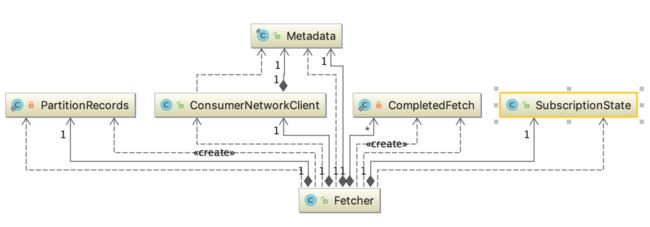
通过前面的介绍,我们知道了offset操作的原理。这一节主要介绍消费者如何从服务端获取消息,KafkaConsumer依赖Fetcher类实现此功能。Fetcher类的主要功能是发送FetchRequest请求,获取指定的消息集合,处理FetchResponse,更新消费位置。Fetcher类依赖的组件:
Fetcher类核心字段:
- client: ConsumerNetworkClient,负责网络通信。
- minBytes:服务端收到FetchRequest后并不是立即响应,而是当可返回的消息数据积累到至少minBytes个字节时才能响应。这样每个FetchResponse中就包含多条消息,提高网络负载。
- maxWaitMs:等待FetchResponse的最长时间,服务端根据此时间决定何时进行响应。
- fetchSize:每次fetch操作的最大字节数。
- maxPollRecords:每次获得Record的最大数量。
- metadata: kafka 集群的元数据。
- subscriptions:记录每个TopicPartition的消费情况。
- completedFetches:List
类型,每个FetchResponse首先会转换成CompletedFetch对象进入此队列缓存,这是并未解析消息。 - keyDeserializer,valueDeserializer:key和value的反序列化器。
- nextInLineRecords: PartitionRecords类型。PartitionRecords保存了CompletedFetch解析后的结果集合,其中有三个字段:records是消息集合,fetchOffset记录了records中第一个消息的offset, partition记录了消息对应的TopicPartition。
Fetcher的核心方法分为三类: - fetch消息的相关方法,用于从Kafka获取消息;
- 更新offset相关的方法,用于更新TopicPartitionState中的position字段;
- 获取Metadata信息的方法,用于获取指定Topic的元信息。
Fetch消息
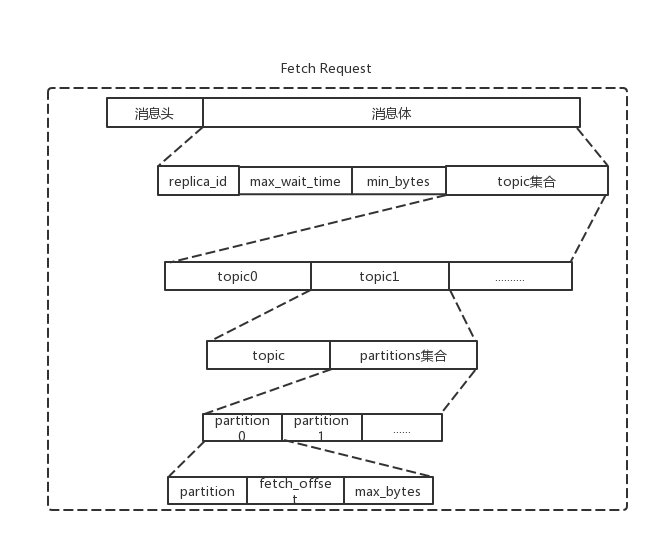
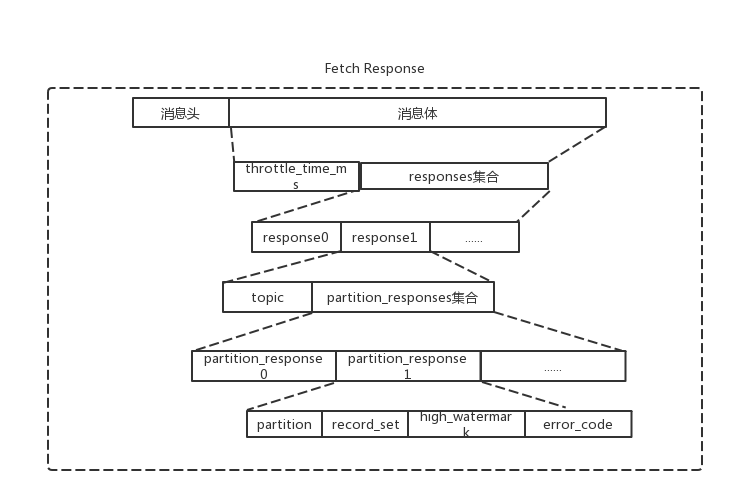
了解下FetchRequest和FetchResponse的消息体格式
FetchRequest字段:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| replica_id | int | 用来标识Follower的id,Consumer和Follower都会使用FetchRequest从Leader那里拉取消息,Consumer默认是-1 |
| max_wait_time | int | 请求最大等待时间 |
| min_bytes | int | 响应的最小负载 |
| fetch_offset | long | 需要fetch的消息offset |
| max_bytes | int | 每次fetch的最大字节数 |
FetchResponse字段:
| high_watermark | long | Leader的high_watermark|
| record_set| byte数组 | fetch到的消息数据|
createFetchRequest()方法用来创建FetchRequest请求,返回值是Map
- 按条件查找fetchable分区。查找条件如下:
- 首先是分配给当前消费者的分区,即SubscriptionState.assign集合中有对应记录的分区。
- 分区未标记为暂停且对应的TopicPartitionState.position不为空。
- nextInLineRecords中没有来自此分区的消息。
- 查找每个fetchable分区的Leader副本所在的Node节点,因为只有分区的Leader副本才能处理读写请求。
- 根据步骤2查找到的Node节点,如果在unsent集合或InFlightRequest中的对应请求队列不为空,则不对此Node发送FetchRequest请求。
4)通过SubscriptionState查找每个分区对应的position,并封装成PartitionData对象。
