导出音视频文件
要读取和写入视听asset,必须使用AVFoundation框架中的导出api。AVAssetExportSession类仅是一个简单的导出的接口,例如修改文件格式或者修剪资源的长度。想要更多的导出需求,我们需要是用AVAssetReader类和AVAssetWriter类
如果想要对asset中的内容操作,那么使用AVAssetReader类。例如,读取asset的track以产生波形的只管表示。要从样本缓冲区或者静止图像等媒体生成asset,使用AVAssetWriter类
注意:asset的读取和编写不能用于实时处理。实际上,AVAssetReader不能用于http实时流等实时源读取。但是,我们可以使用AVAssetWriter对实时数据(例如AVCaptureOutput对象)进行处理。我们需要设置expectsMediaDataInRealTime=yes。对于非实时性源数据,将此属性设置为yes,将导致文件无法正确存取。
读取asset
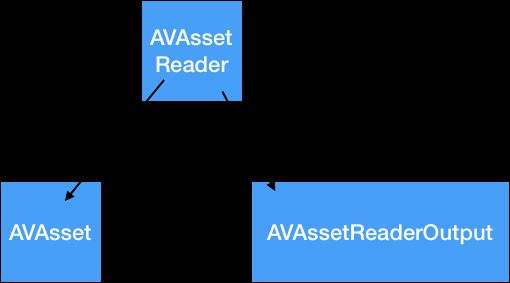
每个AVAssetReader对象一次只能与一个asset相关联,但是asset可以包含多个track。因此,在开始读取asset之前,我们必须要将AVAssetReaderOutput类的具体子类分配给AVAssetReader对象,以便配置媒体数据的读取方式。AVAssetReaderOutput基类有三个具体的子类,可以满足读取asset的要求。他们是AVAssetReaderTrackOutput,AVAssetReaderAudioMixOutput和AVAssetReaderVideoCompositionOutput。
具体关系如图
创建asset的阅读器 -AVAssetReader
NSError *outError;
AVAsset *someAsset = <#AVAsset that you want to read#>;
AVAssetReader *assetReader = [AVAssetReader assetReaderWithAsset:someAsset error:&outError];
BOOL success = (assetReader != nil)
注意:这里必须检测AVAssetReader实例对象是否真正的生成。error包含没有生成的错误信息
设置 AVAssetReaderOutput
创建AVAssetReader后,我们应该设置一个输出。当我们设置输出后,确保alwaysCopiesSampleData属性是NO。通过这种方式,我们可以获得性能改进的好处。
如果只想从一个或者多个track读取媒体数据,并转换数据为其他格式,那么我们应该使用AVAssetReaderTrackOutput类,该类可以从asset中读取每个AVAssetTrack对象。如果想压缩一个音频track成 linear pcm,我们应该如下设置
AVAsset *localAsset = assetReader.asset;
// Get the audio track to read.
AVAssetTrack *audioTrack = [[localAsset tracksWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeAudio] objectAtIndex:0];
// Decompression settings for Linear PCM
NSDictionary *decompressionAudioSettings = @{ AVFormatIDKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kAudioFormatLinearPCM] };
// Create the output with the audio track and decompression settings.
AVAssetReaderOutput *trackOutput = [AVAssetReaderTrackOutput assetReaderTrackOutputWithTrack:audioTrack outputSettings:decompressionAudioSettings];
// Add the output to the reader if possible.
if ([assetReader canAddOutput:trackOutput])
[assetReader addOutput:trackOutput];
注意,这里要是把audioSettings传递为nil,那么就是告诉assetReader以最方便的未压缩格式返回样本。
视频合成输出的行为方式大致相同:我们可以使用AVVideoComposition对象从asset中读取多个track。从多个AVVideoComposition 的track中读取媒体数据并将其解压缩为ARGB。方式如下
AVVideoComposition *videoComposition = <#An AVVideoComposition that specifies how the video tracks from the AVAsset are composited#>;
// Assumes assetReader was initialized with an AVComposition.
AVComposition *composition = (AVComposition *)assetReader.asset;
// Get the video tracks to read.
NSArray *videoTracks = [composition tracksWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeVideo];
// Decompression settings for ARGB.
NSDictionary *decompressionVideoSettings = @{ (id)kCVPixelBufferPixelFormatTypeKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kCVPixelFormatType_32ARGB], (id)kCVPixelBufferIOSurfacePropertiesKey : [NSDictionary dictionary] };
// Create the video composition output with the video tracks and decompression setttings.
