© Conmajia 2012
May 15th, 2012
(注:本文使用 FileStream 类的 Seek() 和 Read() 方法完成文件读取,没有用其他的骚东西。)
我们在编程过程中,经常会和计算机文件读取操作打交道。随着计算机功能和性能的发展,我们需要操作的文件尺寸也是越来越大。在 .NET Framework 中,我们一般使用 FileStream 来读取、写入文件流。当文件只有数十 kB 或者数 MB 时,一般的文件读取方式如 Read()、ReadAll() 等应用起来游刃有余,基本不会感觉到太大的延迟。但当文件越来越大,达到数百 MB 甚至数 GB 时,这种延迟将越来越明显,最终达到不能忍受的程度。
通常定义大小在 2GB 以上的文件为超大文件(当然,这个数值会随着科技的进步,越来越大)。对于这样规模的文件读取,普通方法已经完全不能胜任。这就要求我们使用更高效的方法,如内存映射法、分页读取法等。
内存映射(Memory Mapping)
内存映射的方法可以使用下面的 Windows API 实现。
LPVOID MapViewOfFile(HANDLE hFileMappingObject,
DWORD dwDesiredAccess,
DWORD dwFileOffsetHigh,
DWORD dwFileOffsetLow,
DWORD dwNumberOfBytesToMap);
虽然使用方便,但使用上限制较多,比如规定的分配粒度(Windows下通常为64KB)等。下面贴出内存映射法实例代码供参考,但本文不做进一步讨论。
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Text; 4 using System.Runtime.InteropServices; 5 6 namespace BlueVision.SaYuan.FileMapping 7 { 8 public class ShareMemory 9 { 10 [DllImport( "user32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto )] 11 public static extern IntPtr SendMessage( IntPtr hWnd, int Msg, int wParam, IntPtr lParam ); 12 13 [DllImport( "Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto )] 14 public static extern IntPtr CreateFileMapping( IntPtr hFile, IntPtr lpAttributes, uint flProtect, uint dwMaxSizeHi, uint dwMaxSizeLow, string lpName ); 15 16 [DllImport( "Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto )] 17 public static extern IntPtr OpenFileMapping( int dwDesiredAccess, [MarshalAs( UnmanagedType.Bool )] bool bInheritHandle, string lpName ); 18 19 [DllImport( "Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto )] 20 public static extern IntPtr MapViewOfFile( IntPtr hFileMapping, uint dwDesiredAccess, uint dwFileOffsetHigh, uint dwFileOffsetLow, uint dwNumberOfBytesToMap ); 21 22 [DllImport( "Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto )] 23 public static extern bool UnmapViewOfFile( IntPtr pvBaseAddress ); 24 25 [DllImport( "Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto )] 26 public static extern bool CloseHandle( IntPtr handle ); 27 28 [DllImport( "kernel32", EntryPoint = "GetLastError" )] 29 public static extern int GetLastError(); 30 31 [DllImport( "kernel32.dll" )] 