5)最后按Node进行分类,将发往同一个Node节点的所有TopicPartition封装成一个FetchRequest对象。
createFetchRequest()方法如下:
/**
* Create fetch requests for all nodes for which we have assigned partitions
* that have no existing requests in flight.
*/
private Map createFetchRequests() {
// create the fetch info
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();//获取kafka集群数据
Map> fetchable = new HashMap<>();
//第一步:fetchablePartitions()按照一定的条件过滤后得到可以发送FetchRequest的分区
for (TopicPartition partition : fetchablePartitions()) {
//第二步:查找分区的Leader副本所在的Node
Node node = cluster.leaderFor(partition);
if (node == null) {
metadata.requestUpdate();//如果找不到Leader副本则更新Metadata
//第三步:是否还有pending请求
} else if (this.client.pendingRequestCount(node) == 0) {
// if there is a leader and no in-flight requests, issue a new fetch
Map fetch = fetchable.get(node);
if (fetch == null) {
fetch = new HashMap<>();
fetchable.put(node, fetch);
}
long position = this.subscriptions.position(partition);
//第四步:记录每个分区的对应的position,即要fetch消息的offset
fetch.put(partition, new FetchRequest.PartitionData(position, this.fetchSize));
log.trace("Added fetch request for partition {} at offset {}", partition, position);
}
}
// create the fetches
//第五步:对上面的fetchable集合进行转换,将发往同一个node节点的所有TopicPartition
//的position信息封装成一个FetchRequest对象
Map requests = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry> entry : fetchable.entrySet()) {
Node node = entry.getKey();
FetchRequest fetch = new FetchRequest(this.maxWaitMs, this.minBytes, entry.getValue());
requests.put(node, fetch);
}
return requests;
}
sendFetches()方法的主要功能是将FetchRequest添加到unsent集合中等待发送,并注册FetchResponse处理函数。然后对FetchResponse按TopicPartition分类解析,将获得到的消息数据(未解析的byte数组)和offset组装成CompletedFetch对象并添加到CompletedFetches。sendFetches()方法解析如下:
/**
* Set-up a fetch request for any node that we have assigned partitions for which doesn't already have
* an in-flight fetch or pending fetch data.
