * sizeof(char));
// UInt32 *cookie = (UInt32 *)malloc(cookieSize * sizeof(UInt32));
error = AudioConverterGetProperty(_encodeConvertRef, kAudioConverterCompressionMagicCookie, &cookieSize, cookie);
// log4cplus_info("cookie","cookie size status:%d",(int)error);
if (error == noErr) {
error = AudioFileSetProperty(mRecordFile, kAudioFilePropertyMagicCookieData, cookieSize, cookie);
// log4cplus_info("cookie","set cookie status:%d ",(int)error);
if (error == noErr) {
UInt32 willEatTheCookie = false;
error = AudioFileGetPropertyInfo(mRecordFile, kAudioFilePropertyMagicCookieData, NULL, &willEatTheCookie);
printf("Writing magic cookie to destination file: %u\n cookie:%d \n", (unsigned int)cookieSize, willEatTheCookie);
} else {
printf("Even though some formats have cookies, some files don't take them and that's OK\n");
}
} else {
printf("Could not Get kAudioConverterCompressionMagicCookie from Audio Converter!\n");
}
free(cookie);
}
}
解析
Magic cookie 是一种不透明的数据格式,它和压缩数据文件与流联系密切,如果文件数据为CBR格式(无损),则不需要添加头部信息,如果为VBR需要添加,// if collect CBR needn't set magic cookie , if collect VBR should set magic cookie, if needn't to convert format that can be setting by audio queue directly.
- (void)startAudioUnitRecorder {
OSStatus status;
if (isRunning) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "Start recorder repeat \n");
return;
}
[self initGlobalVar];
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "starup PCM audio encoder \n");
status = AudioOutputUnitStart(_audioUnit);
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "AudioOutputUnitStart status : %d \n",status);
if (status == noErr) {
isRunning = YES;
hostTime = 0;
}
}
-(void)stopAudioUnitRecorder {
if (isRunning == NO) {
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "Stop recorder repeat \n");
return;
}
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder","stop pcm encoder \n");
isRunning = NO;
[self copyEncoderCookieToFile];
OSStatus status = AudioOutputUnitStop(_audioUnit);
if (status != noErr){
// log4cplus_info("Audio Recoder", "stop AudioUnit failed. \n");
}
AudioFileClose(mRecordFile);
}
解析
由于AudioUnit的初始化在本类中初始化方法中完成,所以只需要调用start,stop方法即可控制录制转码过程。切记不可在start方法中完成audio unit对象的创建和初始化,否则会发生异常。