CacheDispatcher 缓存分发
cacheQueue只是一个优先队列,我们在start方法中,分析了CacheDispatcher的构成是需要cacheQueue,然后调用CacheDispatcher.start方法,我们看一下CacheDispatcher得到cacheQueue之后,到底做了什么。
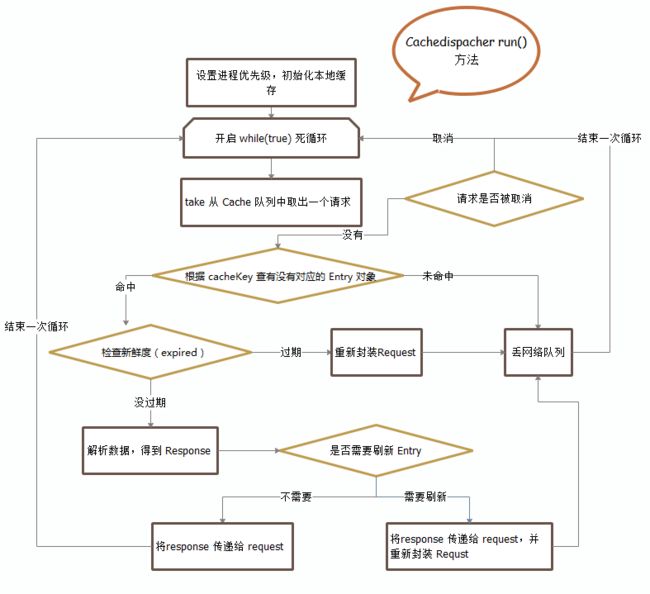
CacheQueue是一个继承于Thread的类,其start方法实质上是调用了run方法,我们看一下run方法所做的事情
@Override
public void run() {
if (DEBUG) VolleyLog.v("start new dispatcher");
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
// Make a blocking call to initialize the cache.
mCache.initialize();
while (true) {
try {
// Get a request from the cache triage queue, blocking until
// at least one is available.
final Request request = mCacheQueue.take();
request.addMarker("cache-queue-take");
// If the request has been canceled, don't bother dispatching it.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("cache-discard-canceled");
continue;
}
// Attempt to retrieve this item from cache.
Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey());
if (entry == null) {
request.addMarker("cache-miss");
// Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher.
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// If it is completely expired, just send it to the network.
if (entry.isExpired()) {
request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request.
request.addMarker("cache-hit");
Response response = request.parseNetworkResponse(
new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders));
request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed");
if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) {
// Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} else {
// Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response,
// but we need to also send the request to the network for
// refreshing.
request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
// Mark the response as intermediate.
response.intermediate = true;
// Post the intermediate response back to the user and have
// the delivery then forward the request along to the network.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Not much we can do about this.
}
}
});
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
}
}
}
我们可以看出其Run方法是一个无限循环的方法,退出的方式只有产生中断异常,也就是其thread对象调用了 interrupt()方法,这个方法是在requestQueue中的stop方法中调用了,上面我们已经分析了。
下面我们主要run方法的执行过程,取出队头的request,然后判断request是否被取消,如果没有就判断该request中取出entity,判断entity的状态,如果entity为空,则将该request放入NetWorkDispatcher中重新请求,如果entity过期了也将该request放入NetWorkDispatcher中重新请求。两者都没有,则从request中entity的内容,重新构造response,然后判断该entity是否需要刷新,不需要就直接Delivery该response,如果需要刷新,则将该response依旧发给用户,但是重新进行请求该刷新entity。
可以用下图的逻辑去看上面的过程
这里,涉及到了Http一个重要的点,缓存。我们看一下,entity中关于缓存是怎么设置的.
