霍夫直线变换介绍

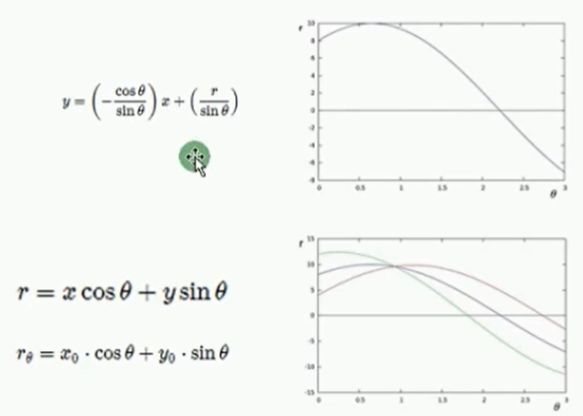

霍夫圆检测
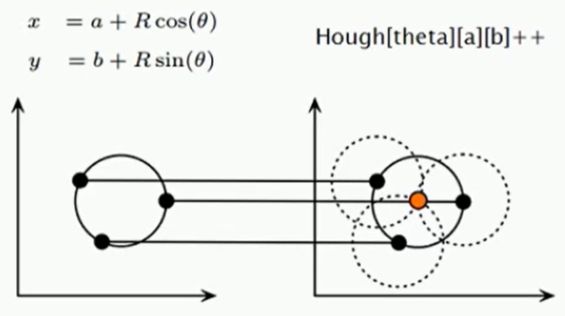


现实中:

example
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
# 关于霍夫变换的相关知识可以看看这个博客:https://blog.csdn.net/kbccs/article/details/79641887
def line_detection(image):
gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize=3)
# cv2.HoughLines()返回值就是(ρ,θ)。ρ 的单位是像素,θ 的单位是弧度。
# 这个函数的第一个参数是一个二值化图像,所以在进行霍夫变换之前要首先进行二值化,或者进行 Canny 边缘检测。
# 第二和第三个值分别代表 ρ 和 θ 的精确度。第四个参数是阈值,只有累加其中的值高于阈值时才被认为是一条直线,
# 也可以把它看成能 检测到的直线的最短长度(以像素点为单位)。
lines = cv.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi/180, 200)
for rho, theta in lines[0]:
a = np.cos(theta)
b = np.sin(theta)
x0 = a * rho
y0 = b * rho
x1 = int(x0 + 1000*(-b))
y1 = int(y0 + 1000*(a))
x2 = int(x0 - 1000*(-b))
y2 = int(y0 - 1000*(a))
cv.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv.imshow("line_detection", image)
def line_detection_possible_demo(image):
gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize=3)
minLineLength = 100
maxLineGap = 10
lines = cv.HoughLinesP(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, 100, minLineLength, maxLineGap)
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in lines[0]:
cv.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv.imshow('hough_lines', image)
# Hough Circle 在xy坐标系中一点对应Hough坐标系中的一个圆,xy坐标系中圆上各个点对应Hough坐标系各个圆,
# 相加的一点,即对应xy坐标系中圆心
# 现实考量:Hough圆对噪声比较敏感,所以做hough圆之前要中值滤波,
# 基于效率考虑,OpenCV中实现的霍夫变换圆检测是基于图像梯度的实现,分为两步:
# 1. 检测边缘,发现可能的圆心候选圆心开始计算最佳半径大小
# 2. 基于第一步的基础上,从
def detection_circles_demo(image):
dst = cv.pyrMeanShiftFiltering(image, 10, 100) # 均值迁移,sp,sr为空间域核与像素范围域核半径
gray = cv.cvtColor(dst, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
"""
. @param image 8-bit, single-channel, grayscale input image.
. @param circles Output vector of found circles. Each vector is encoded as 3 or 4 element
. floating-point vector \f$(x, y, radius)\f$ or \f$(x, y, radius, votes)\f$ .
. @param method Detection method, see #HoughModes. Currently, the only implemented method is #HOUGH_GRADIENT
. @param dp Inverse ratio of the accumulator resolution to the image resolution. For example, if
. dp=1 , the accumulator has the same resolution as the input image. If dp=2 , the accumulator has
. half as big width and height.
累加器图像的分辨率。这个参数允许创建一个比输入图像分辨率低的累加器。
(这样做是因为有理由认为图像中存在的圆会自然降低到与图像宽高相同数量的范畴)。
如果dp设置为1,则分辨率是相同的;如果设置为更大的值(比如2),累加器的分辨率受此影响会变小(此情况下为一半)。
dp的值不能比1小。
. @param minDist Minimum distance between the centers of the detected circles. If the parameter is
. too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one. If it is
. too large, some circles may be missed.
该参数是让算法能明显区分的两个不同圆之间的最小距离。
. @param param1 First method-specific parameter. In case of #HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the higher
. threshold of the two passed to the Canny edge detector (the lower one is twice smaller).
用于Canny的边缘阀值上限,下限被置为上限的一半。
. @param param2 Second method-specific parameter. In case of #HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the
. accumulator threshold for the circle centers at the detection stage. The smaller it is, the more
. false circles may be detected. Circles, corresponding to the larger accumulator values, will be
. returned first.
累加器的阀值。
. @param minRadius Minimum circle radius.
最小圆半径
. @param maxRadius Maximum circle radius. If <= 0, uses the maximum image dimension. If < 0, returns
. centers without finding the radius.
最大圆半径。
"""
circles = cv.HoughCircles(gray, cv.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 20, param1=40, param2=30, minRadius=0, maxRadius=0)
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
print(circles.shape)
for i in circles[0,:]: # draw the outer circle
cv.circle(image, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0, 255, 0), 2) # draw the center of the circle
cv.circle(image, (i[0], i[1]), 2, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv.imshow('detected circles', image)
def main():
src = cv.imread("../images/sudoku.png")
cv.imshow("demo",src)
line_detection(src)
# line_detection_possible_demo(src)
# img = cv.imread("../images/circle.png")
# detection_circles_demo(img)
cv.waitKey(0) # 等有键输入或者1000ms后自动将窗口消除,0表示只用键输入结束窗口
cv.destroyAllWindows() # 关闭所有窗口
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()






