用多了python,基础常用的技能也不多,这里汇总下。
1. 数据类型转换
1.1. int <-> string
//convert int to string : s = str(int_value)
//convert string to int : int = int(str_value)
1.2. string <-> list
//convert string to list : l = list(str)
str0 = "asdf"
list0 = list(str0)
print list0 #['a','s','d','f']
str1 = "www.google.com"
list1 = str1.split(".")
print list1 #['www','google','com']
str2 = "i am yanan"
list2 = str2.split(" ")
print list2 #['i','am','yanan']
//convert list to string : s = "".join(list) 或 s = ".".join(list)
list0 = ['a','b','c']
str0 = "".join(list0)
print str0 #abcd
str1 = ".".join(list0)
print str1 #a.b.c.d
1.3. list <-> dictionary
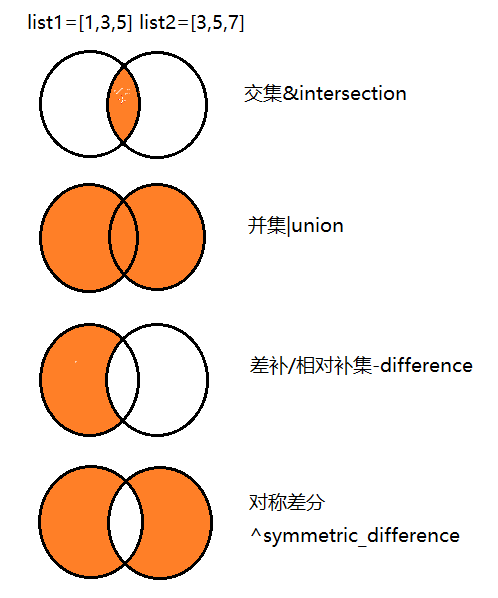
2. 集合:交集、并集、差补、对称差分
相比有序的列表,集合对象是无序的,已经是Python的基本数据类型,被创建的唯一方法是其工厂方法set()和frozenset(),分别对应可变集合set(可以添加或删除元素)和不可变集合frozenset。
list0 = [0,1,3,5,9]
list1 = [1,3,5]
list2 = [3,5,7]
0.list <-> set 列表和集合的互转
//convert list to set : set(list)
>>>s = set(list0)
>>>s
set([0,1,3,5,9])
//convert set to list : list(set)
>>>list(s)
[0,1,3,5,9]
1.操作符和内建方法实现交集、并集、差补、对称差分
1.1. 交集
>>>set(list1) & set(list2)
set([3,5])
>>>list(set(list1) & set(list2))
[3,5]
>>>list(set(list1).intersection(set(list2)))
[3,5]
1.2. 并集
>>>set(list1) | set(list2)
set([1,3,5,7])
>>>list(set(list1) | set(list2))
[1,3,5,7]
>>>list(set(list1).union(set(list2)))
[1,3,5,7]
1.3. 差补或相对补集(s-t指结果中元素只属于s不属于t)
list1 = [1,3,5]
list2 = [3,5,7]
list1相对于list2差1,list2相对于list1差7
>>>set(list1) - set(list2)
set([1])
>>>list(set(list1) - set(list2))
[1]
>>>list(set(list1).difference(set(list2)))
[1]
1.4. 对称差分
>>>set(list1) ^ set(list2)
set([1,7])
>>>list(set(list1) ^ set(list2))
[1,7]
>>>list(set(list1).symmetric_difference(set(list2)))
[1,7]
3. 特殊容器类型的模块:collections
collections模块自Python 2.4版本开始被引入,包含了dict、set、list、tuple以外的一些特殊的容器类型,分别是:
- OrderedDict类:排序字典,是字典的子类。引入自2.7。
- namedtuple()函数:命名元组,是一个工厂函数。引入自2.6。
- Counter类(***):为hashable对象计数,是字典的子类。引入自2.7。
- deque:双向队列。引入自2.4。
- defaultdict:使用工厂函数创建字典,使不用考虑缺失的字典键。引入自2.5。
文档参见:collections.Counter
//计数器Counter
from collections import Counter
>>>li = ['aa','aa','aa','bb','bb','cc']
>>>c = Counter(li)
>>>c
Counter({'aa':3,'bb':2,'cc':1})
>>>c_top_list = c.most_common(2)
>>>c_top_list
[('aa',3),('bb',2)]
>>>c_top_dict = dict(c_top_list)
>>>c_top_dict
{'aa':3,'bb':2}
>>>c_top_sorted_list = sorted(c_top_dict.items(),key=lambda item:item[1],reverse=True)
>>>c_top_sorted_list
[('aa',3),('bb',2)]
4. 文件或目录模块:os
import os
//列出文件夹中所有文件
files_list = []
if os.path.exists(dir_path):
files = os.listdir(dir_path)
files.sort()
