App端主要的就是UI的搭建,和数据的请求,然后将服务端的数据以精美的UI展示出来,通过这种方法将信息传递给普通用户。普通用户在App上进行操作,将用户行为和数据上传到服务端。所以当我们刚开始接触Flutter这一跨平台开发的时候首先可以先了解一下我们的Flutter UI的搭建。
为什么要学习Flutter?
Flutter是Google的开源UI框架,Flutter生成的程序可以直接在Google最新的系统Fuschia上运行, 也可以build成apk在android上运行,或是生成ipa在iOS运行。
一般传统的跨平台解决方案如RN,Weex等都是将程序员编写的代码自动转换成Native代码,最终渲染工作交还给系统,使用类HTML+JS的UI构建逻辑,但是最终会生成对应的自定义原生控件。
Flutter重写了一套跨平台的UI框架。渲染引擎依靠跨平台的Skia图形库来自己绘制。逻辑处理使用支持AOT的Dart语言,执行效率也比JS高很多。
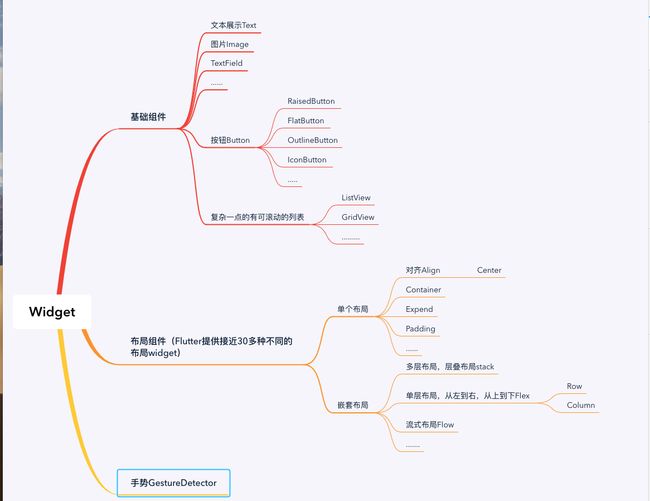
- 一. FlutterUI整体架构
跨平台应用的框架,没有使用WebView或者系统平台自带的控件,使用自身的高性能渲染引擎(Skia)自绘,界面开发语言使用dart,底层渲染引擎使用C, C++
我们可以看到最上层的
Material 和
Cupertino组件,这两个什么玩意呢。
其实很简单
Cupertino库比蒂诺是硅谷核心城市之一,也是 苹果公司的总部,这就很容易理解了,
Cupertino库就是iOS风格的组件。
Material当然就是安卓主流风格的组件了。
从架构图可以看出,这两个组件库都是基于Widget实现的,可以看出这个Widget很基础,很重要啊。
Flutter设计思想是一切皆是Widget,包括UI基础控件,布局方式,手势等都是widget。
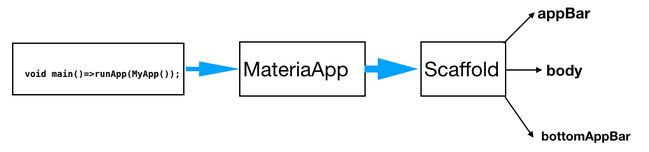
当我们新建一个Flutter工程之后,自带的demo示例如下图:
看一下demo代码:
MaterialApp包裹
MyHomePage,
MyHomePage包裹着
Scaffold,
Scaffold包裹着
AppBar和
body也可以增加
bottomNavigationBar等。
MaterialApp继承StatefulWidget,放在Main 入口内函数中,初始化一个Material风格的App,一般配合Scaffold搭建AppUI架构。
Scaffold系统封装好的脚手架,提供了设置顶部导航栏,底部导航栏,侧边栏。
App UI架构搭建完成之后,看一下基本UI组件的使用和组合。
- 二.下面介绍一下Widget类:
abstract class Widget extends DiagnosticableTree{}我们由此可知Widget是一个不能实例化的抽象类。系统实现的它的两个子类分别为StatefulWidget和StatelessWidget。
StatelessWidget是无状态的控件,很简单,创建之后,被它包裹的Widget上边的数据就不在更新了,当然这个也不知绝对的,可以通过其他方法去更新StatelessWidget中Ui,这个以后再说。
StatefulWidget 这个是有状态的,创建StatefulWidget 同时必须创建对应的State类,构建UI就放在了State类里边,并且可以调用setState(){}函数去从新使用新的状态构建UI。所以在实际开发中,我们要根据具体需求,选择对应的Widget。可以使用StatelessWidget完成的,尽可能的不要用StatefulWidget 。下面举个例子:
StatelessWidget:比如说在一些静态页面构建时,一旦UI构建之后便不需要再去更改UI,这时候可以使用StatelessWidget,比如一般App的关于我们页面。
效果如下
StatefulWidget :我们构建的是动态页面,比如展示的数据是服务器返回来的,或者用户进行交互,需要更新UI斩杀的数据。新建工程自带的demo如下:
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see the
// application has a blue toolbar. Then, without quitting the app, try
// changing the primarySwatch below to Colors.green and then invoke
// "hot reload" (press "r" in the console where you ran "flutter run",
// or simply save your changes to "hot reload" in a Flutter IDE).
