UDP搜索IP和端口
客户端回送数据到服务器的流程
服务器回送数据到客户端
我就直接贴代码了
- UDPConstants
public class UDPConstants {
//公用头部
public static byte[] HEADER = new byte[]{7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7};
//服务器UDP接受端口
public static int PORT_SERVER = 30201;
//客户端回送端口
public static int PORT_CLIENT_RESPONSE = 30202;
}
- TCPConstants
public class TCPConstants {
//服务器固定端口
public static int PORT_SERVER=30401;
}
- ByteUtils
public static boolean startsWith(byte[] source, byte[] match) {
return startsWith(source, 0, match);
}
public static boolean startsWith(byte[] source, int offset, byte[] match) {
if (match.length > (source.length - offset)) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
if (source[offset + i] != match[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
上面三个其实很简单,就是定义一些常量和工具类使用
- Server服务器端
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerProvider.start(TCPConstants.PORT_SERVER);
try {
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ServerProvider.stop();
}
}
- ServerProvider:相当于服务器提供类
public class ServerProvider {
private static Provider PROVIDER_INSTANCE;
public static void start(int port) {
stop();
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Provider provider = new Provider(uuid, port);
provider.start();
PROVIDER_INSTANCE = provider;
}
public static void stop() {
if (PROVIDER_INSTANCE != null) {
PROVIDER_INSTANCE.exit();
PROVIDER_INSTANCE = null;
}
}
private static class Provider extends Thread {
private final byte[] sn;
private final int port;
//tcp端口
private boolean done = false;
//发送
private DatagramSocket ds = null;
//存储消息的buffer
final byte[] buffer = new byte[128];
public Provider(String uuid, int port) {
super();
this.sn = uuid.getBytes();
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
System.out.println("UDPProvider Started.");
try {
// 监听20000 端口
ds = new DatagramSocket(UDPConstants.PORT_SERVER);
// 接收消息的Packet
DatagramPacket receivePack = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);
while (!done) {
// 接收
ds.receive(receivePack);
// 打印接收到的信息与发送者的信息
// 发送者的IP地址
String clientIp = receivePack.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int clientPort = receivePack.getPort();
int clientDataLen = receivePack.getLength();
byte[] clientData = receivePack.getData();
boolean isValid = clientDataLen >= (UDPConstants.HEADER.length + 2 + 4)
&& ByteUtils.startsWith(clientData, UDPConstants.HEADER);
System.out.println("ServerProvider receive form ip:" + clientIp
+ "\tport:" + clientPort + "\tdataValid:" + isValid);
if (!isValid) {
// 无效继续
continue;
}
// 解析命令与回送端口
int index = UDPConstants.HEADER.length;
short cmd = (short) ((clientData[index++] << 8) | (clientData[index++] & 0xff));
int responsePort = (((clientData[index++]) << 24) |
((clientData[index++] & 0xff) << 16) |
((clientData[index++] & 0xff) << 8) |
((clientData[index] & 0xff)));
// 判断合法性
if (cmd == 1 && responsePort > 0) {
// 构建一份回送数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer);
byteBuffer.put(UDPConstants.HEADER);
byteBuffer.putShort((short) 2);
byteBuffer.putInt(port);
byteBuffer.put(sn);
int len = byteBuffer.position();
// 直接根据发送者构建一份回送信息
DatagramPacket responsePacket = new DatagramPacket(buffer,
len,
receivePack.getAddress(),
responsePort);
ds.send(responsePacket);
System.out.println("ServerProvider response to:" + clientIp + "\tport:" + responsePort + "\tdataLen:" + len);
} else {
System.out.println("ServerProvider receive cmd nonsupport; cmd:" + cmd + "\tport:" + port);
}
}
} catch (Exception ignored) {
} finally {
close();
}
// 完成
System.out.println("UDPProvider Finished.");
}
void exit() {
done = true;
close();
}
private void close() {
if (ds != null) {
ds.close();
ds = null;
}
}
}
}
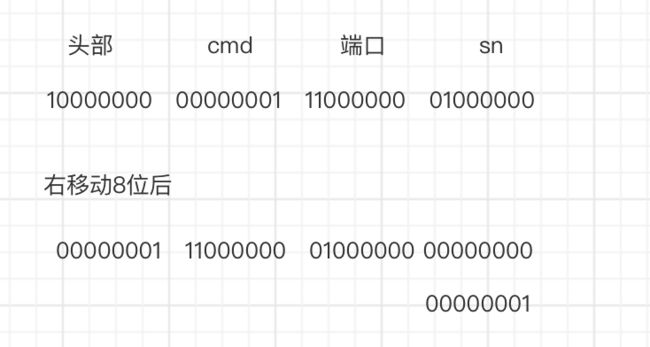
如何获取到cmd?
