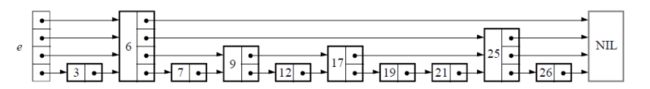
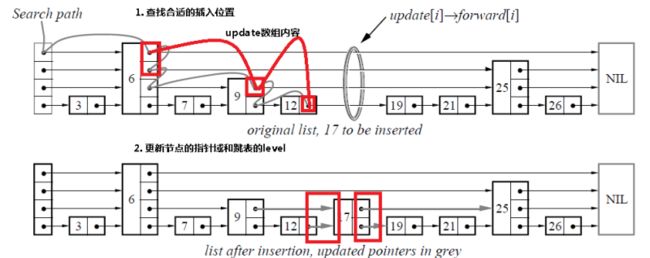
- Java常用集合与映射的线程安全问题深度解析
QQ828929QQ
java安全开发语言
Java常用集合与映射的线程安全问题深度解析一、线程安全基础认知在并发编程环境下,当多个线程同时操作同一集合对象时,若未采取同步措施,可能导致以下典型问题:数据竞争:多个线程同时修改数据导致结果不可预测状态不一致:部分线程看到集合的中间状态内存可见性:线程本地缓存与主内存数据不同步死循环风险:特定操作引发无限循环(如JDK7的HashMap扩容)二、典型非线程安全集合问题分析1.ArrayList
- java集合List,Set,Map怎么理解存储数据有序,无序以及可重复,不可重复
java程序员CC
JAVA基础java面试list
学习java已经有一段时间了,在练习开发项目的过程中经常用到List和Map却不知道其到底有何区别,今天整理了一下知识点对这几个进行浅显易懂的区分。PS:本文中的“有序”指的是存储数据时输入顺序与数据输出顺序相等,“唯一”:指的是不重复首先我们知道java集合有两个接口;一个是Collection,一个是Map;其中Colection衍生出了两个子接口也就是平时我们常见的--List【有序,不唯一
- springboot poi 后端手撕excel自定义表格。包括插入列表、跨行跨列合并
uutale
java应用springbootexcel后端
文章目录前言一、成品展示二、引入二、RestTemplateConfig三、接收实体ReturnResponse四、WriteExcelTableController总结前言这个程序是因为我需要根据数据库返回的数据生成excel,涉及到跨行跨列合并,表格list填充。填充后调用另一个项目的上传接口,把文件转成字节流传输过去,你们在自己进行使用的时候可以把字节流转成file存到本地。这里的代码有很多
- matplotlib中的colormap使用
ghfuidy
pythonpython
colormap的对象分析matplotlib中自带cm库,存储了一些colormap,可供开发人员调用。colormap对象的类型为matplotlib.colors.ListedColormapobject属于matplotlib中自定义的一个对象类型对象调用matplotlib中的这一对象调用需要如下步骤importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt#首先选择matplot中有的c
- 关于数组越界却不会报错
112233123hd
数据结构c++算法学习方法
关于数组越界却不会报错数组越界是不一定报错的,系统对越界的检查是设岗检查。一,在进行顺序表的学习时遇到的问题,下面是代码,大家可以直接去看结论。voidTestSeqList1(){SLs1;SLInit(&s1);/*SLPushBack(&s1,1);SLPushBack(&s1,2);SLPushBack(&s1,3);SLPushBack(&s1,4);SLPushBack(&s1,5);
- Java-校验值区间值的连续性
江节胜-胜行全栈AI
java状态模式开发语言
最新版本更新https://code.jiangjiesheng.cn/article/363?from=csdnc<30,30≤c<60,60≤c<100,100≤c有值时,必须收尾相等。BigDecimalendCheckValue=null;for(BssCompareMethodParameterConfigAddVOconfigRow:actualSampleCompareList){e
- JAVA集合arraylist存取数据_ArrayList集合
月小烟
集合出现的原因数组存储数据是固定存储,当遇到要存储数据的个数不确定的时候数组就不满足了,集合就出现了集合存储数据的个数,可以随着数据量的变化而变化,不会造成越界或者大量的空间浪费存储数据的个数是可变的ArrayList:java.util包下底层维护了一个数组线程不同步(处理速度快)创建ArrayList对象的格式:ArrayList集合名字=newArrayList();:泛型,代表了集合中要存
- element plus table树形数据,增、删、改子节点数据时,进行局部刷新,而不刷新整个页面
catino
vue.jsjavascriptelementui
...constlistLoading=ref(false)//保存节点映射的Mapconstmaps=reactive(newMap())constload=async(row,treeNode,resolve)=>{constpid=row.idmaps.set(pid,{row,treeNode,resolve})constpost_data={parent_id:row.id,}listL
