同步文章 spring bean初始化过程 ,欢迎关注【码农戏码】公众号
从这个简单的代码深入,使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext看一下spring bean的初始化过程
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);
MessagePrinter printer = context.getBean(MessagePrinter.class);
printer.printMessage();
}
设置一个断点,看一下调用过程
bean创建
第一个方法进入AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的构造函数
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
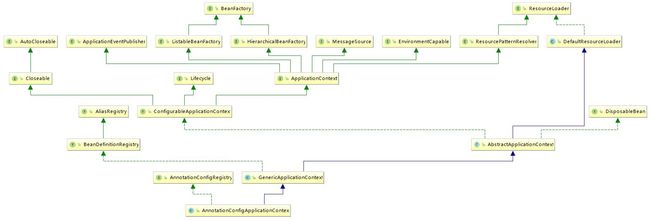
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的类结构
在this()的构造函数里面,定义了两个变量,是用来加载BeanDefinition的,具体使用哪个,就看使用的是传入的参数是什么类型就使用哪个构造函数。
比如我们的例子传入的是class,那就使用的reader
public void register(Class... annotatedClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(annotatedClasses, "At least one annotated class must be specified");
this.reader.register(annotatedClasses);
}
如果传入的是包名,那就使用的是scanner
public void scan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
this.scanner.scan(basePackages);
}
看下这儿使用的reader.register()
public void register(Class... annotatedClasses) {
for (Class annotatedClass : annotatedClasses) {
registerBean(annotatedClass);
}
}
/**
* Register a bean from the given bean class, deriving its metadata from
* class-declared annotations.
* @param annotatedClass the class of the bean
* @param name an explicit name for the bean
* @param qualifiers specific qualifier annotations to consider,
* in addition to qualifiers at the bean class level
*/
public void registerBean(Class annotatedClass, String name, Class... qualifiers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
//真正注册bean信息
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
这个方法的作用,跟注释表达的意思是一样的,从bean class中提取meta data信息。这儿有几个类信息提取类
BeanDefinition
A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values, constructor argument values, and further information supplied by concrete implementations.
BeanDefinitionHolder
Holder for a BeanDefinition with name and aliases.
//BeanDefinitionReaderUtils
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
//这儿就到了DefaultListableBeanFactory里面
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory 它包含了基本Spirng IoC容器所具有的重要功能,开发时不论是使用BeanFactory系列还是ApplicationContext系列来创建容器基本都会使用到DefaultListableBeanFactory类,
可以这么说,在spring中实际上把它当成默认的IoC容器来使用
所有bean的信息都保存在DefaultListableBeanFactory中
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(256);
/** List of bean definition names, in registration order */
private volatile List beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList(256);
上面的registerBean只才注册了一个主类,那别的bean是什么时候注册的呢?
第二步进入到AbstractApplicationContext的refresh(),一大串方法调用,看得头晕了。挑选重要的方法再单独注释
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
//这个就是做准备工作,很简单的变量初始化
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refreshing " + this);
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet();
}
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
看第三个方法是finishBeanFactoryInitialization()
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory){
.
.
.
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
这个方法,就是初始化非延迟加载的单例bean。
下一步就到了DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
//非抽象,非延迟加载的单例类
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
//get方法中进行创建
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
getBean的具体执行,到了AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean方法中
protected T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
//从map中取beanObject
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
.
.
.
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
//单例类开始创建了
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory 再到AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBeanInstance()
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Need to determine the constructor...
//有没有构造函数,有构造函数,使用构造函数创建
Constructor[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
//没有构造函数,直接create
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction没有使用cglib方式,直接使用SimpleInstantiationStrategy.instantiate()
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (bd.getMethodOverrides().isEmpty()) {
Constructor constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction>() {
@Override
public Constructor run() throws Exception {
return clazz.getDeclaredConstructor((Class[]) null);
}
});
}
else {
//取到构造函数
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor((Class[]) null);
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
//根据构造函数创建bean
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
//BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse)
public static T instantiateClass(Constructor ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
//通过构造函数,最原始的创建方式
return ctor.newInstance(args);
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
这个创建过程,它的原理很简单,无非就是把一个Bean创建后,放到一个以beanname作为key的map里面。
单例类是只创建一次,放到map中;而原型类需要每次都去创建一个新的
但现实比理论复杂得多,有很多的附加增强,导致了代码很复杂。
需要先把握核心点,抽丝剥茧
属性注入
对调用链进行分析,大体的流程是
- 创建bean
- 找到@Autowired的对象
- 创建注入对象,并赋值
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
//创建bean对象
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
//这儿进一步丰富BeanDefinition,提取bean的属性,方法信息进行
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
.
.
.
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
到了AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class beanType, String beanName) {
if (beanType != null) {
//查找@Autowired注解的元元素
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
//把这个metadata注册进beanDefinition
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
}
看看查找@Autowired注解元素
private AnnotationAttributes findAutowiredAnnotation(AccessibleObject ao) {
if (ao.getAnnotations().length > 0) {
for (Class type : this.autowiredAnnotationTypes) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(ao, type);
if (attributes != null) {
return attributes;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private final Set> autowiredAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.info("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
对@Autowired元素的赋值
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//赋值行为
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
到AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor里,这个BeanPostProcessor会有很多,这个以后再说
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeanCreationException {
//找到@Autowired的元元素
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
// #InjectionMetadata
public void inject(Object target, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection elementsToIterate =
(this.checkedElements != null ? this.checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//循环每个@Autowired的元素
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
到具体inject方法
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#AutowiredMethodElement#inject()
protected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
//具体的@Autowired方法
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
arguments = new Object[paramTypes.length];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[paramTypes.length];
Set autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(paramTypes.length);
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
//获取到被注入的bean
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
看下resolveDependency()
到了DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency()
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, String beanName,
Set autowiredBeanNames, TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
Class type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
Map matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(type, matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
return (instanceCandidate instanceof Class ?
//这儿又是调用beanFactory.getBean(),又到getBean的流程了
descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this) : instanceCandidate);
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
总结
总结一下,没有总结归纳,就没有结果,也就没有再进一步的基础。
主要就是两方面的一个宏观认识
- bean的创建
IOC就是一个bean的集合,bean的创建也由他负责,那么什么时候创建,怎么创建bean?
需要考虑bean的scope,一种singleton,一种prototype;还有是延迟加载属性
singleton就是只创建一次,会放到一个map中,以便下次使用;prototype就是每次都创建一个新的实例
- bean的属性注入
也一样,什么时候注入,怎么注入
在创建bean之后,先找到需要注入的属性,也就是@Autowired注解的方法,或者属性
方法就需要调用,属性就需要修改值
整体的思路很简单,只是为了满足丰富的功能,以及符合设计原则,代码复杂得多。还需要抽丝剥茧,一层一层深入