首先我们结构是头部+cmd+端口+sn,上图显示(只有cmd数据真实,其实虚构,不影响分析)。我们首先左边移动8位,右边补零,则得到上面图片的第二行数据,clientData[index++] << 8)
随后我们获取cmd的二进制(clientData[index++] & 0xff),左边全部补零,最后进行或(|)运算.或运算是有1显示1,没有显示0
- 客户端client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerInfo info=ClientSearch.searchServer(10000);//10s
System.out.println("Server:"+info);
}
}
- ClientSearch
public class ClientSearch {
private static final int LISTEN_PORT = UDPConstants.PORT_CLIENT_RESPONSE;
public static ServerInfo searchServer(int timeout) {
System.out.println("UDPSearcher Started.");
// 成功收到回送的栅栏
CountDownLatch receiveLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
Listener listener = null;
try {
listener = listen(receiveLatch);
sendBroadcast();
receiveLatch.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 完成
System.out.println("UDPSearcher Finished.");
if (listener == null) {
return null;
}
List devices = listener.getServerAndClose();
if (devices.size() > 0) {
return devices.get(0);
}
return null;
}
private static Listener listen(CountDownLatch receiveLatch) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("UDPSearcher start listen.");
CountDownLatch startDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
Listener listener = new Listener(LISTEN_PORT, startDownLatch, receiveLatch);
listener.start();
startDownLatch.await();
return listener;
}
private static void sendBroadcast() throws IOException {
System.out.println("UDPSearcher sendBroadcast started.");
// 作为搜索方,让系统自动分配端口
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
// 构建一份请求数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
// 头部
byteBuffer.put(UDPConstants.HEADER);
// CMD命名
byteBuffer.putShort((short) 1);
// 回送端口信息
byteBuffer.putInt(LISTEN_PORT);
// 直接构建packet
DatagramPacket requestPacket = new DatagramPacket(byteBuffer.array(),
byteBuffer.position() + 1);
// 广播地址
requestPacket.setAddress(InetAddress.getByName("255.255.255.255"));
// 设置服务器端口
requestPacket.setPort(UDPConstants.PORT_SERVER);
// 发送
ds.send(requestPacket);
ds.close();
// 完成
System.out.println("UDPSearcher sendBroadcast finished.");
}
private static class Listener extends Thread {
private final int listenPort;
private final CountDownLatch startDownLatch;
private final CountDownLatch receiveDownLatch;
private final List serverInfoList = new ArrayList<>();
private final byte[] buffer = new byte[128];
private final int minLen = UDPConstants.HEADER.length + 2 + 4;
private boolean done = false;
private DatagramSocket ds = null;
private Listener(int listenPort, CountDownLatch startDownLatch, CountDownLatch receiveDownLatch) {
super();
this.listenPort = listenPort;
this.startDownLatch = startDownLatch;
this.receiveDownLatch = receiveDownLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
// 通知已启动
startDownLatch.countDown();
try {
// 监听回送端口
ds = new DatagramSocket(listenPort);
// 构建接收实体
DatagramPacket receivePack = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);
while (!done) {
// 接收
ds.receive(receivePack);
// 打印接收到的信息与发送者的信息
// 发送者的IP地址
String ip = receivePack.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = receivePack.getPort();
int dataLen = receivePack.getLength();
byte[] data = receivePack.getData();
boolean isValid = dataLen >= minLen
&& ByteUtils.startsWith(data, UDPConstants.HEADER);
System.out.println("UDPSearcher receive form ip:" + ip
+ "\tport:" + port + "\tdataValid:" + isValid);
if (!isValid) {
// 无效继续
continue;
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer, UDPConstants.HEADER.length, dataLen);
final short cmd = byteBuffer.getShort();
final int serverPort = byteBuffer.getInt();
if (cmd != 2 || serverPort <= 0) {
System.out.println("UDPSearcher receive cmd:" + cmd + "\tserverPort:" + serverPort);
continue;
}
String sn = new String(buffer, minLen, dataLen - minLen);
ServerInfo info = new ServerInfo( sn,serverPort, ip);
serverInfoList.add(info);
// 成功接收到一份
