前言
Google 在2018年推出了 Android Jetpack,在Jetpack里有一种管理fragment的新架构模式,那就是navigation. 字面意思是导航,但是除了做APP引导页面以外.也可以使用在App主页分tab的情况.. 甚至可以一个功能模块就一个activity大部分页面UI都使用fragment来实现,而navigation就成了管理fragment至关重要的架构.
但是,它不单单只能管理fragment也可以管理activity.这点你格外注意.
使用条件
你的Android studio 必需升级到3.2版本以上,此博客正在写的时候Android studio已经到达3.5,所以升级到最新版本即可.
依赖
//navigation implementation 'android.arch.navigation:navigation-fragment:1.0.0' implementation 'android.arch.navigation:navigation-ui:1.0.0'
使用流程
创建navigation目录
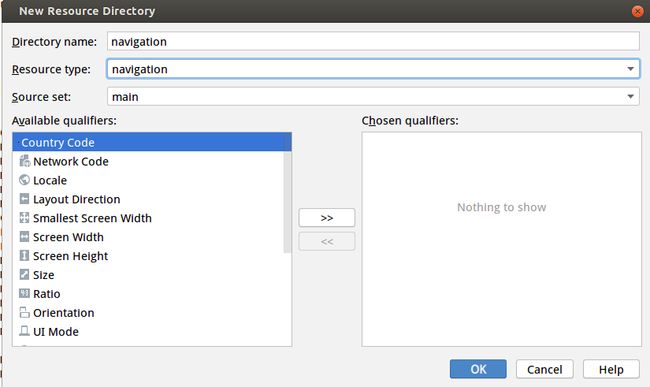
1.选中项目资源文件夹 res 右击 >> New >> New Resource Directory
2.选中navigation 点击创建 (注意这个目录只有在Android studio3.2版本以上才能出现)
创建navigation目录下的xml文件
1.选中项目资源文件夹 res 右击 >> New >> New Resource File
2.选择navigation ,输入xml文件名称,点击ok创建
配置创建的xml文件
上面我们创建了一个叫demo_nav.xml的navigation文件,现在我们需要来设配它来管理fragment
2.切换到Design模式后,我们可以看到下面这个界面(恩,一片空白). 我们可以在左上角点击![]() 添加图标,进入添加内容的操作.
添加图标,进入添加内容的操作.
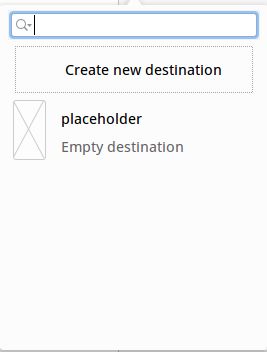
3.点击![]() 后,可以看到下面这个弹窗,这里解释一下:
后,可以看到下面这个弹窗,这里解释一下:
第一个 Create new destinattion,字面意思创建一个新目标(其实就是创建fragment,当然你也可以手动另外创建fragment不一定需要在这里创建)
第二个 placeholder,这个就是重点了. 这是一个管理fragment跳转的节点,我们点击后可以创建它.为了了解它的使用方式,点击3次创建三个节点
4.节点创建后可以看到三个节点(看下面图片,这些节点都是我已经导入fragment了.不要急后面会讲解如何导入).这里有一个重点! 你可以点击这些页面(会有一个蓝点),点击蓝点按住向右分配它需要跳转的另外一个页面.(它会自动生成一些我们跳转的代码)
6.然后点击左下角的Text模式,在Text模式下,可以看到如下代码,在上面的图片中你可以很清楚的看到创建了3个节点,并且是一个跳转一个的.从第一个fragment跳转到第二个fragment,再从第二个fragment跳转到第三个fragment
下面我们来重点讲解下下面的这些代码的关键点了:
在<navigation里的属性:
1.android:id="@+id/demo_nav" 这个属性是你这个xml文件navigation的id,很重要,我们需要在activity的xml布局里引用,记得写上不要忘记
2.app:startDestination="@id/one" 这个属性是你首次加载的第一个页面,很重要,一般就是第一个fragment
在<fragment 里的属性:
其实就是一个节点你也可以理解成一个fragment
1.android:id="@+id/one" 每一个fragment节点都需要有自己的id,很重要. 我们需要在后面的节点上使用这些id指定跳转目标
2.android:name="demo.yt.com.demo.fragment.BlankFragment" 这个属性是你这个节点所对应的fragment(需要你导入指定的fragment文件路径),这个很重要
3.android:label="BlankFragment" 一个标签名称,用于记录这个节点的标签信息(大概可能是在代码里的Intent里获取来知晓此次是那个fragment节点在跳转,没深究了)
4.tools:layout="@layout/fragment_blank" 这个属性不是重要的,设置它后你可以在切换到Design模式后看到,视图页面的fragment的预览图(就在上面的图片里,可以直接看到fragment效果)
在<action 里的属性:
action 负责编写跳转动作
1. android:id="@+id/action_one_to_two" 这个很重要,它是这个跳转动作的id, 这个id我们将在后面的代码中调用,用于执行fragment的跳转
2. app:destination="@id/two" 跳转的目标fragment,这个很重要
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/demo_nav"
app:startDestination="@id/one">
<fragment android:id="@+id/one"
android:name="demo.yt.com.demo.fragment.BlankFragment"
android:label="BlankFragment"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_blank">
<action
android:id="@+id/action_one_to_two"
app:destination="@id/two" />
fragment>
<fragment android:id="@+id/two"
android:name="demo.yt.com.demo.fragment.Blank2Fragment"
