一、基本认知
一个在前端本地运行,可以存储json数据的server。
二、基本使用方式(两种)
1.全局使用
(1)安装
$ npm install -g json-server
(2)使用
【Step1】首先准备一个json文件,如:db.json。
内容形如(db.json):
{
"data1": [{
"id": "001",
"name": "Sherry",
"age": 24,
"friends": [{
"id": "100",
"name": "friend1"
}, {
"id": "200",
"name": "friend2"
}]
}, {
"id": "002",
"name": "Addy",
"age": 26
}],
"data2": {
"id": "003",
"name": "Jack",
"age": 25
},
"data3": [{
"id": "004",
"name": "Rebeca",
"age": 27
}]
}
【Step2】使用全局json-server命令,启动mock服务。这个mock服务,管理的数据,就是db.json。
$ json-server --watch --port 3001 db.json
输出类似以下内容,说明启动成功。
【Step3】使用json-server支持的功能,尝试进行数据访问
【举些栗子】(均为GET请求)
访问:http://localhost:3001/db
访问:http://localhost:3001/data1 (注意:这里不需要加/db,即不需要访问/db/data1)
访问:http://localhost:3001/data1/001
访问:http://localhost:3001/data1/Sherry (只能通过id过滤数据)
「注」
如果想根据其他属性进行过滤,采用:http://localhost:3001/data1?name=Sherry
这里,通过?传参过滤,得到的结果是一个数组。(id过滤,拿到的是一个对象)
即:拿到所有name=Sherry的项。即使结果只有一项,也会返回包含一个数据的数组。
访问:http://localhost:3001/data1/100
http://localhost:3001/data1/friends
http://localhost:3001/data1/friends/100
(只支持匹配第一层数据的id)
「注」(mark坑。请记住这里。)
这就造成了一个问题,如果需要用json-server模拟多层路由嵌套,无法通过db.json中数据的多层嵌套,达到模拟多层路由嵌套的目的。
换句话说,路由只能匹配到db.json这个json最外层的key值。也就是例子中的data1、data2、data3。
而里层的key值,都不会被路由匹配。
至于/data1/001这样的访问方式,相当于对/data1这个路由下的数据,进行一个过滤,类似于从列表页进入详情/编辑页。也就是说,/data1/001相当于在模拟/data1/:id这样的访问方式,访问的仍然是/data1这个接口。这和严格意义上的路由匹配,是不一样的。
访问:http://localhost:3001/data2
访问:http://localhost:3001/data2/003
(只有数组数据,支持id过滤。进一步印证了,这种访问方式类似于列表页进入详情/编辑页)
(3)其他类型请求(POST, PUT, PATCH ,DELETE),json-server的行为。
【举些栗子】
POST访问:/data1 (返回数组的接口)
行为:向/data1对应的数组添加新对象。
对象的属性取决于POST请求中body的设置。
如果body没有设置,json-server仍然会给/data1数组添加一个新对象,并赋予一个默认的id值,新对象有且仅有id这一个属性。
如果用户只设置了id以外的属性,json-server也会给新对象生成一个随机的id值。
POST/PUT/PATCH访问:/data2 (返回对象的接口:行为同访问/data1/001)
行为:修改/data2(或/data1/001)对应的对象属性。
「注」这里对象的id,不再是必需值。
DELETE访问:/data2 (返回的对象的接口)
行为:不进行删除。
DELETE访问:/data1/002 (请求删除数组列表的某一项)
行为:成功删除。
(4)自定义路由
可使用单独的route.json文件,进行自定义路由。(类似于代理转发,拦截请求,并重定向访问)
$ json-server --watch --routes route.json db.json
route.json形如:
{
"/data/*": "/$1", // /data/data1 ==> /data1
"/:resource/:id/show": "/:resource/:id", // /data1/001/show ==> /data1/001
"/data1/:name": "/data1?name=:name", // /data1/Sherry ==> /data1?name=Sherry
"/:anyArray\\?id=:id": "/:anyArray/:id" // /data1?id=002 ==> /data/002
}
(5)自定义配置文件
配置文件默认为json-server.json。形如:
{
"port": 3001,
"watch": true,
"static": "./public",
"read-only": false,
"no-cors": false,
"no-gzip": false,
