本文属于滑动内联动效系列的第一篇。仓库地址
滑动内联动效 指的是 在容器滑动的过程中,其子View对应展现出来的一些效果。而图片平行逆差效果,就是在容器滑动过程中,图片也跟着移动的效果。语言太苍白,直接上效果。
上面图片还带了透明度的变化,但这不是本文的描述范围。
想要提前看整体实现,请直接移步到github仓库
图片平行逆差效果早见于网络,常见思路有两种:
1- 继承滑动容器或者在滑动容器的监听器里做文章
比如ScrollParallexListview..xxRecyclerview..xxParallex等命名的,github上比较好找。这类实现适用性比较单一,换种滑动容器的时候可能就会失效或者bug一堆。而且实现较为复杂,动效改动/添加会比较麻烦。
2- 自定义ImageView
这类实现也是比较常见的实现方式,其优点是可移植性高,在很多地方只要用这个ImageView即可实现平行逆差效果。但是这种方式也具有一些缺点,a-裁剪,这种方式具有天生的缺陷,即当ImageView最初设置layoutparams,在不改变固有比例的情况下,其很可能会被裁剪,具体裁剪规则参见ScaleType属性。b-适用范围小,只适用于图片,特别是有一些其它动画,如缩放和透明度变化时。
本文思路--包装容器(container)
熟悉ScrollBy方法的童鞋知道,其实所有的View都是可滑动的,只是滑动容器(比如ListView)滑动时,动的是子View,非滑动容器(TextView)滑动时,动的是其文本内容。总体来看,所有的view都可滑动,滑动时,动的都是其内容。由此得到灵感,将ImageView放到一个非滑动容器(container)中,那么ImageView将不会被裁剪,而平行逆差效果,却能由这个container的滑动来实现。这样做,既会保留自定义ImageView的高的移植性,又能避免图片被裁剪,而且容器不只滑动,它还能缩放,透明度或者旋转等等效果,使得动画的添加也很方便。
注意:包装容器不应该是常规的滑动容器。
方案分析:
1 获得外面滑动容器的滑动事件。
因为是做滑动内联效果,那么理应得到滑动事件才行。一般的滑动监听接口是不行了,因为我们要做的是兼容多种滑动容器。此时,我们选用的是ViewTreeObserver.OnScrollChangedListener,这接口非常通用,几乎所有可滑动视图体系都会引起它的调用。有接口了,什么时候注册接口呢,当然是view添加到window时啦,此时view的方法onAttachedToWindow开始发挥作用。2 得到滑动容器的位置范围。
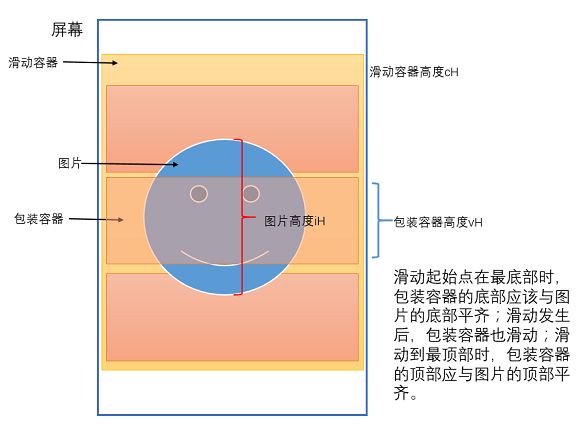
这个滑动容器可大可小,滑动内联效果肯定是与这个有关系的。假设有个点,刚好位于滑动容器的最下边。当滑动进行时,这个点便会跟着向下移动,当其到滑动容器最上边时,这个点刚好走了滑动容器的上下距离。这个过程,也代表了比较理想的内联动效的起始和最终位置。3 确定包装容器和图片的内联滑动
滑动开始了,也知道什么时候内联滑动开始了,那么包装容器和图片应该怎么内联呢。用个图片来标示吧,直观。
好了,方案分析完了。终于到上代码的时候了。
代码实现
- 图片需要保持自身比例,而且不能被容器大小限制或者裁剪,那么这个ImageView就需要重写下测量方法。整体比较简单,就是设定了水平滑动或者纵向滑动。其宽高由滑动方向和图片固有的宽高决定。
public class AdjointImageView extends ImageView {
private boolean isVertical = true;
public AdjointImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public AdjointImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public AdjointImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AdjointContainer);
isVertical = typedArray.getBoolean(R.styleable.AdjointContainer_isVertical, true);
typedArray.recycle();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (getDrawable() == null) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
return;
}
if (isVertical) {
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = width * getDrawable().getIntrinsicHeight() / getDrawable().getIntrinsicWidth();
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
} else {
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int width = height * getDrawable().getIntrinsicWidth() / getDrawable().getIntrinsicHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
}
}
- 重点,包装容器的实现
public class AdjointContainer extends RelativeLayout implements ViewTreeObserver.OnScrollChangedListener {
private boolean enableScrollParallax = true;
private int[] viewLocation = new int[2];//自身位置
//特效集合
private List mAdjointStyles = new ArrayList<>();
//滑动容器的范围,矩形
private Rect parentLocation = new Rect();//parent list rect
//方便获得滑动容器范围
private Locator mLocator;
public AdjointContainer(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public AdjointContainer(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public AdjointContainer(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
//为了使invalidate调用onDraw方法
setBackgroundColor(0x0000);
}
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
getViewTreeObserver().addOnScrollChangedListener(this);
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
getViewTreeObserver().removeOnScrollChangedListener(this);
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
}
//增加动效