32 static extern void GetSystemInfo( out SYSTEM_INFO lpSystemInfo ); 33 34 [StructLayout( LayoutKind.Sequential )] 35 public struct SYSTEM_INFO 36 { 37 public ushort processorArchitecture; 38 ushort reserved; 39 public uint pageSize; 40 public IntPtr minimumApplicationAddress; 41 public IntPtr maximumApplicationAddress; 42 public IntPtr activeProcessorMask; 43 public uint numberOfProcessors; 44 public uint processorType; 45 public uint allocationGranularity; 46 public ushort processorLevel; 47 public ushort processorRevision; 48 } 49 ///50 /// 获取系统的分配粒度 51 /// 52 /// 53 public static uint GetPartitionsize() 54 { 55 SYSTEM_INFO sysInfo; 56 GetSystemInfo( out sysInfo ); 57 return sysInfo.allocationGranularity; 58 } 59 60 const int ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS = 183; 61 62 const int FILE_MAP_COPY = 0x0001; 63 const int FILE_MAP_WRITE = 0x0002; 64 const int FILE_MAP_READ = 0x0004; 65 const int FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS = 0x0002 | 0x0004; 66 67 const int PAGE_READONLY = 0x02; 68 const int PAGE_READWRITE = 0x04; 69 const int PAGE_WRITECOPY = 0x08; 70 const int PAGE_EXECUTE = 0x10; 71 const int PAGE_EXECUTE_READ = 0x20; 72 const int PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE = 0x40; 73 74 const int SEC_COMMIT = 0x8000000; 75 const int SEC_IMAGE = 0x1000000; 76 const int SEC_NOCACHE = 0x10000000; 77 const int SEC_RESERVE = 0x4000000; 78 79 IntPtr m_fHandle; 80 81 IntPtr m_hSharedMemoryFile = IntPtr.Zero; 82 IntPtr m_pwData = IntPtr.Zero; 83 bool m_bAlreadyExist = false; 84 bool m_bInit = false; 85 uint m_MemSize = 0x1400000;//20M 86 long m_offsetBegin = 0; 87 long m_FileSize = 0; 88 FileReader File = new FileReader(); 89 90 91 /// 92 /// 初始化文件 93 /// 94 /// 缓冲大小 95 public ShareMemory( string filename, uint memSize ) 96 { 97 // 分页映射文件时,每页的起始位置startpos,必须为64K的整数倍。 