"routes": "route.json"
}
启用:
# 默认使用:json-server.json配置文件
$ json-server --watch app.js
# 指定配置文件
$ json-server --watch -c jserver.json db.json
2.模块引用
(1)安装
$ npm install json-server
(2)创建mock-server.js文件(除此之外,与全局使用同理,需准备db.json或db.js文件)
mock-server.js形如:
const jsonServer = require('json-server');
const $db = require('./db'); // db.json。或返回db.json数据格式的,db.js文件
const server = jsonServer.create();
const middlewares = jsonServer.defaults();
const router = jsonServer.router($db);
server.use(router);
// Set default middlewares (logger, static, cors and no-cache)
server.use(middlewares);
// To handle POST, PUT and PATCH you need to use a body-parser
server.use(jsonServer.bodyParser);
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('JSON Server is running at 3001');
});
(3)使用
$ node mock-server.js
(4)自定义路由
使用:jsonServer.rewriter()
const jsonServer = require('json-server');
const $db = require('./db'); // db.json。或返回db.json数据格式的,db.js文件
const $routeHandler = require('./routeHandler'); // 引入自定义路由配置文件
const server = jsonServer.create();
const middlewares = jsonServer.defaults();
// 路由格式处理。需要加在 server.use(router) 前
server.use(jsonServer.rewriter($routeHandler($db)));
const router = jsonServer.router($db);
server.use(router);
// Set default middlewares (logger, static, cors and no-cache)
server.use(middlewares);
// To handle POST, PUT and PATCH you need to use a body-parser
server.use(jsonServer.bodyParser);
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('JSON Server is running at 3001');
});
「注」
routeHandler.js需要返回一个json对象,指明路由配置规则。参考route.json。
另外,可以把整个路由挂载到另外一个地址
server.use('/data', router);
即,所有/data/*的请求,都等同于/*请求。
(5)mock数据访问
与全局使用部分介绍规则完全相同。
(6)其他高级用法(mock-server.js)
json-server依赖express开发而来,可进行深度定制。
·自定义请求返回值
// 自定义post请求的返回值
server.post(filePath, (req, res) => {
var contentText = fs.readFileSync(filePath, 'utf-8');
res.send(contentText);
});
// 自定义get请求的返回值
server.get(filePath, (req, res) => {
var contentText = fs.readFileSync(filePath, 'utf-8');
res.send(contentText);
});
「注」
这里的filePath,不可以使用变量,需要指定具体值。如:/data/data1。
这里的server.post和server.get,相当于注册两个监听事件,监听指定的接口,并在相应接口,被前端访问时,执行回调函数。
·自定义输出内容
router.render = (req, res) => {
res.jsonp({
body: res.locals.data
});
}
·自定义用户校验
server.use((req, res, next) => {
if (isAuthorized(req)) { // add your authorization logic here
next();
// continue to JSON Server router
} else {
res.sendStatus(401);
}
});
【附】
json-server内置实现的过滤字段(用于属性字段的过滤,可直接使用)
