default.vcl
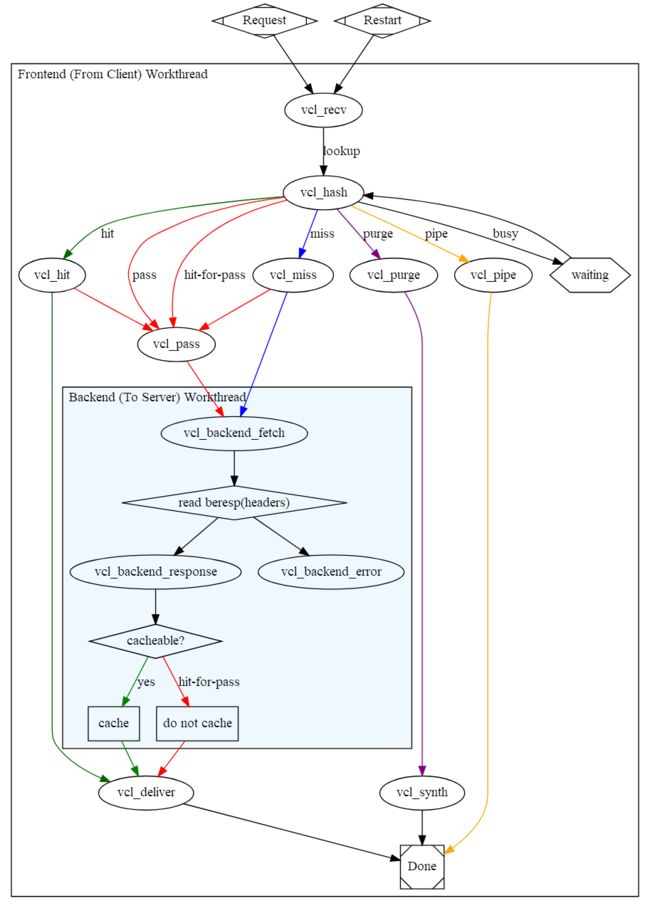
子进程工作流程图示
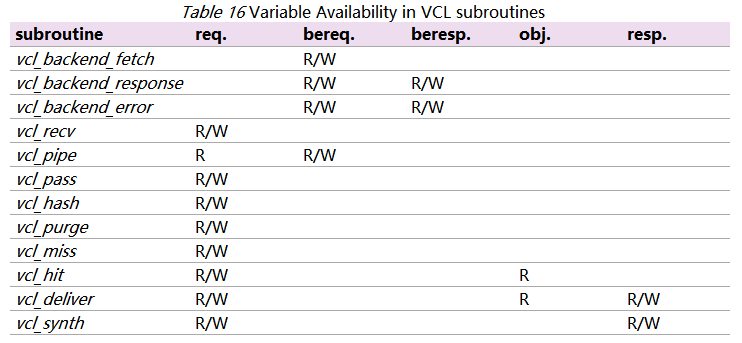
在子进程 VCL 中的可用变量
VCL (Varnish Configuaration Language)
vcl的语法格式
- VCL files start with “vcl 4.0;”
- //, # and /* foo */ for comments;
- Subroutines are declared with the sub keyword; 例如sub vcl_recv { ...};
- No loops, state-limited variables(受限于引擎的内建变量);
- Terminating statements with a keyword for next action as argument of the return() function, i.e.: return(action); # 用于实现状态引擎转换
- Domain-specific;
三类主要语法
sub subroutine {
...
}
if CONDITION {
...
} else {
...
}
return(), hash_data()
VCL Built-in Functions and Keywords
regsub(str, regex, sub)
regsuball(str, regex, sub)
ban(boolean expression)
hash_data(input)
synthetic(str)
call subroutine, return(action),new,
set,unset
==, !=, ~, >, >=, <, <=
逻辑操作符:&&, ||, !