*/
public void sendFetches() {
for (Map.Entry fetchEntry: createFetchRequests().entrySet()) {
final FetchRequest request = fetchEntry.getValue();
//将发往每个Node的FetchRequest都缓存到unsent队列上
client.send(fetchEntry.getKey(), ApiKeys.FETCH, request)
//添加Listener,这是处理FetchResponse的入口
.addListener(new RequestFutureListener() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(ClientResponse resp) {
FetchResponse response = new FetchResponse(resp.responseBody());
Set partitions = new HashSet<>(response.responseData().keySet());
FetchResponseMetricAggregator metricAggregator = new FetchResponseMetricAggregator(sensors, partitions);
//遍历响应的数据
for (Map.Entry entry : response.responseData().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition partition = entry.getKey();
long fetchOffset = request.fetchData().get(partition).offset;
//FetchResponse.PartitionData类型
FetchResponse.PartitionData fetchData = entry.getValue();
//创建 CompletedFetch,并缓存到CompletedFetches队列中
completedFetches.add(new CompletedFetch(partition, fetchOffset, fetchData, metricAggregator));
}
sensors.fetchLatency.record(resp.requestLatencyMs());
sensors.fetchThrottleTimeSensor.record(response.getThrottleTime());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) {
log.debug("Fetch failed", e);
}
});
}
}
但是存储在CompletedFetches队列中的数据还是未解析的FetchResponse.PartitionData对象。在fetchedRecords()方法中会将CompletedFetch中的消息数据进行解析,得到Record集合并返回,同时还会修改对应的TopicPartitionState的position,为下次操作做准备,fetchedRecords()方法代码如下:
/**
* Return the fetched records, empty the record buffer and update the consumed position.
*
* NOTE: returning empty records guarantees the consumed position are NOT updated.
*
* @return The fetched records per partition
* @throws OffsetOutOfRangeException If there is OffsetOutOfRange error in fetchResponse and
* the defaultResetPolicy is NONE
*/
public Map>> fetchedRecords() {
if (this.subscriptions.partitionAssignmentNeeded()) {
return Collections.emptyMap();//需要进行Rebalance操作则返回空集合
} else {
//按照TopicPartition进行分类
Map>> drained = new HashMap<>();
//一次最多取出maxPollRecords条消息
int recordsRemaining = maxPollRecords;
//completedFetches集合的迭代器
Iterator completedFetchesIterator = completedFetches.iterator();
while (recordsRemaining > 0) {//遍历completedFetches集合
if (nextInLineRecords == null || nextInLineRecords.isEmpty()) {
if (!completedFetchesIterator.hasNext())
break;
CompletedFetch completion = completedFetchesIterator.next();
completedFetchesIterator.remove();
//解析CompletedFetch得到一个PartitionRecords对象
nextInLineRecords = parseFetchedData(completion);
} else {
//将nextInLineRecords中的消息添加到drained中
recordsRemaining -= append(drained, nextInLineRecords, recordsRemaining);
}
}
return drained;//将结果集合返回
}
}
/**
* The callback for fetch completion 解析CompletedFetch
*/
private PartitionRecords parseFetchedData(CompletedFetch completedFetch) {
TopicPartition tp = completedFetch.partition;
FetchResponse.PartitionData partition = completedFetch.partitionData;
long fetchOffset = completedFetch.fetchedOffset;
int bytes = 0;
int recordsCount = 0;
PartitionRecords parsedRecords = null;
try {
if (!subscriptions.isFetchable(tp)) {
// this can happen when a rebalance happened or a partition consumption paused
// while fetch is still in-flight
log.debug("Ignoring fetched records for partition {} since it is no longer fetchable", tp);
} else if (partition.errorCode == Errors.NONE.code()) {
// we are interested in this fetch only if the beginning offset matches the
// current consumed position
Long position = subscriptions.position(tp);
if (position == null || position != fetchOffset) {
log.debug("Discarding stale fetch response for partition {} since its offset {} does not match " +
"the expected offset {}", tp, fetchOffset, position);
return null;
}
ByteBuffer buffer = partition.recordSet;
//创建MemoryRecords,其中的ByteBuffer来自FetchResponse
MemoryRecords records = MemoryRecords.readableRecords(buffer);
List> parsed = new ArrayList<>();
boolean skippedRecords = false;
//遍历创建MemoryRecords获取Record集合。
for (LogEntry logEntry : records) {
// Skip the messages earlier than current position.