98 // memSize即缓存区的大小必须是系统分配粒度的整倍说,window系统的分配粒度是64KB 99 this.m_MemSize = memSize; 100 Init( filename ); 101 } 102 103 104 /// 105 /// 默认映射20M缓冲 106 /// 107 /// 108 public ShareMemory( string filename ) 109 { 110 this.m_MemSize = 0x1400000; 111 Init( filename ); 112 } 113 114 ~ShareMemory() 115 { 116 Close(); 117 } 118 119 /// 120 /// 初始化共享内存 121 /// 122 /// 共享内存名称 123 /// 共享内存大小 124 /// 125 /// 126 protected void Init( string strName ) 127 { 128 //if (lngSize <= 0 || lngSize > 0x00800000) lngSize = 0x00800000; 129 130 if ( !System.IO.File.Exists( strName ) ) throw new Exception( "未找到文件" ); 131 132 System.IO.FileInfo f = new System.IO.FileInfo( strName ); 133 134 m_FileSize = f.Length; 135 136 m_fHandle = File.Open( strName ); 137 138 if ( strName.Length > 0 ) 139 { 140 //创建文件映射 141 m_hSharedMemoryFile = CreateFileMapping( m_fHandle, IntPtr.Zero, ( uint )PAGE_READONLY, 0, ( uint )m_FileSize, "mdata" ); 142 if ( m_hSharedMemoryFile == IntPtr.Zero ) 143 { 144 m_bAlreadyExist = false; 145 m_bInit = false; 146 throw new Exception( "CreateFileMapping失败LastError=" + GetLastError().ToString() ); 147 } 148 else 149 m_bInit = true; 150 151 ////映射第一块文件 152 //m_pwData = MapViewOfFile(m_hSharedMemoryFile, FILE_MAP_READ, 0, 0, (uint)m_MemSize); 153 //if (m_pwData == IntPtr.Zero) 154 //{ 155 // m_bInit = false; 156 // throw new Exception("m_hSharedMemoryFile失败LastError=" + GetLastError().ToString()); 157 //} 158 159 } 160 } 161 /// 162 /// 获取高32位 163 /// 164 /// 165 /// 166 private static uint GetHighWord( UInt64 intValue ) 167 { 168 return Convert.ToUInt32( intValue >> 32 ); 169 } 170 /// 171 /// 获取低32位 172 /// 173 /// 174 /// 175 private static uint GetLowWord( UInt64 intValue ) 176 { 177 178 return Convert.ToUInt32( intValue & 0x00000000FFFFFFFF ); 179 } 180 181 /// 182 /// 获取下一个文件块 块大小为20M 183 /// 184 /// false 表示已经是最后一块文件 185 public uint GetNextblock() 186 { 187 if ( !this.m_bInit ) throw new Exception( "文件未初始化。" ); 188 //if ( m_offsetBegin + m_MemSize >= m_FileSize ) return false; 189 190 uint m_Size = GetMemberSize(); 191 if ( m_Size == 0 ) return m_Size; 192 193 // 更改缓冲区大小 194 m_MemSize = m_Size; 195 196 //卸载前一个文件 197 //bool l_result = UnmapViewOfFile( m_pwData ); 198 //m_pwData = IntPtr.Zero; 199 200 201 m_pwData = MapViewOfFile( m_hSharedMemoryFile, FILE_MAP_READ, GetHighWord( ( UInt64 )m_offsetBegin ), GetLowWord( ( UInt64 )m_offsetBegin ), m_Size ); 202 if ( m_pwData == IntPtr.Zero ) 203 { 204 m_bInit = false; 205 