- 使用浏览器原生API实现录屏功能
会说法语的猪
javascriptjavascript开发语言ecmascript
好早之前写了个小deme,本来都忘了,现在无意中又翻出来了,所以也来记录一下吧!废话不说了,直接上代码了:webRTCconstcontrol=document.querySelector('.control')control.addEventListener('click',start)asyncfunctionstart(){co
- 百某田网任务脚本
点云-激光雷达-Slam-三维牙齿
其他智能手机运维自动化
自动化操作百田游戏的任务脚本,特别是用于完成每日任务和积分兑换的功能。主要功能任务管理:脚本通过定时任务查询并执行每天的任务,自动完成任务并兑换积分。每个任务通过调用do_list()和do_task()函数来查询和完成。多账号支持:支持多个账号的登录和管理,账号信息通过baitianGameCookie变量传入,可以通过@或换行符分隔多个账号。积分兑换:根据配置的兑换ID进行积分兑换操作,支持选
- 深入理解 Kafka 的 ConsumerRebalanceListener
t0_54coder
编程问题解决手册kafkalinq分布式
深入理解Kafka的ConsumerRebalanceListener在分布式系统中,数据的一致性和可靠性是至关重要的。ApacheKafka作为一个流行的分布式流处理平台,提供了强大的数据传输和处理能力。在Kafka中,消费者组(ConsumerGroup)的概念允许多个消费者实例共同处理一个主题的数据。然而,当消费者实例的个数发生变化时,如何确保数据的平衡和一致性呢?这就引出了我们今天要讨论的
- 腾讯云Centos Stream 9 yum源
☆凡尘清心☆
腾讯云centos云计算
1.CentOS-Stream-BaseOS.repo#CentOS-Stream-BaseOS.repo##ThemirrorlistsystemusestheconnectingIPaddressoftheclientandthe#updatestatusofeachmirrortopickcurrentmirrorsthataregeographically#closetotheclient
- 力扣刷题|链表面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
柯ran
力扣leetcode算法数据结构链表
题目:实现一种算法,找出单向链表中倒数第k个节点。返回该节点的值。快慢指针思想,画图更容易理解/***Definitionforsingly-linkedlist.*structListNode{*intval;*structListNode*next;*};*/intkthToLast(structListNode*head,intk){assert(head!=NULL);if(head==N
- java中vector和list_java中vector和list的区别
Creamy络
java中vector和list的区别发布时间:2020-06-1917:07:11来源:亿速云阅读:106作者:元一vector的概念Vector类是在java中可以实现自动增长的对象数组,vector在C++标准模板库中的部分内容,它是一个多功能的,能够操作多种数据结构和算法的模板类和函数库。vector的使用连续存储结构:vector是可以实现动态增长的对象数组,支持对数组高效率的访问和在数
- react-native 实现AES RSA MD5加密
花程序媛
importReact,{Component}from'react';import{Platform,StyleSheet,Text,View,Image,Dimensions,ScrollView,TouchableOpacity,Modal,TouchableHighlight,NativeModules,ToastAndroid,Alert,FlatList,}from'react-nati
- 头歌||使用Redis构建任务队列
myy的源代码
redis数据库缓存
第1关:先进先出任务队列编程要求在Begin-End区域编写add_task(task_name)函数,实现将任务加入队列的功能,具体参数与要求如下:方法参数task_name是要加入的任务名称;推入任务的实现:将新的任务从列表task:list的尾部插入。编写pop_task()函数,实现获取一个任务的功能,具体参数与要求如下:获取任务的实现:从列表task:list的头部阻塞式的弹出一个值,最