android:label="BlankFragment"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_blank2">
<action
android:id="@+id/action_two_to_three"
app:destination="@id/three" />
fragment>
<fragment android:id="@+id/three"
android:name="demo.yt.com.demo.fragment.Blank3Fragment"
android:label="BlankFragment"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_blank3"/>
navigation>
让navigation与Activity关联起来
现在我们已经创建了navigation,但是使用它还需要一个根Activity,它毕竟还是需要依托Activity的.
1.创建了一个叫DemoActivity的Activity.这个没啥,下面来看这个Activity的布局xml怎么配(如下xml代码)
我们就关注fragment的一些属性
1.android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment" 这个非常重要,这是你告知fragment需要使用navigation模式的关键属性,另外它是固定死的.你必需写.
2. app:defaultNavHost="true" 这是你实现物理按键(比如返回键),是按一下退出一个fragment 还是直接退出这个Activity的关键属性
3.app:navGraph="@navigation/demo_nav" 很重要,这就是我们前面创建的navigation的xml文件
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".fragment.DemoActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/demo_fragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:navGraph="@navigation/demo_nav"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
实现fragment跳转与返回
进入到DemoActivity后,首先会自动加载到第一个fragment. 然后我们看看如何跳转到其他fragment中
1.从第一个碎片跳转到第二个碎片,关键代码 Navigation.findNavController(getView()).navigate(R.id.action_one_to_two);
public class BlankFragment extends Fragment { private Button mBtnInputFragment2; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); } @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { final View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_blank, container, false);; mBtnInputFragment2 = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_input_fragment2); mBtnInputFragment2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Navigation.findNavController(getView()).navigate(R.id.action_one_to_two);//这个id就是navigation里的action的id } }); return view; } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); } @Override public void onDetach() { super.onDetach(); } }
2.从第二个碎片返回到第一个碎片,关键代码 Navigation.findNavController(getView()).popBackStack();
public class Blank2Fragment extends Fragment { private Button mBtnInputFragment3, mBtnBack; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); } @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_blank2, container, false); mBtnInputFragment3 = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_input_fragment3); mBtnBack = view.findViewById(R.id.back); mBtnInputFragment3.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Navigation.findNavController(getView()).navigate(R.id.action_two_to_three); //进入第三个碎片 } }); mBtnBack.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Navigation.findNavController(getView()).popBackStack(); //返回上一个碎片 } }); return view; } }
end