变量赋值:=
if (obj.hits>0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT via" + " " + server.ip;
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS from " + server.ip;
}
变量类型
req.* # request,表示由客户端发来的请求报文相关;
req.http.*
req.http.User-Agent, req.http.Referer, ...
bereq.* # 由 varnish 发往 BE 主机的 httpd 请求相关;
bereq.http.*
beresp.* # 由 BE 主机响应给 varnish 的响应报文相关;
beresp.http.*
resp.* # 由 varnish 响应给 client 相关;
obj.* # 存储在缓存空间中的缓存对象的属性;只读;
bereq.*, req.*
bereq.http.HEADERS, req.http.HEADERS
bereq.request, req.request # 请求方法;
bereq.url, req.url # 请求的 url;
bereq.proto,req.proto # 请求的协议版本;
bereq.backend # 指明要调用的后端主机;
req.http.Cookie # 客户端的请求报文中 Cookie 首部的值;
req.http.User-Agent ~ "chrome"
beresp.*, resp.*
beresp.http.HEADERS
beresp.status, resp.status # 响应的状态码;
reresp.proto, resp.proto # 协议版本;
beresp.backend.name # BE 主机的主机名;
beresp.ttl # BE 主机响应的内容的余下的可缓存时长;
obj.*
obj.hits # 此对象从缓存中命中的次数;
obj.ttl # 对象的 ttl 值
server.*
server.ip # varnish 主机的 IP;
server.hostname # varnish 主机的 Hostname;
client.*
client.ip # 发请求至 varnish 主机的客户端 IP;
set
unset
示例
vcl_recv {
if (req.url ~ "(?i)^/(login|admin)") {
return(pass);
}
}
- 对于特定类型的资源,例如公开的图片等,取消其私有标识,并强行设定其可以由varnish缓存的时长; 定义在vcl_backend_response中
if (beresp.http.cache-control !~ "s-maxage") {
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i)\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|css|js)$") {
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
set beresp.ttl = 3600s;
}
}
if (req.restarts == 0) {
if (req.http.X-Fowarded-For) {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Forwarded-For + "," + client.ip;
} else {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip;
}
}
缓存对象的修剪:purge, ban
配置purge操作
sub vcl_purge {
return (synth(200,"Purged"));
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
return(purge);
}
...
}
添加此类请求的访问控制法则
acl purgers {
"127.0.0.0"/8;
"10.1.0.0"/16;
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
if (!client.ip ~ purgers) {
return(synth(405,"Purging not allowed for " + client.ip));
}
return(purge);
}
...
}
Banning
ban req.url ~ (?i)^ # (?i) 表示不区分大小写
if (req.method == "BAN") {
ban("req.http.host == " + req.http.host + " && req.url == " + req.url);
# Throw a synthetic page so the request won't go to the backend.
return(synth(200, "Ban added"));
}
定义多个后端主机
backend default {
.host = "172.16.100.6";
.port = "80";
}
backend appsrv {
.host = "172.16.100.7";
.port = "80";
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.url ~ "(?i)\.php$") {
set req.backend_hint = appsrv;
} else {
set req.backend_hint = default;
}
...
}
Director
varnish module
import directors;
import directors; # load the directors
backend server1 {
.host =
.port =
}
backend server2 {
.host =
.port =
}
sub vcl_init {
new GROUP_NAME = directors.round_robin();
GROUP_NAME.add_backend(server1);
GROUP_NAME.add_backend(server2);
}
sub vcl_recv {
# send all traffic to the bar director:
set req.backend_hint = GROUP_NAME.backend();
}
BackEnd Server 健康状态检测
语法
.probe = {
.url=
.timeout=
.interval=
.window=
.threshold=
}
定义检测方法
.probe # 定义健康状态检测方法;
.url # 检测时要请求的 URL,默认为”/";
.request # 发出的具体请求;
.request =
"GET /.healthtest.html HTTP/1.1"
"Host: www.rookie.com"
"Connection: close"
.window # 基于最近的多少次检查来判断其健康状态;
.threshold # 最近 .window 中定义的这么次检查中至有 .threshhold 定义的次数是成功的;成功阈值;
.interval # 检测频度;
.timeout # 超时时长;
.expected_response # 期望的响应码,默认为200;
健康状态检测的配置方式
probe PB_NAME { }
backend NAME = {
.probe = PB_NAME;
...
}
backend NAME {
.probe = {
...
}
}
示例
probe check {
.url = "/.healthcheck.html";
.window = 5;
.threshold = 4;
.interval = 2s;
.timeout = 1s;
}
backend default {
.host = "10.1.0.68";
.port = "80";
.probe = check;
}
backend appsrv {
.host = "10.1.0.69";
.port = "80";
.probe = check;
}
手动设定 BE 主机的状态
sick # 管理down;
healthy # 管理up;
auto # probe auto;
设置后端的主机属性
backend BE_NAME {
...
.connect_timeout = 0.5s;
.first_byte_timeout = 20s;
.between_bytes_timeout = 5s;
.max_connections = 50;
}