//跳过早于position的消息
if (logEntry.offset() >= position) {
parsed.add(parseRecord(tp, logEntry));
bytes += logEntry.size();
} else {
skippedRecords = true;
}
}
recordsCount = parsed.size();
this.sensors.recordTopicFetchMetrics(tp.topic(), bytes, recordsCount);
if (!parsed.isEmpty()) {
log.trace("Adding fetched record for partition {} with offset {} to buffered record list", tp, position);
//将解析后的Record集合封装成PartitionRecords
parsedRecords = new PartitionRecords<>(fetchOffset, tp, parsed);
ConsumerRecord record = parsed.get(parsed.size() - 1);
this.sensors.recordsFetchLag.record(partition.highWatermark - record.offset());
} else if (buffer.limit() > 0 && !skippedRecords) {
// we did not read a single message from a non-empty buffer
// because that message's size is larger than fetch size, in this case
// record this exception
Map recordTooLargePartitions = Collections.singletonMap(tp, fetchOffset);
throw new RecordTooLargeException("There are some messages at [Partition=Offset]: "
+ recordTooLargePartitions
+ " whose size is larger than the fetch size "
+ this.fetchSize
+ " and hence cannot be ever returned."
+ " Increase the fetch size on the client (using max.partition.fetch.bytes),"
+ " or decrease the maximum message size the broker will allow (using message.max.bytes).",
recordTooLargePartitions);
}
} else if (partition.errorCode == Errors.NOT_LEADER_FOR_PARTITION.code()
|| partition.errorCode == Errors.UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION.code()) {
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
} else if (partition.errorCode == Errors.OFFSET_OUT_OF_RANGE.code()) {
if (fetchOffset != subscriptions.position(tp)) {
log.debug("Discarding stale fetch response for partition {} since the fetched offset {}" +
"does not match the current offset {}", tp, fetchOffset, subscriptions.position(tp));
} else if (subscriptions.hasDefaultOffsetResetPolicy()) {
log.info("Fetch offset {} is out of range for partition {}, resetting offset", fetchOffset, tp);
subscriptions.needOffsetReset(tp);
} else {
throw new OffsetOutOfRangeException(Collections.singletonMap(tp, fetchOffset));
}
} else if (partition.errorCode == Errors.TOPIC_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED.code()) {
log.warn("Not authorized to read from topic {}.", tp.topic());
throw new TopicAuthorizationException(Collections.singleton(tp.topic()));
} else if (partition.errorCode == Errors.UNKNOWN.code()) {
log.warn("Unknown error fetching data for topic-partition {}", tp);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected error code " + partition.errorCode + " while fetching data");
}
} finally {
completedFetch.metricAggregator.record(tp, bytes, recordsCount);
}
return parsedRecords;
}
//在fetchedRecords()方法中将消息添加到drained集合中,还更新了TopicPartitionState的position字段。
private int append(Map>> drained,
PartitionRecords partitionRecords,
int maxRecords) {
if (partitionRecords.isEmpty())
return 0;
if (!subscriptions.isAssigned(partitionRecords.partition)) {
// this can happen when a rebalance happened before fetched records are returned to the consumer's poll call
log.debug("Not returning fetched records for partition {} since it is no longer assigned", partitionRecords.partition);
} else {
// note that the consumed position should always be available as long as the partition is still assigned
long position = subscriptions.position(partitionRecords.partition);
if (!subscriptions.isFetchable(partitionRecords.partition)) {
// this can happen when a partition is paused before fetched records are returned to the consumer's poll call