throw new Exception( "映射文件块失败" + GetLastError().ToString() ); 206 } 207 m_offsetBegin = m_offsetBegin + m_Size; 208 209 return m_Size; //创建成功 210 } 211 /// 212 /// 返回映射区大小 213 /// 214 /// 215 private uint GetMemberSize() 216 { 217 if ( m_offsetBegin >= m_FileSize ) 218 { 219 return 0; 220 } 221 else if ( m_offsetBegin + m_MemSize >= m_FileSize ) 222 { 223 long temp = m_FileSize - m_offsetBegin; 224 return ( uint )temp; 225 } 226 else 227 return m_MemSize; 228 } 229 230 /// 231 /// 关闭内存映射 232 /// 233 public void Close() 234 { 235 if ( m_bInit ) 236 { 237 UnmapViewOfFile( m_pwData ); 238 CloseHandle( m_hSharedMemoryFile ); 239 File.Close(); 240 } 241 } 242 243 /// 244 /// 从当前块中获取数据 245 /// 246 /// 数据 247 /// 起始数据 248 /// 数据长度,最大值=缓冲长度 249 /// 读取完成是否卸载缓冲区 250 /// 251 public void Read( ref byte[] bytData, int lngAddr, int lngSize, bool Unmap ) 252 { 253 if ( lngAddr + lngSize > m_MemSize ) 254 throw new Exception( "Read操作超出数据区" ); 255 if ( m_bInit ) 256 { 257 // string bb = Marshal.PtrToStringAuto(m_pwData);// 258 Marshal.Copy( m_pwData, bytData, lngAddr, lngSize ); 259 } 260 else 261 { 262 throw new Exception( "文件未初始化" ); 263 } 264 265 if ( Unmap ) 266 { 267 bool l_result = UnmapViewOfFile( m_pwData ); 268 if ( l_result ) 269 m_pwData = IntPtr.Zero; 270 } 271 } 272 273 /// 274 /// 从当前块中获取数据 275 /// 276 /// 数据 277 /// 起始数据 278 /// 数据长度,最大值=缓冲长度 279 /// 280 /// 281 /// 282 public void Read( ref byte[] bytData, int lngAddr, int lngSize ) 283 { 284 if ( lngAddr + lngSize > m_MemSize ) 285 throw new Exception( "Read操作超出数据区" ); 286 if ( m_bInit ) 287 { 288 Marshal.Copy( m_pwData, bytData, lngAddr, lngSize ); 289 } 290 else 291 { 292 throw new Exception( "文件未初始化" ); 293 } 294 } 295 296 /// 297 /// 从当前块中获取数据 298 /// 299 /// 缓存区偏移量 300 /// 数据数组 301 /// 数据数组开始复制的下标 302 /// 数据长度,最大值=缓冲长度 303 /// 304 /// 305 /// 返回实际读取值 306 public uint ReadBytes( int lngAddr, ref byte[] byteData, int StartIndex, uint intSize ) 307 { 308 if ( lngAddr >= m_MemSize ) 309 throw new Exception( "起始数据超过缓冲区长度" ); 310 311 if ( lngAddr + intSize > m_MemSize ) 312 intSize = m_MemSize - ( uint )lngAddr; 313 314 if ( m_bInit ) 315 { 316 IntPtr s = new IntPtr( ( long )m_pwData + lngAddr ); // 地址偏移 317 Marshal.Copy( s, byteData, StartIndex, ( int )intSize ); 318 } 319 else 320 { 321 throw new Exception( "文件未初始化" ); 322 } 323 324 return intSize; 325 } 326 327 /// 328 /// 写数据 329 /// 330 /// 数据 331 /// 起始地址 332 /// 个数 333 /// 334 private int Write( byte[] bytData, int lngAddr, int lngSize ) 335 { 336 if ( lngAddr + lngSize > m_MemSize ) return 2; //超出数据区 337 if ( m_bInit ) 338 { 339 Marshal.Copy( bytData, lngAddr, m_pwData, lngSize ); 340 } 341 else 342 { 343 return 1; //共享内存未初始化 344 } 345 return 0; //写成功 346 } 347 } 348 internal class FileReader 349 { 350 const uint GENERIC_READ = 0x80000000; 351 const uint OPEN_EXISTING = 3; 352 System.IntPtr handle; 353 354 [DllImport( "kernel32", SetLastError = true )] 355 public static extern System.IntPtr CreateFile( 356 string FileName, // file name 357 uint DesiredAccess, // access mode 358 uint ShareMode, // share mode 359 uint SecurityAttributes, // Security Attributes 360 uint CreationDisposition, // how to create 361 uint FlagsAndAttributes, // file attributes 362 int hTemplateFile // handle to template file 363 ); 364 365 [System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport( "kernel32", SetLastError = true )] 366 static extern bool CloseHandle 367 ( 368 System.IntPtr hObject // handle to object 369 ); 370 371 372 373 public IntPtr Open( string FileName ) 374 { 375 // open the existing file for reading 376 handle = CreateFile 377 ( 378 FileName, 379 GENERIC_READ, 380 0, 381 0, 382 OPEN_EXISTING, 383 0, 384 0 385 ); 386 387 if ( handle != System.IntPtr.Zero ) 388 { 389 return handle; 390 } 391 else 392 { 393 throw new Exception( "打开文件失败" ); 394 } 395 } 396 397 public bool Close() 398 { 399 return CloseHandle( handle ); 400 } 401 } 402 }
分页读取法(Paging)
另外一种高效读取文件的方法就是分页法,也叫分段法(Segmentation),对应的读取单位被称作页(Page)和段(Segment)。其基本思想是将整体数据分割至较小的粒度再进行处理,以便满足时间、空间和性能方面的要求。分页法的概念使用相当广泛,如嵌入式系统中的分块处理(Blocks)和网络数据的分包传输(Packages)。
在开始研究分页法前,先来看看在超大文件处理中,最为重要的问题:高速随机访问。桌面编程中,分页法通常应用于文字处理、阅读等软件,有时也应用在大型图片显示等方面。这类软件的一个特点就是数据的局部性,无论需要处理的文件有多么大,使用者的注意力(也可以称为视口ViewPort)通常只有非常局部的一点(如几页文档和屏幕大小的图片)。这就要求了接下来,我们要找到一种能够实现高速的随机访问,而这种访问效果还不能和文件大小有关(否则就失去了高速的意义)。事实上,以下我们研究的分页法就是利用了「化整为零」的方法,通过只读取和显示用户感兴趣的那部分数据,达到提升操作速度的目的。