- 【C++】Vector和List的区别
信手斩龙
C++
在学习stl的时候,总是有同学分不清楚Vector和List的使用,在这里我总结一下它们的区别和使用方法。一、底层结构 vector的底层结构是动态顺序表,在内存中是一段连续的空间。 list的底层结构是带头节点的双向循环链表,在内存中不是一段连续的空间。二、支持随机访问 vector支持随机访问,可以利用下标精准定位到一个元素上,访问某个元素的时间复杂度是O(1)。 list不支持随机访问,要
- list和vector的区别
Ashen—one
listwindows数据结构
1>list可以按值删除vector和deque没有给定的函数,需要find();和erase();一起使用才能做到2>list删除元素会释放空间,vector不会3>list是双向迭代器,vector是随机迭代器4>list内部排序是指针指向的更改,vector涉及对象的创建和销毁5>vector改变元素,导致迭代器失效deque删除的时候不会导致迭代器失效(非迭代器位置),插入会导致迭代器失效
- 【leetcode hot 100 39】组合总和
longii11
leetcodewindows算法
错误解法一:每一次回溯都遍历提供的数组classSolution{publicList>combinationSum(int[]candidates,inttarget){List>result=newArrayList>();Listtemp=newArrayList();intsum=0;backtrack(candidates,target,result,temp,sum);returnre
- kvm虚拟机的基本使用
千航@abc
kvm虚拟化linuxcentos运维kvm虚拟化virsh
[root@kvm~]#virshdestroy虚拟机名#关闭虚拟机[root@kvm~]#virshundefine虚拟机名#删除虚拟机[root@kvm~]#virshstart虚拟机名#开启虚拟机[root@kvm~]#virshconsole虚拟机名#登录虚拟机[root@kvm~]#virshlist--all#显示所有虚拟机[root@kvm~]#virshconsole虚拟机名#连接
- Pyhton 基础
368.
pythonpython开发语言
初识PythonPython是一种解释型语言Python使用缩进对齐组织代码执行,所以没有缩进的代码,都会在载入时自动执行数据类型:整形int无限大浮点型float小数复数complex由实数和虚数组成Python中有6个标准的数据类型:Number(数字)String(字符串)List(列表)Tuple(元组)Sets(集合)Dictionart(字典)其中不可变得数据:Number(数字)St
- JavaScript HTML DOM 节点列表
宇哥资料
JavaScriptjavascripthtml开发语言
NodeList对象是一个从文档中获取的节点列表(集合)。NodeList对象类似HTMLCollection对象。一些旧版本浏览器中的方法(如:getElementsByClassName())返回的是NodeList对象,而不是HTMLCollection对象。所有浏览器的childNodes属性返回的是NodeList对象。大部分浏览器的querySelectorAll()返回NodeLis
- c++ stl库有哪些技术
C++ 老炮儿的技术栈
c++算法学习笔记c++
C++STL(标准模板库)包含以下一些重要技术:容器-序列容器:如vector(动态数组),支持快速随机访问和尾部插入/删除;list(双向链表),适合频繁的插入和删除操作;deque(双端队列),能在两端高效地进行插入和删除。-关联容器:像map(键值对映射),基于红黑树实现,提供快速的查找、插入和删除操作;set(集合),同样基于红黑树,元素唯一且有序。迭代器提供了一种统一的方式来访问容器中的
- Redis操作命令详解
HaYiBoy
软件工具安装数据库缓存redis
Redis(RemoteDictionaryServer,远程字典服务)是一个开源的键值存储系统,通常用作数据库、缓存或消息传递系统。它支持多种数据结构,如字符串(strings)、哈希(hashes)、列表(lists)、集合(sets)、有序集合(sortedsets)等。本文将详细介绍Redis的一些常用操作命令,帮助你更好地使用Redis。1.连接命令1.1redis-cliredis-c
- redis
java
一、redis常用的数据类型有String、list、hash、set、Zset1.String是普通的字符串,存储一些简单的数据,例如用户登陆的时候后端保存短信验证码2.hash相当于Java中的hashmap,可以定义一个键之后,后面设置多个值,例如用于存储用户信息,商品信息等等3.set是$tring类型的无序集合,但是其中的元素是唯一的,中间不能出现重复元素,当输入时有重复元素存储的时候能