AVAssetReaderOutput *videoCompositionOutput = [AVAssetReaderVideoCompositionOutput assetReaderVideoCompositionOutputWithVideoTracks:videoTracks videoSettings:decompressionVideoSettings];
// Associate the video composition used to composite the video tracks being read with the output.
videoCompositionOutput.videoComposition = videoComposition;
// Add the output to the reader if possible.
if ([assetReader canAddOutput:videoCompositionOutput])
[assetReader addOutput:videoCompositionOutput];
读取asset的媒体数据
在设置所需的所有输出后开始读取asset,我们应该调用startReading方法。接下来,使用copyNextSampleBuffer方法从每个输出中单独检索媒体数据。要是使用单个输出启动assert reader并读取所有的媒体,请看下列例子:
// Start the asset reader up.
[self.assetReader startReading];
BOOL done = NO;
while (!done)
{
// Copy the next sample buffer from the reader output.
CMSampleBufferRef sampleBuffer = [self.assetReaderOutput copyNextSampleBuffer];
if (sampleBuffer)
{
// Do something with sampleBuffer here.
CFRelease(sampleBuffer);
sampleBuffer = NULL;
}
else
{
// Find out why the asset reader output couldn't copy another sample buffer.
if (self.assetReader.status == AVAssetReaderStatusFailed)
{
NSError *failureError = self.assetReader.error;
// Handle the error here.
}
else
{
// The asset reader output has read all of its samples.
done = YES;
}
}
}
写asset
AVAssetWriter 类可以将多个源的媒体数据写入指定文件格式的单个文件。我们不需要将AVAssetWriter和asset联系在一起,但是需要有输出文件与之对应。这是因为AVAssetWriter可以使用多个源写入媒体数据,因此我们必须要为每个单独的track创建AVAssetWriterInput对象。每一个AVAssetWriterInput对象都已CMSampleBufferRef对象的形式接受数据,如果想要追加数据到CVPixelBufferRef对象上,应该使用AVAssetWriterInputPixelBufferAdaptor类。
创建AVAssetWriter对象
创建AVAssetWriter对象,我们需要指定一个输出路径的url。
NSError *outError;
NSURL *outputURL = <#NSURL object representing the URL where you want to save the video#>;
AVAssetWriter *assetWriter = [AVAssetWriter assetWriterWithURL:outputURL
fileType:AVFileTypeQuickTimeMovie
error:&outError];
BOOL success = (assetWriter != nil);
设置asset的 输入源
使用AVAssetWriter对象可以写入媒体数据,我们必须至少设置一个输入源。例如,我们将媒体数据转换成了CMSampleBufferRef对象,那么我们只需要使用AVAssetWriterInput类即可。要设置将音频媒体数据压缩为128kbps aac 并将其连接到AVAssetWriter ,步骤如下
// Configure the channel layout as stereo.
AudioChannelLayout stereoChannelLayout = {
.mChannelLayoutTag = kAudioChannelLayoutTag_Stereo,
.mChannelBitmap = 0,
.mNumberChannelDescriptions = 0
};
// Convert the channel layout object to an NSData object.
NSData *channelLayoutAsData = [NSData dataWithBytes:&stereoChannelLayout length:offsetof(AudioChannelLayout, mChannelDescriptions)];
// Get the compression settings for 128 kbps AAC.
NSDictionary *compressionAudioSettings = @{
AVFormatIDKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC],
AVEncoderBitRateKey : [NSNumber numberWithInteger:128000],
AVSampleRateKey : [NSNumber numberWithInteger:44100],
AVChannelLayoutKey : channelLayoutAsData,
AVNumberOfChannelsKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInteger:2]
};
// Create the asset writer input with the compression settings and specify the media type as audio.