log.debug("Not returning fetched records for assigned partition {} since it is no longer fetchable", partitionRecords.partition);
} else if (partitionRecords.fetchOffset == position) {
// we are ensured to have at least one record since we already checked for emptiness
//获取消息集合,最多maxRecords个消息
List> partRecords = partitionRecords.take(maxRecords);
long nextOffset = partRecords.get(partRecords.size() - 1).offset() + 1;//最后一个消息的offset
log.trace("Returning fetched records at offset {} for assigned partition {} and update " +
"position to {}", position, partitionRecords.partition, nextOffset);
List> records = drained.get(partitionRecords.partition);
if (records == null) {
records = partRecords;
drained.put(partitionRecords.partition, records);
} else {
records.addAll(partRecords);
}
//更新SubscriptionState对应的TopicPartitionState的position字段
subscriptions.position(partitionRecords.partition, nextOffset);
return partRecords.size();
} else {
// these records aren't next in line based on the last consumed position, ignore them
// they must be from an obsolete request
log.debug("Ignoring fetched records for {} at offset {} since the current position is {}",
partitionRecords.partition, partitionRecords.fetchOffset, position);
}
}
partitionRecords.discard();
return 0;
}
parseFetchedData()方法中使用了MemoryRecords迭代器遍历消息,这里涉及到了压缩消息的处理,下个章节再介绍。
更新position
第一次消费某个Topic分区,服务器内部Offsets Topic中并没有记录当前消费者在此分区上的消费位置,所以消费者无法从服务器获取最近提交的offset。此时如果用户手动指定消费者的起始offset,则可以从指定offset开始消费,否则不然就需要重置TopicPartitionState.position字段。
重置TopicPartitionState.position字段的过程中涉及到OffsetsRequest和OffsetsResponse,格式如下:OffsetsRequest需要说明的字段是timestamp,取值为-1和-2,分别表示LATEST,EARLIEST两种重置策略。OffsetsResponse需要说明的是offsets,它是服务端返回的offset集合。
Fetcher.updateFetchPositions()方法中实现了重置,实现逻辑如下:
1)检测position是否为空,如果非空则不需要进行重置操作。
2)如果设置了resetStrategy,则按照指定的重置策略进行重置操作。
3)有LATEST,EARLIEST两种重置策略:EARLIEST是将position重置为当前最小的offset;而LATEST是将position重置为当前最大的offset。
4)LATEST,EARLIEST两种重置策略都会向GroupCoordinator发送OffsetsRequest,请求指定offset。OffsetsRequest的发送逻辑和OffsetsResponse的处理逻辑跟上面的类似。
5)如果没有指定重置策略,则将position重置为committed。
- 如果committed为空,则使用默认的重置策略。默认重置策略是LATEST策略。
Fetcher.updateFetchPositions()具体实现如下:
/**
* Update the fetch positions for the provided partitions.
* @param partitions the partitions to update positions for
* @throws NoOffsetForPartitionException If no offset is stored for a given partition and no reset policy is available
*/
public void updateFetchPositions(Set partitions) {
// reset the fetch position to the committed position
for (TopicPartition tp : partitions) {
//检测position是否为空,如果非空则不需要进行重置操作。
if (!subscriptions.isAssigned(tp) || subscriptions.isFetchable(tp))
continue;
if (subscriptions.isOffsetResetNeeded(tp)) {
//按照指定的重置策略进行重置操作。
resetOffset(tp);
} else if (subscriptions.committed(tp) == null) {
//如果committed为空,则使用默认的重置策略
// there's no committed position, so we need to reset with the default strategy
subscriptions.needOffsetReset(tp);
resetOffset(tp);
} else {
//如果没有指定重置策略且subscriptions.committed(tp)不为空 ,则将position重置为committed。
long committed = subscriptions.committed(tp).offset();
log.debug("Resetting offset for partition {} to the committed offset {}", tp, committed);
subscriptions.seek(tp, committed);
}
}
}
listOffset()方法实现了对OffsetsRequest的发送和OffsetsResponse的处理,与前面介绍的类似。
获取集群元数据
Fetcher中还提供了获取Metadata信息的相关方法。涉及sendMetadataRequest(),getTopicMetadata(),getAllTopicMetadata()三个方法。
基本逻辑是发送MetadataRequest请求到负载最小的Node节点,并阻塞等待MetadataResponse,正常收到响应后对其解析,得到集群元数据。
需要注意的是,Fetcher提供的这三个获取集群元数据的方法并不会更新Fetcher.metadata字段中保存的集群元数据。第二章介绍过,更新Metadata使用的事NetworkClient.DefaultMetadataUpdater,同样也是发送MetadataRequest请求。