- rust学习笔记16-206.反转链表(递归)
水蜜桃one
学习笔记链表
rust函数递归在14中已经提到,接下来我们把206.反转链表,用递归法实现递归函数通常包含两个主要部分:基准条件(BaseCase):递归终止的条件,避免无限递归。递归步骤(RecursiveStep):将问题分解为更小的子问题,并调用自身来解决这些子问题。//Definitionforsingly-linkedlist.#[derive(PartialEq,Eq,Clone,Debug)]pu
- yum彻底卸载软件包(包含依赖)
mighty13
Linuxcentos卸载yum依赖history
概述yum命令安装软件包时会自动依赖包,但yumremove子命令只卸载该软件包而不能卸载依赖。如果需要删除安装时自动安装的依赖包,则可以使用yumhistory子命令回滚安装事务以达到目的。具体操作查看yum操作(事务)历史[root@localhost~]#yumhistorylist或yumhistoryLoading"fastestmirror"pluginConfigtime:0.007
- 顺序表以及顺序表的操作(数据结构初阶)
猫天帝
数据结构
线性表在学习顺序表之前,我们需要先了解一下什么是线性表。线性表(linearlist)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。物理结构与逻辑结构:所谓物理结构,就是数据实际
- java常用数据转换
bestwinner
javapythonwindows
1.List与数组互转ArrayListlist=newArrayListlist1=Arrays.stream(array1).collect(Collectors.toList());String[]cateArray=cateList.toArray(newString[cateList.size()]);2.new集合对像importcom.google.common.collect.Li
- c语言中longjmp()函数,C语言的反人类函数:setjmp和longjmp的详细剖析
weixin_39822629
c语言中longjmp()函数
我希望看这篇文章的你对C++的传统异常处理,即try...catch...throw有了解(不是WindowsSEH),这样才能方便你最深入的理解这2个C语言的反人类函数。当然如果不了解就先看下面的“C++式的异常处理”,如果感觉自己了解了,可以直接skip看到“C语言中的模拟”。【C++式的异常处理】首先,我们写一个类,请不要想这个类有什么特别的地方,其只是为了打印出来构造和析构。classCF
- 312个免费高速HTTP代理IP(能隐藏自己真实IP地址)
yangshangchuan
高速免费superwordHTTP代理
124.88.67.20:843
190.36.223.93:8080
117.147.221.38:8123
122.228.92.103:3128
183.247.211.159:8123
124.88.67.35:81
112.18.51.167:8123
218.28.96.39:3128
49.94.160.198:3128
183.20
- pull解析和json编码
百合不是茶
androidpull解析json
n.json文件:
[{name:java,lan:c++,age:17},{name:android,lan:java,age:8}]
pull.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<stu>
<name>java
- [能源与矿产]石油与地球生态系统
comsci
能源
按照苏联的科学界的说法,石油并非是远古的生物残骸的演变产物,而是一种可以由某些特殊地质结构和物理条件生产出来的东西,也就是说,石油是可以自增长的....
那么我们做一个猜想: 石油好像是地球的体液,我们地球具有自动产生石油的某种机制,只要我们不过量开采石油,并保护好
- 类与对象浅谈
沐刃青蛟
java基础
类,字面理解,便是同一种事物的总称,比如人类,是对世界上所有人的一个总称。而对象,便是类的具体化,实例化,是一个具体事物,比如张飞这个人,就是人类的一个对象。但要注意的是:张飞这个人是对象,而不是张飞,张飞只是他这个人的名字,是他的属性而已。而一个类中包含了属性和方法这两兄弟,他们分别用来描述对象的行为和性质(感觉应该是
- 新站开始被收录后,我们应该做什么?
IT独行者
PHPseo
新站开始被收录后,我们应该做什么?