public void addStyle(AdjointStyle aAdjointStyle) {
mAdjointStyles.add(aAdjointStyle);
}
public void removeStyle(AdjointStyle aAdjointStyle) {
mAdjointStyles.remove(aAdjointStyle);
}
public void clearStyles(){
mAdjointStyles.clear();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mLocator != null) {
parentLocation = mLocator.getLocation();
}
if (!enableScrollParallax || parentLocation==null||parentLocation.bottom == 0) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
return;
}
getLocationInWindow(viewLocation);
for (int i = 0; i < mAdjointStyles.size(); i++) {
mAdjointStyles.get(i).transform(this, canvas, viewLocation, parentLocation);
}
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
public void setLocator(Locator aLocator) {
mLocator = aLocator;
}
@Override
public void onScrollChanged() {
if (enableScrollParallax) {
invalidate();
requestLayout();
}
}
}
容器做的工作主要有,接收滑动事件,确定滑动位置,增/删动效,通知动效对象执行动效。而动效对象的添加,是通过策略模式和观察者模式来实现。
- 纵向平行逆差效果
public class VerticalMoveStyle implements AdjointStyle {
@Override
public void onAttachedToImageView(AdjointContainer view) {
}
@Override
public void onDetachedFromImageView(AdjointContainer view) {
}
@Override
public void transform(AdjointContainer aContainer, Canvas canvas, int[] viewLocation, Rect parentLocation) {
if (aContainer.getChildCount() != 1) {
return;
}
if (aContainer.getChildAt(0) instanceof AdjointImageView) {
ALog.single().ld("transform-begin");
AdjointImageView childView = (AdjointImageView) aContainer.getChildAt(0);
Drawable drawable = (childView).getDrawable();
int iWidth = drawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
int iHeight = drawable.getIntrinsicHeight();
int y = viewLocation[1];
int ptop = parentLocation.top;
int pbottom = parentLocation.bottom;
ALog.single().ld("parentLocation.bottom--" + parentLocation.bottom);
if (iWidth <= 0 || iHeight <= 0) {
return;
}
int vWidth = aContainer.getWidth() - aContainer.getPaddingLeft() - aContainer.getPaddingRight();
int vHeight = aContainer.getHeight() - aContainer.getPaddingTop() - aContainer.getPaddingBottom();
int dHeight = ScreenUtil.getScreenHeight(aContainer.getContext());
dHeight = dHeight < pbottom ? dHeight : pbottom;
if (iWidth * vHeight < iHeight * vWidth || iHeight > vHeight) {
// avoid over scroll
if (y < ptop - vHeight) {
y = ptop - vHeight;
} else if (y > dHeight) {
y = dHeight;
}
y = y - ptop;
ALog.single().ld("target y:" + y);
float imgScale = (float) vWidth / (float) iWidth;
float imgMaxMoveScope = Math.abs((iHeight * imgScale - vHeight));
int itemMaxMoveScope = pbottom - ptop - vHeight;
float translateY = -(imgMaxMoveScope * y / itemMaxMoveScope);
canvas.translate(0, translateY);
}
}
}
}
这个动效的实现思路基本就是上面那个图片的体现。
到这个时候,一个可移植性比较高的滑动平行逆差效果就实现了,简单简洁。怎么使用呢,还是上代码吧,一种相当简易的使用,放到ScrollView中。
----步骤 1
布局代码
......省略某些
...other view...
... ...
---步骤 2
获得滑动容器的位置信息,以Rect标示,并提供一个Locator来传递给AdjointContainer.省略了一些,就是onCreate方法中获得滑动容器的位置,提供给包装容器。
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements Locator...
mContainer1 = (AdjointContainer) findViewById(R.id.adcontainer1);
.. {
mScrollView.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mScrollView.getGlobalVisibleRect(mR);
mContainer1.setLocator(SecondActivity.this);
}
});
.. }
@Override
public Rect getLocation() {
return mR;
}
---步骤 3
创建AdjointStyle对象,并设置给容器。
AdjointStyle style= new VerticalMoveStyle().minScale(0.9f);
mContainer1.addStyle(style);
此时,滑动容器滑动时,图片也会滑动,产生逆差效果。