receiveDownLatch.countDown();
}
} catch (Exception ignored) {
} finally {
close();
}
System.out.println("UDPSearcher listener finished.");
}
private void close() {
if (ds != null) {
ds.close();
ds = null;
}
}
List getServerAndClose() {
done = true;
close();
return serverInfoList;
}
}
}
- ServerInfo只是一个实体类的封装
public class ServerInfo {
private String sn;
private int port;
private String address;
public ServerInfo(String sn, int port, String address) {
this.sn = sn;
this.port = port;
this.address = address;
}
.....
}
UDP实现点对点传输
首先客户端我们需要获取数据和读取数据,在上面一步,我们其实已经获取到TCP的IP和端口号
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerInfo info = UDPSearcher.searchServer(10000);
System.out.println("Server:" + info);
if (info != null) {
try {
TCPClient.linkWith(info);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class TCPClient {
public static void linkWith(ServerInfo info) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket();
// 超时时间
socket.setSoTimeout(3000);
// 连接本地,端口2000;超时时间3000ms
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress(Inet4Address.getByName(info.getAddress()), info.getPort()), 3000);
System.out.println("已发起服务器连接,并进入后续流程~");
System.out.println("客户端信息:" + socket.getLocalAddress() + " 端口号:" + socket.getLocalPort());
System.out.println("服务器信息:" + socket.getInetAddress() + " 端口号:" + socket.getPort());
try {
ReadHandler readHandler = new ReadHandler(socket.getInputStream());
readHandler.start();
// 发送接收数据
write(socket);
// 退出操作
readHandler.exit();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("异常关闭");
}
// 释放资源
socket.close();
System.out.println("客户端已退出~");
}
private static void write(Socket client) throws IOException {
// 构建键盘输入流
InputStream in = System.in;
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
// 得到Socket输出流,并转换为打印流
OutputStream outputStream = client.getOutputStream();
PrintStream socketPrintStream = new PrintStream(outputStream);
do {
// 键盘读取一行
String str = input.readLine();
// 发送到服务器
socketPrintStream.println(str);
if ("bye".equalsIgnoreCase(str)) {
break;
}
} while (true);
// 资源释放
socketPrintStream.close();
}
static class ReadHandler extends Thread {
private boolean done = false;
private final InputStream inputStream;
ReadHandler(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
// 得到输入流,用于接收数据
BufferedReader socketInput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
do {
String str;
try {
// 客户端拿到一条数据
str = socketInput.readLine();
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
continue;
}
if (str == null) {
System.out.println("连接已关闭,无法读取数据!");
break;
}
// 打印到屏幕
System.out.println(str);
} while (!done);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!done) {
System.out.println("连接异常断开:" + e.getMessage());
}
} finally {
// 连接关闭
try {
if(inputStream!=null){
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
void exit() {
done = true;
try {
if(inputStream!=null){
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 服务器端:将数据传给封装好的tcp传输给客户端
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//tcp的端口
TCPServer tcpServer = new TCPServer(TCPConstants.PORT_SERVER);
boolean isSucceed = tcpServer.start();
if (!isSucceed) {
System.out.println("Start TCP server failed!");
return;
}
ServerProvider.start(TCPConstants.PORT_SERVER);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;
do {
str = bufferedReader.readLine();
tcpServer.broadcast(str);
} while (!"bye".equalsIgnoreCase(str));
ServerProvider.stop();
tcpServer.stop();
}
}
public class TCPServer {
private final int port;
private ClientListener mListener;
private List clientHandlerList = new ArrayList<>();
public TCPServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public boolean start() {
try {
ClientListener listener = new ClientListener(port);
mListener = listener;
listener.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void stop() {
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.exit();