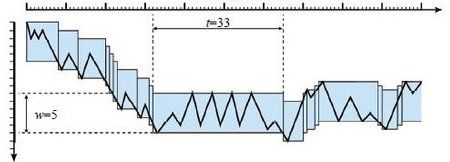
参考上图,假设计算机上有某文件F,其内容为「01234567890123456」(引号「」中的内容,不含引号,下同),文件大小为FileLength=17字节,以PageSize=3对F进行分页,总页数PageCount=6,得到页号为0~5的6个页面(图中页码=页号+1)。各页面所含数据如下表所示。
| 页号 | 页码 | 内容 | 至头部偏移量 (Hex) | 长度 |
| 0 | 1 | 012 | 00 01 02 | 3 |
| 1 | 2 | 345 | 03 04 05 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 | 678 | 06 07 08 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 | 901 | 09 0a 0b | 3 |
| 4 | 5 | 234 | 0c 0d 0e | 3 |
| 5 | 6 | 56 | 0f 10 | 2 |
可以看到,最后一页的长度为2(最后一页长度总是小于PageSize)。
当我们要读取「第n页」的数据(即页码=n)时,实际上读取的是页号PageNumber=n-1的内容。例如n=3时,PageNumber=2,数据为「678」,该页数据偏移量范围从0x06至0x08,长度为3(PageSize)。为便于讲述,在此约定:以下文字中,均只涉及页号,即PageNumber。
参考图2,设当PageNumber=x时,页x的数据范围为[offsetStart, offsetEnd],那么可以用如下的代码进行计算(C#2.0)。
1 offsetStart = pageNumber * pageSize; 2 3 if(offsetStart + pageSize < fileSize) 4 { 5 offsetEnd = offsetStart + pageSize; 6 } 7 else 8 { 9 offsetEnd = fileSize - 1; 10 }
我们常用的System.IO.FileStream类有两个重要的方法:Seek()和Read()。
1 // 将该流的当前位置设置为给定值。 2 public override long Seek ( 3 long offset, 4 SeekOrigin origin 5 ) 6 7 // 从流中读取字节块并将该数据写入给定缓冲区中。 8 public override int Read ( 9 [InAttribute] [OutAttribute] byte[] array, 10 int offset, 11 int count 12 )
利用这两个方法,我们可以指定每次读取的数据起始位置(offsetStart)和读取长度(offsetEnd - offsetStart),这样就可以读到任意指定的页数据。我们可以遍历读取所有页,这就相当于普通读取整个文件(实际操作中,一般不会有需求一次读取上GB的文件)。
1 指定PageNumber,读取页数据 2 byte[] getPage(Int64 pageNumber) 3 { 4 if (fileStream == null || !fileStream.CanSeek || !fileStream.CanRead) 5 return null; 6 7 if (pageNumber < 0 || pageNumber >= pageCount) 8 return null; 9 10 // absolute offileStreamet of read range 11 Int64 offsetStart = (Int64)pageNumber * (Int64)pageSize; 12 Int64 offsetEnd = 0; 13 14 if (pageNumber < pageCount - 1) 15 // not last pageNumber 16 offsetEnd = offsetStart + pageSize - 1; 17 else 18 // last pageNumber 19 offsetEnd = fileSize - 1; 20 21 byte[] tmp = new byte[offsetEnd - offsetStart + 1]; 22 23 fileStream.Seek(offsetStart, SeekOrigin.Begin); 24 int rd = fileStream.Read(tmp, 0, (Int32)(offsetEnd - offsetStart + 1)); 25 26 return tmp; 27 }