AVAssetWriterInput *assetWriterInput = [AVAssetWriterInput assetWriterInputWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeAudio outputSettings:compressionAudioSettings];
// Add the input to the writer if possible.
if ([assetWriter canAddInput:assetWriterInput])
[assetWriter addInput:assetWriterInput];
注意:如果要以存储的格式写入媒体数据,请在outputSettings传递nil。仅当使用fileType为AVFileTypeQuickTimeMovie初始化才传递为nil。
如果asset writer的input 可以选择性的包含一些元数据,或者分别使用元数据和transform属性为特定的track指定不同的transfrom。对于将数据源是一个视频track的asset writer的input,我们可以通过执行下列操作维护视频的原始transform。
AVAsset *videoAsset = <#AVAsset with at least one video track#>;
AVAssetTrack *videoAssetTrack = [[videoAsset tracksWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeVideo] objectAtIndex:0];
assetWriterInput.transform = videoAssetTrack.preferredTransform;
注意:metadata 和transform 属性要在启动AVAssetWriter之前开启。
将媒体数据写入到输出文件时,有时候可能需要分配像素缓冲区。因此,使用AVAssetWriterInputPixelBufferAdaptor类。为了获取最高效率,我们应该提供一个缓冲池。看下列代码
NSDictionary *pixelBufferAttributes = @{
kCVPixelBufferCGImageCompatibilityKey : [NSNumber numberWithBool:YES],
kCVPixelBufferCGBitmapContextCompatibilityKey : [NSNumber numberWithBool:YES],
kCVPixelBufferPixelFormatTypeKey : [NSNumber numberWithInt:kCVPixelFormatType_32ARGB]
};
AVAssetWriterInputPixelBufferAdaptor *inputPixelBufferAdaptor = [AVAssetWriterInputPixelBufferAdaptor assetWriterInputPixelBufferAdaptorWithAssetWriterInput:self.assetWriterInput sourcePixelBufferAttributes:pixelBufferAttributes];
所有的AVAssetWriterInputPixelBufferAdaptor和一个asset 的input关联。并且intput必须是AVMediaTypeVideo类型的媒体数据
编写媒体数据
当我们为AVAssetWriter配置所有的inputs 时,我们就可以编写媒体数据了。通过调用startWriting方法启动写入数据。然后需要调用startSessionAtSourceTime:方法来启动编写会话。每个媒体数据都有个时间范围,AVAssetWriter通过这个来一次编写input。看下列例子:
CMTime halfAssetDuration = CMTimeMultiplyByFloat64(self.asset.duration, 0.5);
[self.assetWriter startSessionAtSourceTime:halfAssetDuration];
//Implementation continues.
通过,要结束写的session,我们必须调用endSessionAtSourceTime方法。但是,如果我们写的session已经写到文件末尾了,只需要调用finishWriting即可。
// Prepare the asset writer for writing.
[self.assetWriter startWriting];
// Start a sample-writing session.
[self.assetWriter startSessionAtSourceTime:kCMTimeZero];
// Specify the block to execute when the asset writer is ready for media data and the queue to call it on.
[self.assetWriterInput requestMediaDataWhenReadyOnQueue:myInputSerialQueue usingBlock:^{
while ([self.assetWriterInput isReadyForMoreMediaData])
{
// Get the next sample buffer.
CMSampleBufferRef nextSampleBuffer = [self copyNextSampleBufferToWrite];
if (nextSampleBuffer)
{
// If it exists, append the next sample buffer to the output file.
[self.assetWriterInput appendSampleBuffer:nextSampleBuffer];
CFRelease(nextSampleBuffer);
nextSampleBuffer = nil;
}
else
{
// Assume that lack of a next sample buffer means the sample buffer source is out of samples and mark the input as finished.
[self.assetWriterInput markAsFinished];
break;
}
}
}];
重新编码assets
我们可以串联 AVAssetReader 和AVAssetWriter,将asset从一种表示转换成另一种表示。使用这些对象,我们可以比使用AVAssetExportSession对象更多的控制转换。例如,我们可以选择要在输出文件中表示那些轨道,指定自己的输出格式,或者在转换过程中修改asset。此过程的第一步是根据需要设置
AVAssetReader和AVAssetWriter 的input。当AVAssetReader和AVAssetWriter完全配置完毕后,,分别调用startReading和startWriting方法启动它们。看下列代码
NSString *serializationQueueDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ serialization queue", self];
// Create a serialization queue for reading and writing.
dispatch_queue_t serializationQueue = dispatch_queue_create([serializationQueueDescription UTF8String], NULL);
// Specify the block to execute when the asset writer is ready for media data and the queue to call it on.
[self.assetWriterInput requestMediaDataWhenReadyOnQueue:serializationQueue usingBlock:^{
while ([self.assetWriterInput isReadyForMoreMediaData])
{
// Get the asset reader output's next sample buffer.