百度终于开始收录自己的网站了,作为站长,你是不是觉得那一刻很有成就感呢,同时,你是不是又很茫然,不知道下一步该做什么了?至少我当初就是这样,在这里和大家一份分享一下新站收录后,我们要做哪些工作。
至于如何让百度快速收录自己的网站,可以参考我之前的帖子《新站让百
- oracle 连接碰到的问题
文强chu
oracle
Unable to find a java Virtual Machine--安装64位版Oracle11gR2后无法启动SQLDeveloper的解决方案
作者:草根IT网 来源:未知 人气:813标签:
导读:安装64位版Oracle11gR2后发现启动SQLDeveloper时弹出配置java.exe的路径,找到Oracle自带java.exe后产生的路径“C:\app\用户名\prod
- Swing中按ctrl键同时移动鼠标拖动组件(类中多借口共享同一数据)
小桔子
java继承swing接口监听
都知道java中类只能单继承,但可以实现多个接口,但我发现实现多个接口之后,多个接口却不能共享同一个数据,应用开发中想实现:当用户按着ctrl键时,可以用鼠标点击拖动组件,比如说文本框。
编写一个监听实现KeyListener,NouseListener,MouseMotionListener三个接口,重写方法。定义一个全局变量boolea
- linux常用的命令
aichenglong
linux常用命令
1 startx切换到图形化界面
2 man命令:查看帮助信息
man 需要查看的命令,man命令提供了大量的帮助信息,一般可以分成4个部分
name:对命令的简单说明
synopsis:命令的使用格式说明
description:命令的详细说明信息
options:命令的各项说明
3 date:显示时间
语法:date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT]
- eclipse内存优化
AILIKES
javaeclipsejvmjdk
一 基本说明 在JVM中,总体上分2块内存区,默认空余堆内存小于 40%时,JVM就会增大堆直到-Xmx的最大限制;空余堆内存大于70%时,JVM会减少堆直到-Xms的最小限制。 1)堆内存(Heap memory):堆是运行时数据区域,所有类实例和数组的内存均从此处分配,是Java代码可及的内存,是留给开发人
- 关键字的使用探讨
百合不是茶
关键字
//关键字的使用探讨/*访问关键词private 只能在本类中访问public 只能在本工程中访问protected 只能在包中和子类中访问默认的 只能在包中访问*//*final 类 方法 变量 final 类 不能被继承 final 方法 不能被子类覆盖,但可以继承 final 变量 只能有一次赋值,赋值后不能改变 final 不能用来修饰构造方法*///this()
- JS中定义对象的几种方式
bijian1013
js
1. 基于已有对象扩充其对象和方法(只适合于临时的生成一个对象):
<html>
<head>
<title>基于已有对象扩充其对象和方法(只适合于临时的生成一个对象)</title>
</head>
<script>
var obj = new Object();
- 表驱动法实例
bijian1013
java表驱动法TDD
获得月的天数是典型的直接访问驱动表方式的实例,下面我们来展示一下:
MonthDaysTest.java
package com.study.test;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.study.MonthDays;
public class MonthDaysTest {
@T
- LInux启停重启常用服务器的脚本
bit1129
linux
启动,停止和重启常用服务器的Bash脚本,对于每个服务器,需要根据实际的安装路径做相应的修改
#! /bin/bash
Servers=(Apache2, Nginx, Resin, Tomcat, Couchbase, SVN, ActiveMQ, Mongo);
Ops=(Start, Stop, Restart);
currentDir=$(pwd);
echo
- 【HBase六】REST操作HBase
bit1129
hbase
HBase提供了REST风格的服务方便查看HBase集群的信息,以及执行增删改查操作
1. 启动和停止HBase REST 服务 1.1 启动REST服务
前台启动(默认端口号8080)
[hadoop@hadoop bin]$ ./hbase rest start
后台启动
hbase-daemon.sh start rest
启动时指定
- 大话zabbix 3.0设计假设
ronin47
What’s new in Zabbix 2.0?
去年开始使用Zabbix的时候,是1.8.X的版本,今年Zabbix已经跨入了2.0的时代。看了2.0的release notes,和performance相关的有下面几个:
:: Performance improvements::Trigger related da
- http错误码大全
byalias
http协议javaweb
响应码由三位十进制数字组成,它们出现在由HTTP服务器发送的响应的第一行。
响应码分五种类型,由它们的第一位数字表示:
1)1xx:信息,请求收到,继续处理
2)2xx:成功,行为被成功地接受、理解和采纳
3)3xx:重定向,为了完成请求,必须进一步执行的动作
4)4xx:客户端错误,请求包含语法错误或者请求无法实现
5)5xx:服务器错误,服务器不能实现一种明显无效的请求
- J2EE设计模式-Intercepting Filter
bylijinnan
java设计模式数据结构
Intercepting Filter类似于职责链模式
有两种实现
其中一种是Filter之间没有联系,全部Filter都存放在FilterChain中,由FilterChain来有序或无序地把把所有Filter调用一遍。没有用到链表这种数据结构。示例如下:
package com.ljn.filter.custom;
import java.util.ArrayList;
- 修改jboss端口
chicony
jboss
修改jboss端口
%JBOSS_HOME%\server\{服务实例名}\conf\bindingservice.beans\META-INF\bindings-jboss-beans.xml