class Entry {
/** The data returned from cache. */
public byte[] data;
/** ETag for cache coherency. */
public String etag;
/** Date of this response as reported by the server. */
public long serverDate;
/** The last modified date for the requested object. */
public long lastModified;
/** TTL for this record. */
public long ttl;
/** Soft TTL for this record. */
public long softTtl;
/** Immutable response headers as received from server; must be non-null. */
public Map responseHeaders = Collections.emptyMap();
/** True if the entry is expired. */
boolean isExpired() {
return this.ttl < System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/** True if a refresh is needed from the original data source. */
boolean refreshNeeded() {
return this.softTtl < System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
这里的过期方法判断与是否需要刷新都是通过TTL与softTTL和现在时间对比而得到的。
缓存
这里说一下Volley的缓存机制,涉及到Http缓存,需要解析Http响应报文的头部。
public static Cache.Entry parseCacheHeaders(NetworkResponse response) {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Map headers = response.headers;
long serverDate = 0;
long lastModified = 0;
long serverExpires = 0;
long softExpire = 0;
long finalExpire = 0;
long maxAge = 0;
long staleWhileRevalidate = 0;
boolean hasCacheControl = false;
boolean mustRevalidate = false;
String serverEtag;
String headerValue;
headerValue = headers.get("Date");
if (headerValue != null) {
serverDate = parseDateAsEpoch(headerValue);
}
// 获取响应体的Cache缓存策略.
headerValue = headers.get("Cache-Control");
if (headerValue != null) {
hasCacheControl = true;
String[] tokens = headerValue.split(",");
for (String token : tokens) {
token = token.trim();
if (token.equals("no-cache") || token.equals("no-store")) {
// no-cache|no-store代表服务器禁止客户端缓存,每次需要重新发送HTTP请求
return null;
} else if (token.startsWith("max-age=")) {
// 获取缓存的有效时间
try {
maxAge = Long.parseLong(token.substring(8));
} catch (Exception e) {
maxAge = 0;
}
} else if (token.startsWith("stale-while-revalidate=")) {
try {
staleWhileRevalidate = Long.parseLong(token.substring(23));
} catch (Exception e) {
staleWhileRevalidate = 0;
}
} else if (token.equals("must-revalidate") || token.equals("proxy-revalidate")) {
// 需要进行新鲜度验证
mustRevalidate = true;
}
}
}
// 获取服务器资源的过期时间
headerValue = headers.get("Expires");
if (headerValue != null) {
serverExpires = parseDateAsEpoch(headerValue);
}
// 获取服务器资源最后一次的修改时间
headerValue = headers.get("Last-Modified");
if (headerValue != null) {
lastModified = parseDateAsEpoch(headerValue);
}
// 获取服务器资源标识
serverEtag = headers.get("ETag");
// 计算缓存的ttl和softTtl
if (hasCacheControl) {
softExpire = now + maxAge * 1000;
finalExpire = mustRevalidate
? softExpire
: softExpire + staleWhileRevalidate * 1000;
} else if (serverDate > 0 && serverExpires >= serverDate) {
// Default semantic for Expire header in HTTP specification is softExpire.
softExpire = now + (serverExpires - serverDate);
finalExpire = softExpire;
}
Cache.Entry entry = new Cache.Entry();
entry.data = response.data;
entry.etag = serverEtag;
entry.softTtl = softExpire;
entry.ttl = finalExpire;
entry.serverDate = serverDate;
entry.lastModified = lastModified;
entry.responseHeaders = headers;
return entry;
}
这里设计到缓存,就要先得到Http的cache-control的headervalue,如果是no-cahce||no-store就不需要再处理缓存,虽然on-cache在浏览器那边还是保存了请求的资源,但这里去没有处理。如果headervalue中有MaxAge,这个值是判断缓存存在的有效时间。如果headervalue中有stale-while-revalidate,这个值是缓存过期的可用时间,即使缓存过期,在stale-while-revalidate时间内依旧可用。如果headervalue中有must-revalidate就意味着
从必须再验证缓存的新鲜度,然后再用。
然后继续解析header与缓存有关的内容,如Expires(这是一个不推荐的标签),Last-Modified(最近被修改的时间),ETag(服务器资源标识)。
然后如果有缓存控制就计算缓存的TTL与SoftTTL,SoftTTL就是softExpire,其值就是maxAge + 当前时间,而TTL是finalTTL其值是 先判断是否过期就再验证,如果是的话,其值就是softExpire,如果不是的话,其值就是softExpire加上staleWhileRevalidate(缓存过期有效时间)。
如果没有缓存控制,softExpire = now + (serverExpires - serverDate);
所以,说回上面,CacheQueue中缓存的判断,isExpire就是判断finalTTL是否超过当前时间,而refreshNeeded则是判断softExpire是否超过当前时间。