}
for (ClientHandler clientHandler : clientHandlerList) {
clientHandler.exit();
}
clientHandlerList.clear();
}
public void broadcast(String str) {
for (ClientHandler clientHandler : clientHandlerList) {
clientHandler.send(str);
}
}
private class ClientListener extends Thread {
private ServerSocket server;
private boolean done = false;
private ClientListener(int port) throws IOException {
server = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("服务器信息:" + server.getInetAddress() + " P:" + server.getLocalPort());
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
System.out.println("服务器准备就绪~");
// 等待客户端连接
do {
// 得到客户端
Socket client;
try {
client = server.accept();
} catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
try {
// 客户端构建异步线程
ClientHandler clientHandler = new ClientHandler(client,
new ClientHandler.CloseNotify() {
@Override
public void onSelfClosed(ClientHandler handler) {
clientHandlerList.remove(handler);
}
});
// 读取数据并打印
clientHandler.readToPrint();
clientHandlerList.add(clientHandler);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("客户端连接异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
} while (!done);
System.out.println("服务器已关闭!");
}
void exit() {
done = true;
try {
server.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
实际真正逻辑在ClientHandler
public class ClientHandler {
private final Socket socket;
private final ClientReadHandler readHandler;
private final ClientWriteHandler writeHandler;
private final CloseNotify closeNotify;
public ClientHandler(Socket socket, CloseNotify closeNotify) throws IOException {
this.socket = socket;
this.readHandler = new ClientReadHandler(socket.getInputStream());
this.writeHandler = new ClientWriteHandler(socket.getOutputStream());
this.closeNotify = closeNotify;
System.out.println("新客户端连接:" + socket.getInetAddress() +
" P:" + socket.getPort());
}
public void exit() {
readHandler.exit();
writeHandler.exit();
CloseUtils.close(socket);
System.out.println("客户端已退出:" + socket.getInetAddress() +
" P:" + socket.getPort());
}
public void send(String str) {
writeHandler.send(str);
}
public void readToPrint() {
readHandler.start();
}
private void exitBySelf() {
exit();
closeNotify.onSelfClosed(this);
}
public interface CloseNotify {
void onSelfClosed(ClientHandler handler);
}
class ClientReadHandler extends Thread {
private boolean done = false;
private final InputStream inputStream;
ClientReadHandler(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
// 得到输入流,用于接收数据
BufferedReader socketInput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
do {
// 客户端拿到一条数据
String str = socketInput.readLine();
if (str == null) {
System.out.println("客户端已无法读取数据!");
// 退出当前客户端
ClientHandler.this.exitBySelf();
break;
}
// 打印到屏幕
System.out.println(str);
} while (!done);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!done) {
System.out.println("连接异常断开");
ClientHandler.this.exitBySelf();
}
} finally {
// 连接关闭
CloseUtils.close(inputStream);
}
}
void exit() {
done = true;
CloseUtils.close(inputStream);
}
}
class ClientWriteHandler {
private boolean done = false;
private final PrintStream printStream;
private final ExecutorService executorService;
ClientWriteHandler(OutputStream outputStream) {
this.printStream = new PrintStream(outputStream);
this.executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
}
void exit() {
done = true;
CloseUtils.close(printStream);
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
void send(String str) {
executorService.execute(new WriteRunnable(str));
}
class WriteRunnable implements Runnable {
private final String msg;
WriteRunnable(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (ClientWriteHandler.this.done) {
return;
}
try {
ClientWriteHandler.this.printStream.println(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
ClientReadHandler和ClientWriteHandler实现 数据的发送和接收数据并行