for i in range(len(files)):
file_path = os.path.join(dir_path,files[i])
files_list.append(file_path)
print files_list #absolute path of all files in dir_path
//创建文件夹
if not os.path.exists(dir_path):
os.system('mkdir %s'%dir_path)
//取存在的非空的文件
if os.path.exists(file_path):
if os.path.getsize(file_path):#返回文件大小,如果文件不存在就返回错误
print 'file exists and is not empty.'
//区别文件几个路径
os.path.abspath(path) #返回绝对路径
os.path.dirname(path) #返回文件路径
os.path.basename(path) #返回文件名
//删除某种类型的文件-扩展名区别-
os.path.splitext(path) #分割路径,返回文件路径名和文件扩展名的元组
if os.path.splitext(file_path)[1] == '.txt' :
os.remove(file_path)
shutil:高级的文件操作模块-复制、删除等,对os的补充
import shutil
shutil.rmtree(dir_path) 递归删除一个目录以及目录内的所有内容
5. 获取命令行参数
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os
import time
import sys
'''some function description of current script'''
def method1():
code...
def main():
##some global paras
time_start = time.time()
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print 'no pe or se, no viruses or bacterias specified.'
sys.exit()
if sys.argv[1].startswith('-'):
option = sys.argv[1][1:]
if option == 'version':
print 'Version 1.0.0\n----------------'
if option == 'help':
print 'this is NGS analisis pipelines.\nMainly,for se or pe sequencing,viruses or bacterias identification.\n----------------'
if sys.argv[1] != '-se' and sys.argv[1]!= '-pe' and len(sys.argv) == 2:
print 'And,you need to resign the para as \'-pe\'or\'-se\'.'
sys.exit()
if sys.argv[1] == '-se' or sys.argv[1]== '-pe':
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
print 'you need to supply the para(\'-viruses\'or\'-bacterias\').'
sys.exit()
if sys.argv[2] != '-viruses' and sys.argv[2]!= '-bacterias' and len(sys.argv) == 3:
print 'you need to resign the para as \'-viruses\'or\'-bacterias\'.'
sys.exit()
else:
if sys.argv[1].startswith('-') and sys.argv[2].startswith('-'):
option_method = sys.argv[1][1:]
option_database = sys.argv[2][1:]
if option_method == 'pe':
print 'this is for pair end input fastq datas.'
if option_database == 'viruses':
pipeliner_pe(base_path,option_database)
if option_method == 'se':
print 'this is for single end input fastq datas.'
if option_database == 'viruses':
pipeliner_se(base_path,option_database)
time_end = time.time()
total_time = time_end - time_start
print 'total_time:%s'%(total_time)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
6. 生物信息中,求read的反向互补序列
seq = 'ATGCATGC'
"".join(list(reversed(seq)))
seq[::-1]
MORE is comming:
- 读写excel模块:xlrd/xlwt/pandas
- 画图模块:matplotlib
- 访问MySQL数据库
END