Google 标签: rapid-pvst, mstp, loopguard, 迁移
Rapid-pvst是cisco的私有协议,其特点如下:
1,每个vlan一个stp数,因此在vlan多的环境中会比较消耗CPU和MEMORY;
2,RPVST收敛快,视vlan数量而定。一般20-30个vlan的情况下,拓扑收敛会导致4-5个丢包;
3,RPVST内置uplinkfast和backbonefast;
4,RPVST兼容loopguard、rootguard等特性;
5,规划配置简单,后续vlan的变更不会影响全局交换网络环境的收敛。
1,每个vlan一个stp数,因此在vlan多的环境中会比较消耗CPU和MEMORY;
2,RPVST收敛快,视vlan数量而定。一般20-30个vlan的情况下,拓扑收敛会导致4-5个丢包;
3,RPVST内置uplinkfast和backbonefast;
4,RPVST兼容loopguard、rootguard等特性;
5,规划配置简单,后续vlan的变更不会影响全局交换网络环境的收敛。
MSTP是通用标准,各网络设备厂商都使用此标准。
其特点除了基本包含RPVST所有优点包括上述的后三点外,最重要的特点是:多个vlan可以映射到一个实例,可以从交换网络中实际存在的stp拓扑来规划实例。这样针对多vlan的环境,很好的解决了CPU和MEMORY消耗情况以及收敛时间问题。
但是由于MSTP是基于域协商管理的,在整个域内各交换机必须保持三要素一致才能达到同步。三要素为domain、reversion以及instance。因此交换网络维护中需要新增vlan的情况下会导致MSTP域内的instance不一致的情况。通常MSTP规划时需要做最长远考虑,尽可能的避免后续vlan的变更导致异常。默认情况下,所有vlan都被映射在内部实例IST0中,不过最好尽可能的不要将业务数据vlan映射在IST0内。
常用的规划配置如下:
spanning-tree mst configuration
name xxx.xxx
revision 10
instance 1 vlan 2-1001
instance 2 vlan 1006-4094
exit
spanning-tree mst 0-1 priority 24576
spanning-tree mst 2 priority 28672
spanning-tree mode mst
其特点除了基本包含RPVST所有优点包括上述的后三点外,最重要的特点是:多个vlan可以映射到一个实例,可以从交换网络中实际存在的stp拓扑来规划实例。这样针对多vlan的环境,很好的解决了CPU和MEMORY消耗情况以及收敛时间问题。
但是由于MSTP是基于域协商管理的,在整个域内各交换机必须保持三要素一致才能达到同步。三要素为domain、reversion以及instance。因此交换网络维护中需要新增vlan的情况下会导致MSTP域内的instance不一致的情况。通常MSTP规划时需要做最长远考虑,尽可能的避免后续vlan的变更导致异常。默认情况下,所有vlan都被映射在内部实例IST0中,不过最好尽可能的不要将业务数据vlan映射在IST0内。
常用的规划配置如下:
spanning-tree mst configuration
name xxx.xxx
revision 10
instance 1 vlan 2-1001
instance 2 vlan 1006-4094
exit
spanning-tree mst 0-1 priority 24576
spanning-tree mst 2 priority 28672
spanning-tree mode mst
在做rapid-pvst向mstp迁移时,有以下注意点:
1,确保MSTP规划考虑全面,尽可能避免后续新增vlan导致MSTP的收敛;
2,与其他stp共存时,确保所有vlan的root为MST的IST实例;
3,确保任何vlan都开启stp;
4,确保交换机互联使用trunk模式;
5,迁移过程需要先将命令配置完成后才能启用MST模式;
6,迁移过程可以先从分布层即root层开始处理,然后再配置接入交换机;
7,迁移前关闭所有guard特性,如loopguard、rootguard等,这个非常重要;
8,迁移方案设计之前最好搭建模拟环境进行测试,以尽量避免不可预知的风险。
1,确保MSTP规划考虑全面,尽可能避免后续新增vlan导致MSTP的收敛;
2,与其他stp共存时,确保所有vlan的root为MST的IST实例;
3,确保任何vlan都开启stp;
4,确保交换机互联使用trunk模式;
5,迁移过程需要先将命令配置完成后才能启用MST模式;
6,迁移过程可以先从分布层即root层开始处理,然后再配置接入交换机;
7,迁移前关闭所有guard特性,如loopguard、rootguard等,这个非常重要;
8,迁移方案设计之前最好搭建模拟环境进行测试,以尽量避免不可预知的风险。
下面是本人在一个配置了loopguard特性的交换环境中做迁移的试验情况:
在没有配置
loopguard
的情况下的
debug span events
:
2924#sh log
00:48:47: RSTP(1): updt roles, superior bpdu on Fa0/1 (synced=0)
00:48:47: RSTP(1): synced Fa0/1
00:48:47: RSTP(1): transmitting an agreement on Fa0/1 as a response to a proposal
//在root层迁移过程中,2924的vlan1接收到了2948的vlan1的bpdu信息。
00:48:50: RSTP(19): Fa0/1 rcvd info expired
00:48:50: RSTP(19): updt roles, information on root port Fa0/1 expired
00:48:50: RSTP(19): we become the root bridge
00:48:50: RSTP(19): Fa0/1 is now designated
//在root层迁移过程中,2924的vlan19接收不到2948的vlan19的bpdu信息,所以自认为root bridge。后面的vlan20和21同样如此。
00:48:50: RSTP(20): Fa0/1 rcvd info expired
00:48:50: RSTP(20): updt roles, information on root port Fa0/1 expired
00:48:50: RSTP(20): we become the root bridge
00:48:50: RSTP(20): Fa0/1 is now designated
00:48:50: RSTP(21): Fa0/1 rcvd info expired
00:48:50: RSTP(21): updt roles, information on root port Fa0/1 expired
00:48:50: RSTP(21): we become the root bridge
00:48:50: RSTP(21): Fa0/1 is now designated
00:48:52: RSTP(19): updt roles, superior bpdu on Fa0/1 (synced=0)
00:48:52: RSTP(19): Fa0/1 is now root port
//这里表明2924的vlan19接收到2948的vlan19的bpdu信息并将Fa0/1协商成RP,后续的vlan20和21同样如此。这个协商过程在2s内完成。Root层在接收到接入层2924的bpdu后识别其处于PVST模式,所以其mst向pvst兼容,并分vlan传递bpdu包。
00:48:52: RSTP(20): updt roles, superior bpdu on Fa0/1 (synced=0)