CMSampleBufferRef sampleBuffer = [self.assetReaderOutput copyNextSampleBuffer];
if (sampleBuffer != NULL)
{
// If it exists, append this sample buffer to the output file.
BOOL success = [self.assetWriterInput appendSampleBuffer:sampleBuffer];
CFRelease(sampleBuffer);
sampleBuffer = NULL;
// Check for errors that may have occurred when appending the new sample buffer.
if (!success && self.assetWriter.status == AVAssetWriterStatusFailed)
{
NSError *failureError = self.assetWriter.error;
//Handle the error.
}
}
else
{
// If the next sample buffer doesn't exist, find out why the asset reader output couldn't vend another one.
if (self.assetReader.status == AVAssetReaderStatusFailed)
{
NSError *failureError = self.assetReader.error;
//Handle the error here.
}
else
{
// The asset reader output must have vended all of its samples. Mark the input as finished.
[self.assetWriterInput markAsFinished];
break;
}
}
}
}];
export 真是汇总demo
上面都是知识片段,看知识片段还不能完全了解具体的使用,我们下列就具体的编写一个demo来看看
demo的具体步骤如下
- 1.使用串行队列异步处理读取和写入的视听数据
- 2.初始化AVAssetReader对象,配置两个output,一个视频另一个音频
- 3.初始化AVASsetWriter对象,配置两个inputs,一个音频一个视频
- 4.使用AVAssetReader对象异步将获取的数据传输给AVASsetWriter对象
- 5.用dispatch goupe通知重新编码过程的完成。
- 6允许用户在开始后取消重新编码过程
强制引用属性
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVCaptureSession * captureSession;
@property (nonatomic,strong) dispatch_queue_t mainSerializationQueue;
@property (nonatomic,strong) dispatch_queue_t rwAudioSerializationQueue;
@property (nonatomic,strong) dispatch_queue_t rwVideoSerializationQueue;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVURLAsset *asset;
@property (nonatomic,strong) NSURL *outputURL;
@property (nonatomic,assign) BOOL cancelled;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVAssetReader *assetReader;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVAssetWriter *assetWriter;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVAssetReaderTrackOutput *assetReaderAudioOutput;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVAssetWriterInput *assetWriterAudioInput;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVAssetReaderTrackOutput *assetReaderVideoOutput;
@property (nonatomic,strong) AVAssetWriterInput *assetWriterVideoInput;
@property (nonatomic,strong) dispatch_group_t dispatchGroup;
@property (nonatomic,assign) BOOL audioFinished;
@property (nonatomic,assign) BOOL videoFinished;
-(AVURLAsset * )getAVAssetABC{
NSURL *fileURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"abc" withExtension:@"mp4"];
AVURLAsset * asset = [AVURLAsset URLAssetWithURL:fileURL options:nil];
return asset;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *path = [[[paths objectAtIndex:0]stringByAppendingPathComponent:[NSUUID UUID].UUIDString] stringByAppendingString:@".mov"];
self.path = path;
NSLog(@"%@",self.path);
// [self edit];
// [self capture];
[self readerWriter];
}
-(void)readerWriter{
NSString *serializationQueueDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ serialization queue", self];
// Create the main serialization queue.
self.mainSerializationQueue = dispatch_queue_create([serializationQueueDescription UTF8String], NULL);
NSString *rwAudioSerializationQueueDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ rw audio serialization queue", self];
// Create the serialization queue to use for reading and writing the audio data.
self.rwAudioSerializationQueue = dispatch_queue_create([rwAudioSerializationQueueDescription UTF8String], NULL);
NSString *rwVideoSerializationQueueDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ rw video serialization queue", self];
// Create the serialization queue to use for reading and writing the video data.
self.rwVideoSerializationQueue = dispatch_queue_create([rwVideoSerializationQueueDescription UTF8String], NULL);
self.asset = [self getAVAssetABC];
self.cancelled = NO;
self.outputURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:self.path];;
[self.asset loadValuesAsynchronouslyForKeys:@[@"tracks"] completionHandler:^{
// Once the tracks have finished loading, dispatch the work to the main serialization queue.
dispatch_async(self.mainSerializationQueue, ^{
// Due to asynchronous nature, check to see if user has already cancelled.
if (self.cancelled)
return;
BOOL success = YES;
NSError *localError = nil;
// Check for success of loading the assets tracks.
success = ([self.asset statusOfValueForKey:@"tracks" error:&localError] == AVKeyValueStatusLoaded);
if (success)
{
// If the tracks loaded successfully, make sure that no file exists at the output path for the asset writer.
NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
NSString *localOutputPath = [self.outputURL path];
if ([fm fileExistsAtPath:localOutputPath])
success = [fm removeItemAtPath:localOutputPath error:&localError];
}
if (success)
success = [self setupAssetReaderAndAssetWriter:&localError];
if (success)
success = [self startAssetReaderAndWriter:&localError];
if (!success)
[self readingAndWritingDidFinishSuccessfully:success withError:localError];
});
}];
}
- (BOOL)setupAssetReaderAndAssetWriter:(NSError **)outError
{
self.assetReader = [[AVAssetReader alloc] initWithAsset:self.asset error:outError];
BOOL success = (self.assetReader != nil);
if (success)
{
// If the asset reader was successfully initialized, do the same for the asset writer.
self.assetWriter = [[AVAssetWriter alloc] initWithURL:self.outputURL fileType:AVFileTypeQuickTimeMovie error:outError];
success = (self.assetWriter != nil);
}
if (success)
{
// If the reader and writer were successfully initialized, grab the audio and video asset tracks that will be used.
AVAssetTrack *assetAudioTrack = nil, *assetVideoTrack = nil;
NSArray *audioTracks = [self.asset tracksWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeAudio];
if ([audioTracks count] > 0)
assetAudioTrack = [audioTracks objectAtIndex:0];
NSArray *videoTracks = [self.asset tracksWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeVideo];
if ([videoTracks count] > 0)
assetVideoTrack = [videoTracks objectAtIndex:0];
///音频输入和输出
if (assetAudioTrack)
{
// If there is an audio track to read, set the decompression settings to Linear PCM and create the asset reader output.
NSDictionary *decompressionAudioSettings = @{ AVFormatIDKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kAudioFormatLinearPCM] };
self.assetReaderAudioOutput = [AVAssetReaderTrackOutput assetReaderTrackOutputWithTrack:assetAudioTrack outputSettings:decompressionAudioSettings];
[self.assetReader addOutput:self.assetReaderAudioOutput];
// Then, set the compression settings to 128kbps AAC and create the asset writer input.
AudioChannelLayout stereoChannelLayout = {
.mChannelLayoutTag = kAudioChannelLayoutTag_Stereo,
.mChannelBitmap = 0,
.mNumberChannelDescriptions = 0
};
NSData *channelLayoutAsData = [NSData dataWithBytes:&stereoChannelLayout length:offsetof(AudioChannelLayout, mChannelDescriptions)];
NSDictionary *compressionAudioSettings = @{
AVFormatIDKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC],
AVEncoderBitRateKey : [NSNumber numberWithInteger:128000],
AVSampleRateKey : [NSNumber numberWithInteger:44100],
AVChannelLayoutKey : channelLayoutAsData,
AVNumberOfChannelsKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInteger:2]
};
self.assetWriterAudioInput = [AVAssetWriterInput assetWriterInputWithMediaType:[assetAudioTrack mediaType] outputSettings:compressionAudioSettings];
[self.assetWriter addInput:self.assetWriterAudioInput];
}
if (assetVideoTrack)
{
// If there is a video track to read, set the decompression settings for YUV and create the asset reader output.
NSDictionary *decompressionVideoSettings = @{
(id)kCVPixelBufferPixelFormatTypeKey : [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kCVPixelFormatType_422YpCbCr8],
(id)kCVPixelBufferIOSurfacePropertiesKey : [NSDictionary dictionary]
};
self.assetReaderVideoOutput = [AVAssetReaderTrackOutput assetReaderTrackOutputWithTrack:assetVideoTrack outputSettings:decompressionVideoSettings];
[self.assetReader addOutput:self.assetReaderVideoOutput];
CMFormatDescriptionRef formatDescription = NULL;
// Grab the video format descriptions from the video track and grab the first one if it exists.