// Notice that the counter didn't reset back to zero; the application
// is not restarted.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
_MyHomePageState createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.display1,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
- 三.常用控件的学习
1.Text文本展示类
类似iOS的UILabel控件,系统提供了丰富的配置属性。
const Text(this.data, {
Key key,
this.style,//单独的style类,可以设置字体颜色,字体大小,字重,字间距等强大功能
this.strutStyle,
this.textAlign,//对齐方式
this.textDirection,字体显示方向
this.locale,
this.softWrap,
this.overflow,
this.textScaleFactor,
this.maxLines,//最大显示行数
this.semanticsLabel,
}) : assert(data != null),
textSpan = null,
super(key: key);
当然也同样支持不同样式的复杂文本的显示:
const Text.rich(this.textSpan, {
Key key,
this.style,
this.strutStyle,
this.textAlign,
this.textDirection,
this.locale,
this.softWrap,
this.overflow,
this.textScaleFactor,
this.maxLines,
this.semanticsLabel,
}) : assert(textSpan != null),
data = null,
super(key: key);
富文本显示可以使用RichText。
2.Image
Image.asset:从asset资源文件获取图片;
Image.network:从网络获取图片;
Image.file:从本地资源文件回去图片;
Image.memory:从内存资源获取图片;
FadeInImage带有一个占位图的Image,比如网络较慢,或者网络图片请求失败的时候,会有一个占位图。
注意Image有一个Fit属性,用于设置图片内容适应方式,类似于iOS ImageView contenMode。
class GCImageTest extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_GCImageTestState createState() => _GCImageTestState();
}
class _GCImageTestState extends State {
Widget buildImage (url,BoxFit fit){
return Container(
child: Image.network(url,fit:fit,width: 350,height: 100,),
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
buildImage("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2942065216,1819114681&fm=27&gp=0.jpg", BoxFit.fill),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
buildImage("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2942065216,1819114681&fm=27&gp=0.jpg", BoxFit.cover),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
buildImage("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2942065216,1819114681&fm=27&gp=0.jpg", BoxFit.fitWidth),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
buildImage("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2942065216,1819114681&fm=27&gp=0.jpg", BoxFit.contain),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
buildImage("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2942065216,1819114681&fm=27&gp=0.jpg", BoxFit.fitHeight),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
buildImage("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2942065216,1819114681&fm=27&gp=0.jpg", BoxFit.scaleDown),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
FadeInImage.assetNetwork(
image:"",
placeholder:"lib/static/[email protected]",
)
],
);
}
}
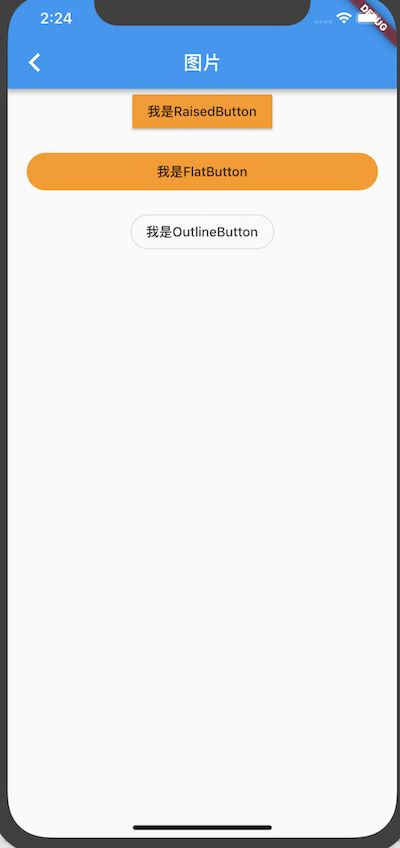
3.按钮
RaisedButton:凸起的按钮,周围有阴影,其实就是Android中的Material Design风格的Button ,继承自MaterialButton。
FlatButton :扁平化的按钮,继承自MaterialButton。
OutlineButton:带边框的按钮,继承自MaterialButton。
IconButton :图标按钮,继承自StatelessWidget。
这些按钮都可以通过设置shape来设置其圆角:
class _GCButtonTestState extends State {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width,
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
RaisedButton(
highlightColor: Colors.red,
color: Colors.orange,
child: Text("我是RaisedButton"),
onPressed: () {},
),
Container(
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width,
height: 80,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: FlatButton(
shape: const RoundedRectangleBorder(
side: BorderSide.none,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(50))),
