序
本文主要解读下nginx lua module的主要方法和api。
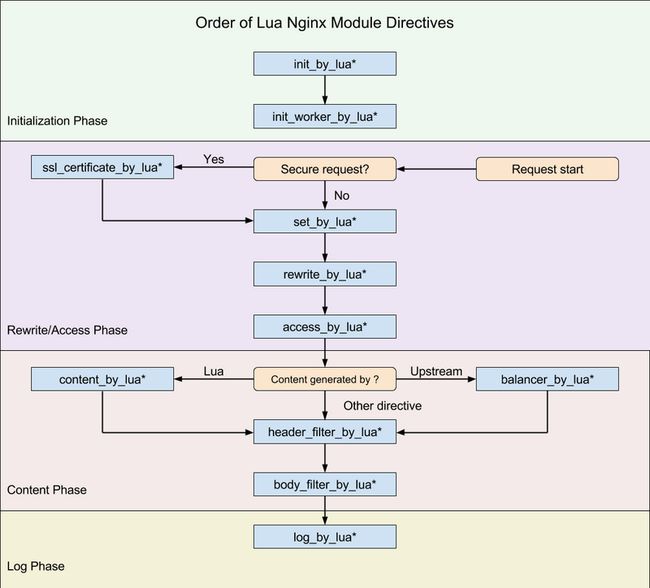
ngx_lua运行阶段
initialization phase
- init_by_lua
用在http模块,常用于全局变量的申请
- init_worker_by_lua
在每个nginx worker进程启动时调用指定的lua代码
rewrite / access phase
- set_by_lua:
设置一个变量,计算变量供后续使用 - rewrite_by_lua
可替代HttpRewriteModule的rewrite指令来使用的,优先级低于rewrite指令
- access_by_lua
可以用来修改请求参数
content phase
- content_by_lua
由ngx返回内容,而不走proxied后端
- header_filter_by_lua
可以用来修改后端response的header
- body_filter_by_lua
一般会在一次请求中被调用多次, 因为这是实现基于 HTTP 1.1 chunked 编码的所谓“流式输出”的。
log phase
- log_by_lua
在请求结束的时候运行,可以做些统计工作
nginx api for lua
ngx.cookie_time
ngx.cookie_time(ngx.time() + 60 * 30) -- 设置Cookie过期时间为30分钟
ngx.ctx
当前请求的上下文
ngx.decode_args
decode为table
local decoded_uri=ngx.decode_args("arg1=day1&arg2= monday");
print_t(decoded_uri);
function print_t(t)
for k, v in pairs(t) do
if type(v) == table then
ngx.say(k, ": ", table.concat(v), "
");
else
ngx.say(k, ": ", v, "
");
end
end
end
ngx.encode_args
将table编码为表单提交格式,a1=arg1&a2=arg2
ngx.say("encode args ", ngx.encode_args({a1="arg1", a2="arg2"}), "
");
ngx.eof
标识response结束,ngx.eof()只是结束响应流的输出,中断HTTP连接,后面的代码逻辑还会继续在服务端执行
ngx.req.read_body()
local uri_args = ngx.req.get_uri_args(1)
ngx.say(cjson.encode{result="refuse"})
ngx.eof()
ngx.escape_uri
uri编码
local fileName = "专辑列表.csv"
ngx.header.content_type = "text/csv;charset=utf-8"
ngx.header["Content-disposition"] = "attachment;filename=" .. ngx.escape_uri(fileName)
ngx.exec
内部重定向
location /foo {
content_by_lua '
return ngx.exec('/some-location', 'a=3&b=5&c=6');
';
}
ngx.exit
当传入的status >= 200(200即为ngx.HTTP_OK),ngx.exit() 会中断当前请求,并将传入的状态码(status)返回给nginx。
当传入的status == 0(0即为ngx.OK)则 ngx.exit() 会中断当前执行的phrase(ngx-lua模块处理请求的阶段,如content_by_lua*),进而继续执行下面的phrase。
对于 ngx.exit() 需要进一步注意的是参数status的使用,status可以传入ngx-lua所定义的所有的HTTP状态码常量(如:ngx.HTTP_OK、ngx.HTTP_GONE、ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR等)和两个ngx-lua模块内核常量(只支持NGX_OK和NGX_ERROR这两个,如果传入其他的如ngx.AGAIN等则进程hang住)。
文档中推荐的 ngx.exit() 最佳实践是同 return 语句组合使用,目的在于增强请求被终止的语义(return ngx.exit(...))。
if not ngx.var.arg_token then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Unauthorized")
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED)
end
配合使用return,增强退出语义,防止出错
ngx.flush
ngx.say("Hello, Lua!")
ngx.flush(true)
设置为true的话,则ngx.print或者ngx.say的内容等写入send buffer之后才返回
ngx.get_phase
返回当前的处理阶段,init, init_worker,
ssl_cert, set, rewrite, balancer, access, content, header_filter, body_filter, log, or
timer这几个之一
ngx.http_time
ngx.header['Content-Type'] = 'application/json; charset=utf-8';
ngx.header['Expires'] = ngx.http_time( ngx.time() + max_age );
ngx.say(ngx.http_time(1290079655))
-- yields "Thu, 18 Nov 2010 11:27:35 GMT"
ngx.is_subrequest
如果是subrequest则返回true
ngx.localtime
从NGINX's cache中返回yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss格式的时间
ngx.location.capture
用于子请求,返回: status, header, body, and truncated (a Boolean to represent if the body is truncated).
ngx.log
第一个参数是log基本(one of ngx.STDERR, ngx.EMERG, ngx.ALERT,ngx.CRIT, ngx.ERR, ngx.WARN, ngx.NOTICE, ngx.INFO, and ngx.DEBUG)
后续可以接多个参数来打印log
ngx.now
从NGINX's cache返回epoch time以来的毫秒数
ngx.now() 是有误差的,因为使用了nginx 自身的时间缓存。对于精度要求较高的计时,应使用下面的调用序列:
ngx.update_time()
local now = ngx.now()
值得一提的是,ngx.now() 只有毫秒精度。
ngx.parse_http_time
local time = ngx.parse_http_time("Thu, 18 Nov 2010 11:27:35 GMT")
if time == nil then
...
end
ngx.print
打印到response body.
ngx.say
打印到response body并换行
ngx.status
http status状态码
ngx.time
从nginx cached返回epoch time以来的秒数(no syscall involved unlike Lua's date library).
ngx.today
从NGINX's cache返回当前日期,格式 yyyy-mm-dd
ngx.unescape_uri
ngx.say(ngx.unescape_uri("b%20r56+7"))
-- 返回b r56 7
ngx.update_time
更新NGINX's time cache
ngx.utctime
从NGINX's cache返回UTC time,格式yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss
doc
- nginx基本配置与参数说明
- nginx配置文件说明
- nginx与lua的执行顺序和步骤说明
- ngx_lua用例说明
- ngx_lua 模块
- lua-nginx-module模块里ngx_lua的所有指令以及可用ngx所有方法
- 由一条OpenResty Error log谈谈ngx.exit与ngx.eof的区别
- ngx_Lua模块中的重定向