NSArray *videoFormatDescriptions = [assetVideoTrack formatDescriptions];
if ([videoFormatDescriptions count] > 0)
formatDescription = (__bridge CMFormatDescriptionRef)[videoFormatDescriptions objectAtIndex:0];
CGSize trackDimensions = {
.width = 0.0,
.height = 0.0,
};
// If the video track had a format description, grab the track dimensions from there. Otherwise, grab them direcly from the track itself.
if (formatDescription)
trackDimensions = CMVideoFormatDescriptionGetPresentationDimensions(formatDescription, false, false);
else
trackDimensions = [assetVideoTrack naturalSize];
NSDictionary *compressionSettings = nil;
// If the video track had a format description, attempt to grab the clean aperture settings and pixel aspect ratio used by the video.
if (formatDescription)
{
NSDictionary *cleanAperture = nil;
NSDictionary *pixelAspectRatio = nil;
CFDictionaryRef cleanApertureFromCMFormatDescription = CMFormatDescriptionGetExtension(formatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionExtension_CleanAperture);
if (cleanApertureFromCMFormatDescription)
{
cleanAperture = @{
AVVideoCleanApertureWidthKey : (id)CFDictionaryGetValue(cleanApertureFromCMFormatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionKey_CleanApertureWidth),
AVVideoCleanApertureHeightKey : (id)CFDictionaryGetValue(cleanApertureFromCMFormatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionKey_CleanApertureHeight),
AVVideoCleanApertureHorizontalOffsetKey : (id)CFDictionaryGetValue(cleanApertureFromCMFormatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionKey_CleanApertureHorizontalOffset),
AVVideoCleanApertureVerticalOffsetKey : (id)CFDictionaryGetValue(cleanApertureFromCMFormatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionKey_CleanApertureVerticalOffset)
};
}
CFDictionaryRef pixelAspectRatioFromCMFormatDescription = CMFormatDescriptionGetExtension(formatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionExtension_PixelAspectRatio);
if (pixelAspectRatioFromCMFormatDescription)
{
pixelAspectRatio = @{
AVVideoPixelAspectRatioHorizontalSpacingKey : (id)CFDictionaryGetValue(pixelAspectRatioFromCMFormatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionKey_PixelAspectRatioHorizontalSpacing),
AVVideoPixelAspectRatioVerticalSpacingKey : (id)CFDictionaryGetValue(pixelAspectRatioFromCMFormatDescription, kCMFormatDescriptionKey_PixelAspectRatioVerticalSpacing)
};
}
// Add whichever settings we could grab from the format description to the compression settings dictionary.
if (cleanAperture || pixelAspectRatio)
{
NSMutableDictionary *mutableCompressionSettings = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
if (cleanAperture)
[mutableCompressionSettings setObject:cleanAperture forKey:AVVideoCleanApertureKey];
if (pixelAspectRatio)
[mutableCompressionSettings setObject:pixelAspectRatio forKey:AVVideoPixelAspectRatioKey];
compressionSettings = mutableCompressionSettings;
}
}
// Create the video settings dictionary for H.264.
NSMutableDictionary *videos = (NSMutableDictionary *) @{
AVVideoCodecKey : AVVideoCodecH264,
AVVideoWidthKey : [NSNumber numberWithDouble:trackDimensions.width],
AVVideoHeightKey : [NSNumber numberWithDouble:trackDimensions.height]
};
NSMutableDictionary * videoSettings = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
[videoSettings setDictionary:videos];
// Put the compression settings into the video settings dictionary if we were able to grab them.
if (compressionSettings)
[videoSettings setObject:compressionSettings forKey:AVVideoCompressionPropertiesKey];
// Create the asset writer input and add it to the asset writer.
self.assetWriterVideoInput = [AVAssetWriterInput assetWriterInputWithMediaType:[assetVideoTrack mediaType] outputSettings:videoSettings];
[self.assetWriter addInput:self.assetWriterVideoInput];
}
}
return success;
}
- (BOOL)startAssetReaderAndWriter:(NSError **)outError
{
BOOL success = YES;
// Attempt to start the asset reader.
success = [self.assetReader startReading];
if (!success)
*outError = [self.assetReader error];
if (success)
{
// If the reader started successfully, attempt to start the asset writer.
success = [self.assetWriter startWriting];
if (!success)
*outError = [self.assetWriter error];
}
if (success)
{
// If the asset reader and writer both started successfully, create the dispatch group where the reencoding will take place and start a sample-writing session.
self.dispatchGroup = dispatch_group_create();
[self.assetWriter startSessionAtSourceTime:kCMTimeZero];
self.audioFinished = NO;
self.videoFinished = NO;
if (self.assetWriterAudioInput)
{
// If there is audio to reencode, enter the dispatch group before beginning the work.
dispatch_group_enter(self.dispatchGroup);
// Specify the block to execute when the asset writer is ready for audio media data, and specify the queue to call it on.