highlightColor: Colors.red,
color: Colors.orange,
child: Text("我是FlatButton"),
onPressed: () {},
),
),
OutlineButton(
shape: const RoundedRectangleBorder(
side: BorderSide.none,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(20))),
onPressed: () {},
child: Text("我是OutlineButton"),
),
],
),
);
}
}
效果如下:
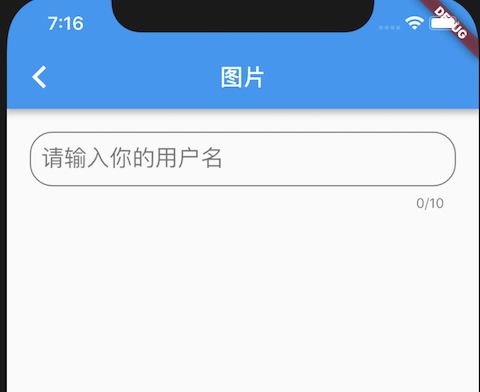
4.TextField
用户输入控件:
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return KeyboardAvoider(
focusPadding:20,
autoScroll: true,
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20),
// color: Colors.green,
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width,
height:80,
child: TextField(
decoration: InputDecoration(
//设置边框,占位符等
border: OutlineInputBorder(
borderSide: BorderSide(
width: 5,
color: Colors.grey,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(20)),
),
contentPadding: EdgeInsets.all(10),
icon: Icon(Icons.text_fields),
hintText: "请输入你的用户名"),
keyboardType:TextInputType.text,//键盘类型
textInputAction: TextInputAction.done, //键盘 return 按钮设置
maxLines: 1,
autocorrect: true, //是否自动更正
autofocus: false, //是否自动对焦
// obscureText: true, //是否是密码
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
focusNode: _contentFocusNode,//控制是否为第一响应, _contentFocusNode.unfocus();收起键盘,FocusScope.of(context).requestFocus(_contentFocusNode.unfocus)请求成为第一响应
onEditingComplete: () {
},
controller: controller, //监听输入动作,可以在controller里设置默认值controller.text = "默认值";
onSubmitted:(String text){
print(text);
_contentFocusNode.unfocus();
} ,//提交信息
onChanged: (String text){
},
onTap: (){
},//文字输入有变化
),
),
);
}
}
注意的是在实际使用过程中TextField是不允许被键盘遮挡的,当TextField父节点时可滚动视图时,系统会自动上拉,不被键盘遮挡。但是如果TextField父节点不是滚动视图时候,可以使用第三方
KeyboardAvoider进行包裹,这样输入时候也不会被键盘遮盖。controller也必须主动销毁
- 四常用布局类
1.0Flex布局
direction:布局方向可以设置,纵向和横向。
mainAxisAlignment:主轴对齐方向,如果横向布局,那么Y轴是主节点。如果纵向布局那么X轴是主轴。
crossAxisAlignment:副轴对齐方式。
children:顾名思义上边字节点集合。
这一点不理解的话,我举个:
class GCFlexRowlayoutTest extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Flex(
direction: Axis.horizontal,//布局方向
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,//主轴对齐方向,因为是横向的布局,所以主轴是X方向
// crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.end,//副轴对齐方式,底部对齐
children: [
Flexible(
flex: 1,//设置宽度比例
child: Container(
height: 100,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
Flexible(
flex: 2,
child: Container(
height: 150,
color: Colors.grey,
),
),
Flexible(
flex: 1,
child: Container(
height: 50,
color: Colors.green,
),
)
],
);
}
}
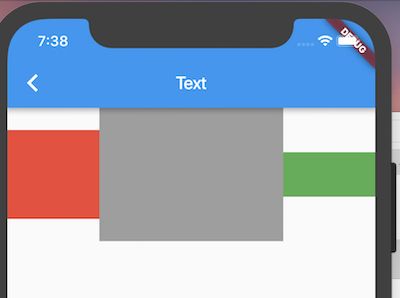
首先我先注释掉crossAxisAlignment:效果如下:
可见副轴(即这里的Y轴),默认对齐方向是居中对齐。
下面我设置:
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.end
效果如下:
此时设置的为Y轴的end方向对齐。其它对齐方式,可以自行试用一下。
1.0.1Row布局类
行布局类,是Flex的子类,基本功能同Flex,布局方向为横向布局
1.0.2Column布局类
列布局类,是Flex的子类,基本功能同Flex,布局方向为纵向布局
实际开发中,我们都是比较长使用这两者嵌套进行复杂UI
构建。
2.Stack层叠布局
如下图效果:
代码实现如下:
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Container(
height: 100,
width: 100,
child: Stack(
children: [
ClipOval(
child: Image.asset(
"lib/static/[email protected]",
fit: BoxFit.fill,
),
),
Positioned(
left: 25,
right: 10,
top: 10,
child: Text("添加水印"),
),
Positioned(
right: 5,
top: 10,
child: ClipOval(
child: Container(
width: 10,
height:10,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
),
],
),
),
);
Stack配合Positioned,FractionalOffset进行定位布局。
Positioned({
Key key,
this.left,
this.top,
this.right,
this.bottom,
this.width,
this.height,
@required Widget child,
})