由于每次读取的数据长度(PageSize)远远小于文件长度(FileSize),所以使用分页法能够只读取程序需要的那部分数据,最大化提高程序的运行效率。下表是笔者在实验环境下对分页法读取文件的运行效率的测试。
CPU:Intel Core i3 380M @ 2.53GHz
内存:DDR3 2048MB x2
硬盘:TOSHIBA MK3265GSX (320 GB) @ 5400 RPM
为尽量保证测试质量,测试前系统进行了重装、硬盘整理等维护操作。该硬盘性能测试结果如下图所示。
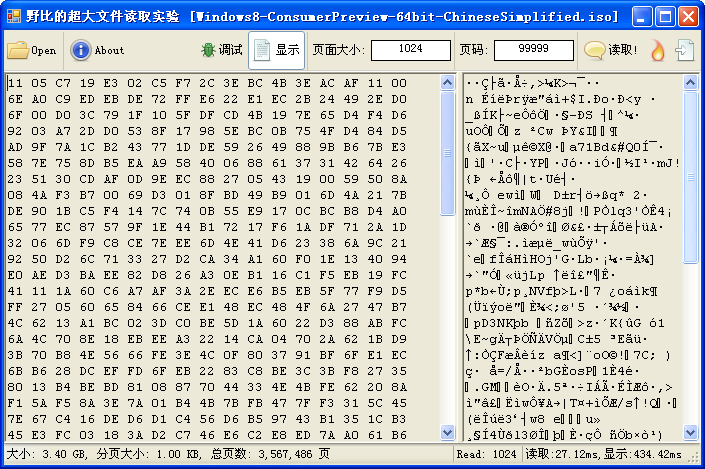
下面是为了测试分页法而制作的超大文件读取器界面截图,图中读取的是本次试验的用例之一Windows8消费者预览版光盘镜像(大小:3.40GB)。
本次测试选择了「大、中、小」3种规格的测试文件作为测试用例,分别为:
| # | 文件名 | 文件内容 | 大小(KB) |
| 1 | AlishaHead.png | Poser Pro 6贴图 | 11,611 |
| 2 | ubuntu-11.10-desktop-i386.iso | Ubuntu11.10桌面版镜像 | 711,980 |
| 3 | Windows8-ConsumerPreview-64bit-ChineseSimplified.iso | Windows8消费者预览版64位简体中文版镜像 | 3,567,486 |
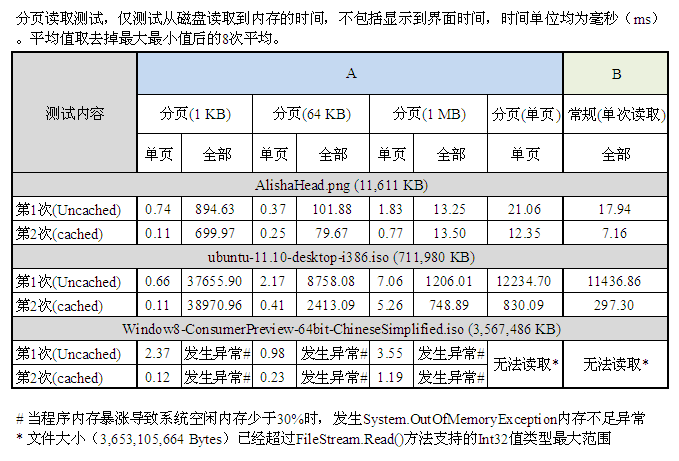
通过进行多次读取,采集到如下表A所示的文件读取数据结果。表中项目「分页(单页)」表示使用分页读取法,但设置页面大小为文件大小(即只有1页)进行读取。同样的,为了解分页读取的性能变化情况,使用普通读取方法(一次读取)采集到另一份数据结果,如下表B所示。
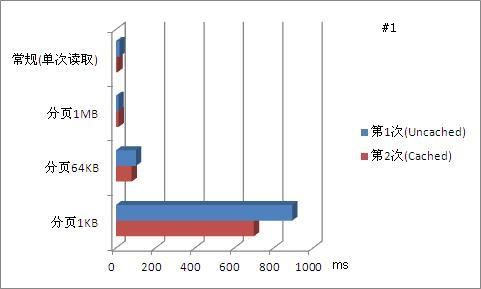
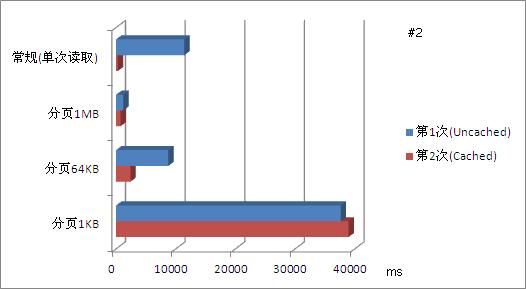
对用例#1,该用例大小仅11MB,使用常规(单次)读取方法,仅用不到20ms即将全部内容读取完毕。而当采用分页法,随着分页大小越来越小,文件被划分为更多的页面,尽管随机访问文件内容使得文件操作更加方便,但在读取整个文件的时候,分页却带来了更多的消耗。例如当分页大小为1KB时,文件被分割为11,611个页面。读取整个文件时,需要重复调用11,611次FileStream.Read()方法,增加了很多消耗,如下图所示。(图中数据仅为全文读取操作对比)
从图中可以看到,当分页尺寸过分的小(1KB)时,这种过度追求微粒化反而导致了操作性能下降。可以看到,即实现了微粒化,能够进行随机访问,同时仍保有一定量的操作性能,分页大小为64KB和1MB是不错的选择。实际上,上文介绍的MapViewOfFile函数的推荐分页大小正是64KB。
对用例#2,该用例大小为695.29MB,达到较大的尺寸,因此对读取缓存(cache)需求较高,同时也对合适的分页尺寸提出了要求。可以看到,和用例#1不同,当文件尺寸从11.34MB增加到近700MB时,分页尺寸随之相应的扩大,是提高操作性能的好方法(下图中1MB分页)。
对用例#3,该用例达到3.4GB大小,符合我们对超大文件的定义。通过前述2个用例的分析,可以推测,为获得最佳性能,分页大小需继续提高(比如从1MB提高到4MB)。由于本次试验时间仓促,考虑不周,未使用「边读取、边丢弃」的测试算法,导致分页读取用例#3的数据时,数据不断在内存中积累,最终引发System.OutOfMemoryException异常,使得分页读取完整文件这项测试不能正常完成。这一问题,需在下次的试验当中加以解决和避免。
引发System.OutOfMemoryException
尽管如此,通过试验,仍然可以清楚的看到,在常规文件(GB以下级别)操作中,分页法具有高度灵活性,但额外开销大,全文读取速度慢的问题。当操作超大文件(GB以上级别)时,分页法的优势开始显现。极高的数据读取灵活性带来的是和文件大小无关的随机页面访问速度(仅和分页大小有关)。在这个级别上,文件大小往往远远超过常规方法所能读取的最大值(0x7FFFFFFF),因此只有使用分页法,积少成多,才能完成读取完整文件的工作。
分页法使用简单,思路清晰,具有很高的灵活性和与文件长度无关的随机读取能力,最大支持文件大小理论上能够达到8,388,608 TB(Int64)。但同时它也具有额外开销大的特点,因此不适合小文件的操作。
通过扩展该方法,我们可以几乎在所有需要大量、重复、大范围算法处理的程序中加以应用分页法的「化整为零」思想,以减少计算粒度,实现计算的可持续进行。
分页法,以及上文提到的内存映射法,其实均早已出现多年,更是广泛应用于各个行业。笔者之所以仍旧撰写此文,一则锻炼自己的编程能力、语言归纳能力、文字写作能力,二则加深对方法的理解,通过试验得出的现象来深入方法的本质。鉴于笔者才疏学浅,在此妄言,有些词不达意,甚至谬误之处,还望各位读者多加批评、指正。
(全文完)
© Conmajia 2012