[self.assetWriterAudioInput requestMediaDataWhenReadyOnQueue:self.rwAudioSerializationQueue usingBlock:^{
// Because the block is called asynchronously, check to see whether its task is complete.
if (self.audioFinished)
return;
BOOL completedOrFailed = NO;
// If the task isn't complete yet, make sure that the input is actually ready for more media data.
while ([self.assetWriterAudioInput isReadyForMoreMediaData] && !completedOrFailed)
{
// Get the next audio sample buffer, and append it to the output file.
CMSampleBufferRef sampleBuffer = [self.assetReaderAudioOutput copyNextSampleBuffer];
if (sampleBuffer != NULL)
{
BOOL success = [self.assetWriterAudioInput appendSampleBuffer:sampleBuffer];
CFRelease(sampleBuffer);
sampleBuffer = NULL;
completedOrFailed = !success;
}
else
{
completedOrFailed = YES;
}
}
if (completedOrFailed)
{
// Mark the input as finished, but only if we haven't already done so, and then leave the dispatch group (since the audio work has finished).
BOOL oldFinished = self.audioFinished;
self.audioFinished = YES;
if (oldFinished == NO)
{
[self.assetWriterAudioInput markAsFinished];
}
dispatch_group_leave(self.dispatchGroup);
}
}];
}
if (self.assetWriterVideoInput)
{
// If we had video to reencode, enter the dispatch group before beginning the work.
dispatch_group_enter(self.dispatchGroup);
// Specify the block to execute when the asset writer is ready for video media data, and specify the queue to call it on.
[self.assetWriterVideoInput requestMediaDataWhenReadyOnQueue:self.rwVideoSerializationQueue usingBlock:^{
// Because the block is called asynchronously, check to see whether its task is complete.
if (self.videoFinished)
return;
BOOL completedOrFailed = NO;
// If the task isn't complete yet, make sure that the input is actually ready for more media data.
while ([self.assetWriterVideoInput isReadyForMoreMediaData] && !completedOrFailed)
{
// Get the next video sample buffer, and append it to the output file.
CMSampleBufferRef sampleBuffer = [self.assetReaderVideoOutput copyNextSampleBuffer];
if (sampleBuffer != NULL)
{
BOOL success = [self.assetWriterVideoInput appendSampleBuffer:sampleBuffer];
CFRelease(sampleBuffer);
sampleBuffer = NULL;
completedOrFailed = !success;
}
else
{
completedOrFailed = YES;
}
}
if (completedOrFailed)
{
// Mark the input as finished, but only if we haven't already done so, and then leave the dispatch group (since the video work has finished).
BOOL oldFinished = self.videoFinished;
self.videoFinished = YES;
if (oldFinished == NO)
{
[self.assetWriterVideoInput markAsFinished];
}
dispatch_group_leave(self.dispatchGroup);
}
}];
}
// Set up the notification that the dispatch group will send when the audio and video work have both finished.
dispatch_group_notify(self.dispatchGroup, self.mainSerializationQueue, ^{
BOOL finalSuccess = YES;
NSError *finalError = nil;
// Check to see if the work has finished due to cancellation.
if (self.cancelled)
{
// If so, cancel the reader and writer.
[self.assetReader cancelReading];
[self.assetWriter cancelWriting];
}
else
{
// If cancellation didn't occur, first make sure that the asset reader didn't fail.
if ([self.assetReader status] == AVAssetReaderStatusFailed)
{
finalSuccess = NO;
finalError = [self.assetReader error];
}
// If the asset reader didn't fail, attempt to stop the asset writer and check for any errors.
if (finalSuccess)
{
finalSuccess = [self.assetWriter finishWriting];
if (!finalSuccess)
finalError = [self.assetWriter error];
}
}
// Call the method to handle completion, and pass in the appropriate parameters to indicate whether reencoding was successful.
[self readingAndWritingDidFinishSuccessfully:finalSuccess withError:finalError];
});
}
// Return success here to indicate whether the asset reader and writer were started successfully.
return success;
}