00:48:52: RSTP(20): Fa0/1 is now root port
00:48:52: RSTP(21): updt roles, superior bpdu on Fa0/1 (synced=0)
00:48:52: RSTP(21): Fa0/1 is now root port
00:48:54: RSTP(19): Fa0/1 received a tc ack
00:48:54: RSTP(20): Fa0/1 received a tc ack
00:48:54: RSTP(21): Fa0/1 received a tc ack
2924#
在配置了
loopguard
的情况下的
debug span events
:
2924#sh log
00:54:50: RSTP(1): updt roles, superior bpdu on Fa0/1 (synced=0)
00:54:50: RSTP(1): synced Fa0/1
00:54:50: RSTP(1): transmitting an agreement on Fa0/1 as a response to a proposal
00:54:54: RSTP(19): Fa0/1 rcvd info expired
00:54:54: %SPANTREE-2-LOOPGUARD_BLOCK: Loop guard blocking port FastEthernet0/1 on VLAN0019.
00:54:54: RSTP(19): updt roles, information on root port Fa0/1 expired
00:54:54: RSTP(19): we become the root bridge
00:54:54: RSTP(19): Fa0/1 is now designated
00:54:54: RSTP(20): Fa0/1 rcvd info expired
00:54:54: RSTP(20): updt roles, information on root port Fa0/1 expired
00:54:54: RSTP(20): we become the root bridge
00:54:54: RSTP(20): Fa0/1 is now designated
00:54:54: RSTP(21): Fa0/1 rcvd info expired
00:54:54: RSTP(21): updt roles, information on root port Fa0/1 expired
00:54:54: RSTP(21): we become the root bridge
00:54:54: RSTP(21): Fa0/1 is now designated
//可以看出2924在后续接收到2948的各vlan的bpdu之前就被LOOPGUARD_BLOCK挡住了。
继续分析如下:
Assume that we have a c3560 switch which we call it Switch-A and a c2960 switch called Switch-B.
Assume that we have a c3560 switch which we call it Switch-A and a c2960 switch called Switch-B.
1. In the normal way, if you don't configure loop guard on the interface of B, before change the RSTP to MST, A will send a BPDU to B every two seconds per VLAN. When we configure A with MST, A will send a new MST BPDU with Vlan1 which is native Vlan to B, but actually only Vlan1 can receive this BPDU, and after 6 seconds the other Vlans don't receive the BPDU, then the other Vlans will think the time is expired and all of the Vlans on B except Vlan1 will become the designated ports. So B is the root bridge of RSTP. Then B sends BPDUs to A with the designated ports, when A receives the BPDUs, it will detect that B is running RSTP, so the interface should be boundary port, and it should send out BPDUs per Vlan so both of the two switch can communicate with each other with all of the configured Vlans.
When the Vlans receive BPDUs from A again, they will found that the priority of A is higher and they are superior BPDUs, then they will change their roles to root ports. Then everything is working as expected now!!
2. If we configured loop guard on the interface of B, so when B found that it misses 3 BPDUs which is expected to receive from A, then it blocks all Vlans whose role is expired. So only Vlan1 is forwarding because it can receive BPDU. Then here is our problem, Vlan1 is root port, so it would not send BPDU to A, and the other Vlans are blocked so they wouldn't send BPDU to A either, so A will never find that the other end is running RSTP, so it would not treat the interface as boundary port, nor send BPDU per Vlan. Then Vlans of B except vlan1 will keep the status of inconsistent.
So what we must do before change RSTP to MST is remove the loop guard on the interfaces, or shut/no shut the physical interface after the Vlans are blocked.
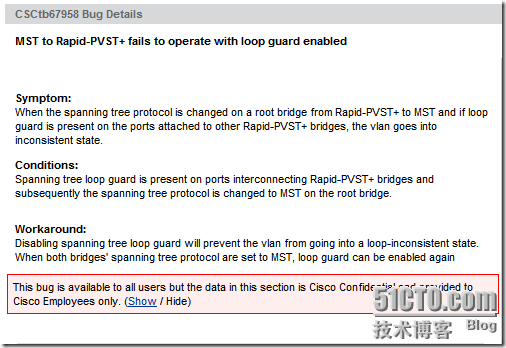
By the way, here is the Bug ID: CSCtb67958 as bellow. I thinks this is not a real bug because this is the mechanism issue between STP negotiation and loop guard.