「注」过滤字段,只针对数组数据。(毕竟只有数组需要过滤)
_gte: 大于等于
_lte: 小于等于
_ne: 不等于
_like: 包含
例:http://localhost:3001/data1?age_gte=20&age_lte=30
_page:访问第几页数据
_limit:一页多少条(默认一页10条)
_sort:设定排序字段
_order:设定排序的方式(升序:asc;降序:desc;默认升序)
例:http://localhost:3001/data1?_sort=age&_order=asc
_start:数据截取起始坐标
_end:数据截取终止坐标
_limit:截取数据条数
例:http://localhost:3001/data1?_start=0&_end=1
http://localhost:3001/data1?_start=0&_limit=2
「注」
截取指定的那些数组项。使用类似Array.slice。
q:全文搜索关键字
_embed:关联子实体。用来获取包含下级资源的数据。
_expand:关联父实体。用来获取包含上级资源的数据。
【详解 —— json-server的关系图谱(类似数据库级联)】
有如下db.json(comments中的项,关联了postId。所以posts是上级资源、comments是下级资源):
{
"posts": [
{ "id": 1, "title": "post的第一个title", "author": "typicode" },
{ "id": 2, "title": "post的第二个title", "author": "tangcaiye" }
],
"comments": [
{ "id": 1, "body": "some comment1111", "postId": 2 },
{ "id": 2, "body": "some comment2222", "postId": 1 }
],
"profile": { "name": "typicode" }
}
说明:
comments每个item的postId,指明当前comment与posts的关联。
即:第一条comment指明,它关联posts中id=2的item,也就是 { "id": 2, "title": "post的第二个title", "author": "tangcaiye" } 这个对象。注意,这里的命名方式,严格遵循字面匹配。期望和posts数组进行关联时,关联id的key,叫做postId,期望和tests数组进行关联,关联id的key,就叫做testId。
访问测试_embed:
http://localhost:3001/posts?_embed=comments
解析:
访问/posts接口,添加comments字段,初始化为空数组。并在comments接口中查找对应postId的数据项,添加到comments数组中。
如上例,_embed=comments,则给/posts接口的每一项,添加comments: [ ]。当comments接口的数据项指明了postId,如 { "id": 2, "body": "some comment2222", "postId": 1 },则在posts接口中,找到id等于1的item,即 { "id": 1, "title": "post的第一个title", "author": "typicode", "comments": [ ] },并把 { "id": 2, "body": "some comment2222", "postId": 1 } 这个的数据对象,添加到comments数组中去。
生成数据项:
{
"id": 1,
"title": "post的第一个title",
"author": "typicode",
"comments": [ {
"id": 2,
"body": "some comment2222",
"postId": 1
} ]
}
访问测试_expand:
http://localhost:3001/comments?_expand=post
解析:
访问/comments接口,并为它的每一个数据项,扩展url指明的字段。字段的值,取决于当前comment数据项的关联id值。
如上例,_expend=post,则给/comments的每一个包含postId的项,在posts中找到对应的post,添加到comment中。如:对 { "id": 1, "body": "some comment1111", "postId": 2 } 进行扩展。posts中,postId为2的项是 { "id": 2, "title": "post的第二个title", "author": "tangcaiye" },则扩展后:
生成数据项:
{
"id": 1,
"body": "some comment1111",
"postId": 2,
"post": {
"id": 2,
"title": "post的第二个title",
"author": "tangcaiye"
}
}
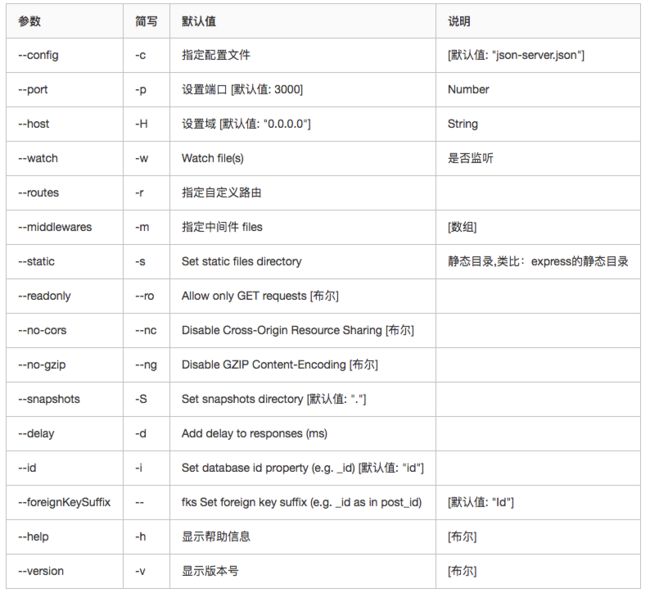
【其他】json-server相关启动参数
语法:json-server [options]
options列表:
#参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/fly_dragon/p/9186722.html
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010449453