中找到
<!-- The ports-default bindings are obtained by taking the base bindin
- c++ 用类模版实现数组类
CrazyMizzz
C++
最近c++学到数组类,写了代码将他实现,基本具有vector类的功能
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class Array
{
public:
//构造函数
- hadoop dfs.datanode.du.reserved 预留空间配置方法
daizj
hadoop预留空间
对于datanode配置预留空间的方法 为:在hdfs-site.xml添加如下配置
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.du.reserved</name>
<value>10737418240</value>
- mysql远程访问的设置
dcj3sjt126com
mysql防火墙
第一步: 激活网络设置 你需要编辑mysql配置文件my.cnf. 通常状况,my.cnf放置于在以下目录: /etc/mysql/my.cnf (Debian linux) /etc/my.cnf (Red Hat Linux/Fedora Linux) /var/db/mysql/my.cnf (FreeBSD) 然后用vi编辑my.cnf,修改内容从以下行: [mysqld] 你所需要: 1
- ios 使用特定的popToViewController返回到相应的Controller
dcj3sjt126com
controller
1、取navigationCtroller中的Controllers
NSArray * ctrlArray = self.navigationController.viewControllers;
2、取出后,执行,
[self.navigationController popToViewController:[ctrlArray objectAtIndex:0] animated:YES
- Linux正则表达式和通配符的区别
eksliang
正则表达式通配符和正则表达式的区别通配符
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/1976579
首先得明白二者是截然不同的
通配符只能用在shell命令中,用来处理字符串的的匹配。
判断一个命令是否为bash shell(linux 默认的shell)的内置命令
type -t commad
返回结果含义
file 表示为外部命令
alias 表示该
- Ubuntu Mysql Install and CONF
gengzg
Install
http://www.navicat.com.cn/download/navicat-for-mysql
Step1: 下载Navicat ,网址:http://www.navicat.com/en/download/download.html
Step2:进入下载目录,解压压缩包:tar -zxvf navicat11_mysql_en.tar.gz
- 批处理,删除文件bat
huqiji
windowsdos
@echo off
::演示:删除指定路径下指定天数之前(以文件名中包含的日期字符串为准)的文件。
::如果演示结果无误,把del前面的echo去掉,即可实现真正删除。
::本例假设文件名中包含的日期字符串(比如:bak-2009-12-25.log)
rem 指定待删除文件的存放路径
set SrcDir=C:/Test/BatHome
rem 指定天数
set DaysAgo=1
- 跨浏览器兼容的HTML5视频音频播放器
天梯梦
html5
HTML5的video和audio标签是用来在网页中加入视频和音频的标签,在支持html5的浏览器中不需要预先加载Adobe Flash浏览器插件就能轻松快速的播放视频和音频文件。而html5media.js可以在不支持html5的浏览器上使video和audio标签生效。 How to enable <video> and <audio> tags in
- Bundle自定义数据传递
hm4123660
androidSerializable自定义数据传递BundleParcelable
我们都知道Bundle可能过put****()方法添加各种基本类型的数据,Intent也可以通过putExtras(Bundle)将数据添加进去,然后通过startActivity()跳到下一下Activity的时候就把数据也传到下一个Activity了。如传递一个字符串到下一个Activity
把数据放到Intent
- C#:异步编程和线程的使用(.NET 4.5 )
powertoolsteam
.net线程C#异步编程
异步编程和线程处理是并发或并行编程非常重要的功能特征。为了实现异步编程,可使用线程也可以不用。将异步与线程同时讲,将有助于我们更好的理解它们的特征。
本文中涉及关键知识点
1. 异步编程
2. 线程的使用
3. 基于任务的异步模式
4. 并行编程
5. 总结
异步编程
什么是异步操作?异步操作是指某些操作能够独立运行,不依赖主流程或主其他处理流程。通常情况下,C#程序
- spark 查看 job history 日志
Stark_Summer
日志sparkhistoryjob
SPARK_HOME/conf 下:
spark-defaults.conf 增加如下内容
spark.eventLog.enabled true spark.eventLog.dir hdfs://master:8020/var/log/spark spark.eventLog.compress true
spark-env.sh 增加如下内容
export SP
- SSH框架搭建
wangxiukai2015eye
springHibernatestruts
MyEclipse搭建SSH框架 Struts Spring Hibernate
1、new一个web project。
2、右键项目,为项目添加Struts支持。
选择Struts2 Core Libraries -<MyEclipes-Library>
点击Finish。src目录下多了struts