为了演示Spring中对象是如何创建并放到spring容器中,这里新建一个maven项目:
其中pom.xm文件中只引入了一个依赖:
org.springframework spring-context 5.0.9.RELEASE
其实我们只需要这一个,不过spring还是会自动导入他别的依赖,例如spring core,spring aop:
需要说明的是我这里并没有建spring boot项目,只是引入一个spring context依赖的maven项目。
新建一个config配置类,并没有@Configuration注解:
@ComponentScan("component")
public class MyConfig {
}
只有一个@ComponentScan注解,去扫描指定包。
新建一个类(bean),只有@Component注解:
@Component public class People { }
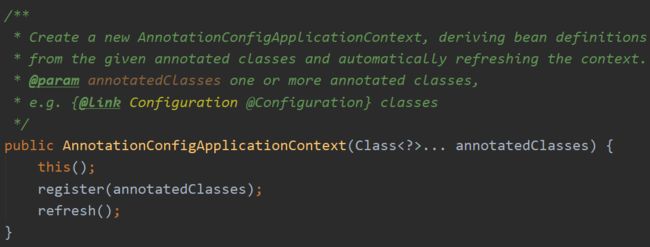
新建Test类,此类去创建spring context(spring上下文,或者说是spring容器):
import config.MyConfig; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //通过注解配置类初始化 spring上下文 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class); //还有一种通过xml来初始化 spring上下文,这里就不介绍了。 //ClassPathXmlApplicationContext System.out.println(annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("people")); } }
项目结构如图:
我们只关注bean的创建,所以在 new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class) 时会去扫描类,然后实例化。
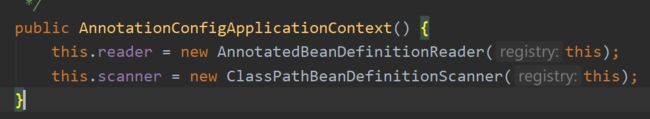
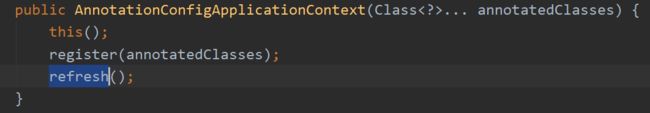
this()调用此类的构造器:
这个reader和scanner和这里bean实例化没有关系,是一些扩展。我们关注他的父类构造器:
![]()
可见this()方法就是建立一个beanFactory工厂,至于细节暂时不去深入。
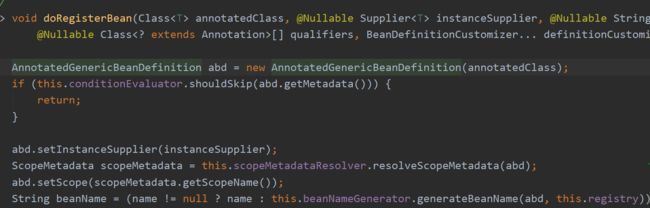
register()方法作用是新建一个BeanDefinition。
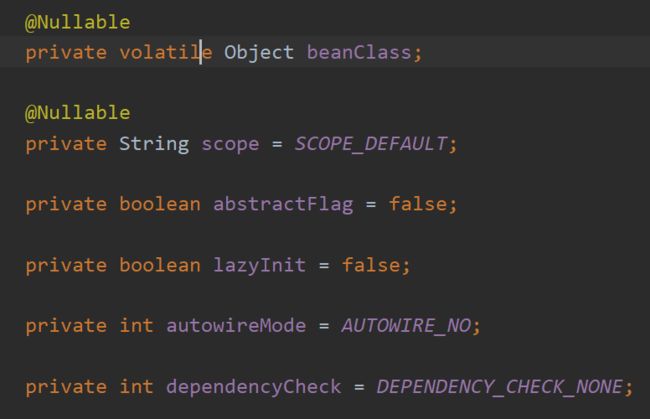
BeanDefinition顾名思义就是spring定义的一个描述bean的类,这个是接口,其描述类的属性由其子类扩展,比如class,lazy(懒加载)等等:
上面时AbstarctBeanDefinition类下的属性。spring根据我们的类(不管是@Service,@Controller,或者是通过@Bean方式),生成对应的BeanDefinition对象。
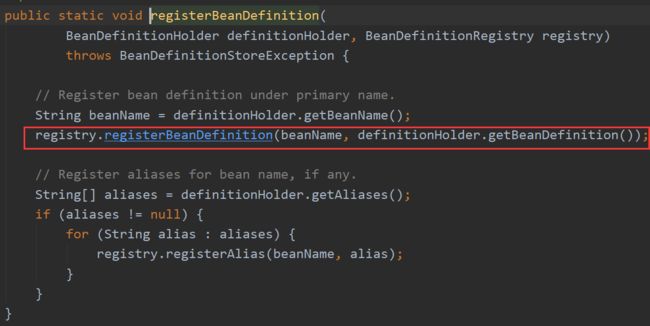
再把它放到一个Map中:
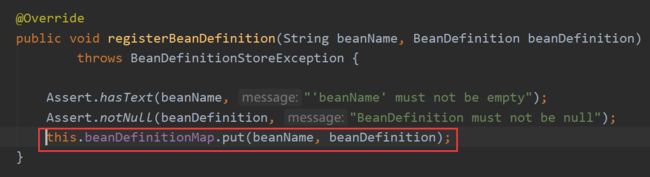
registerBeanDefinition有三个实现方法,不管哪个都有下面这一句:
即把各个BeanDefinition对象放入beanDefinitionMap中去,而这些map的集合就是spring 的容器。
所以register()做了两件事:
1:生成对应BeanDefinition对象;
2:放入beanDefinitionMap中。
最后再来看refresh()方法:
这个方法是spring中最复杂也是最重要的方法:
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
其中invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法需要讲一讲,详见下一篇。
Spring Boot源码(五):BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor