Netty 权威指南笔记(一):网络 I/O 模型和 Java IO 入门
Java I/O 模型的实现离不开底层操作系统的支持,所以这里先讲一下 Linux 网络 I/O 模型。
Linux 网络 I/O 模型简介
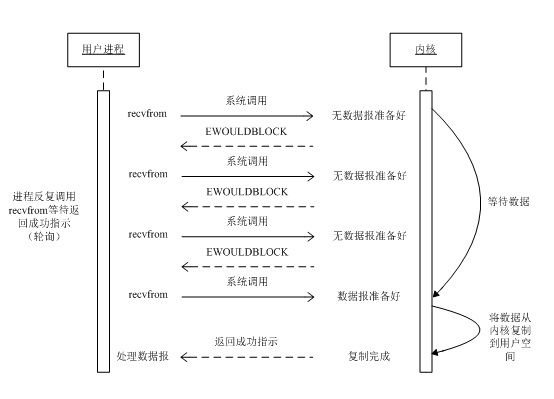
同步阻塞 I/O 模型
最常见的模型是同步阻塞 I/O 模型,用户进程调用 recvfrom 的时候,会阻塞,一直等到响应数据被复制到用户空间的缓冲区或发生错误时才返回。
观看上面的流程图,我们可以发现,一次 I/O 请求包括以下几个步骤:
- 用户进程发起系统调用。
- 内核处理。
- 将数据从内核复制到用户空间。
同步非阻塞 I/O 模型
在同步非阻塞 I/O 模型中,用户进程发起 recvfrom 系统调用时,如果缓冲区没有数据,操作会立即返回 EWOULDBLOCK,此后用户进程可以继续轮询,直到有数据返回。
和同步阻塞 I/O 模型不同的地方在于,recvfrom 系统调用会立即返回,用户进程可以做其他任务后再来检查数据是否已经返回。
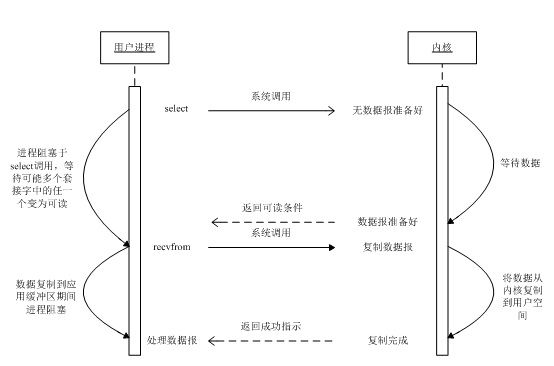
I/O 复用模型
Linux 提供 select/poll,进程通过将多个 fd 传递给 select 系统调用,阻塞在 select 操作上,让 select 帮我们侦测多个 fd 是否已经处于就绪状态。跟同步非阻塞 I/O 模型的对比我们发现,I/O 复用模型相当于把原来由用户进程负责的轮询操作,进行封装,放到了 select 调用里。
轮询的缺点是,当 fd 数量较多时,性能会比较差。所以 Linux 又提供了基于事件驱动的 epoll 系统调用来代替 select 的轮询。
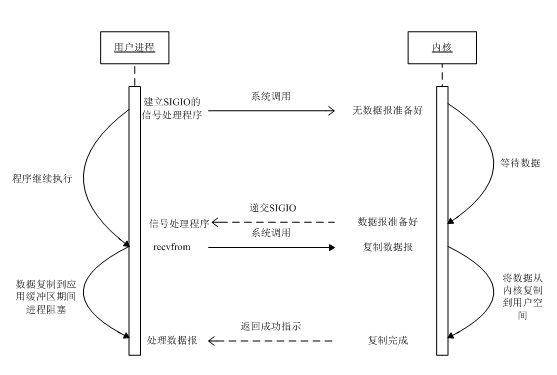
信号驱动 I/O 模型
在这种模型下,我们首先开启套接字的信号驱动式 I/O 功能,并通过 sigaction 系统调用安装一个信号处理函数。系统调用将立即返回,我们的进程继续工作,也就是说他没有被阻塞。当数据报准备好读取时,内核就为该进程产生一个 SIGIO 信号。我们随后就可以在信号处理函数中调用 read 读取数据报,并通知主循环数据已经准备好待处理,也可以立即通知主循环,让它读取数据报。
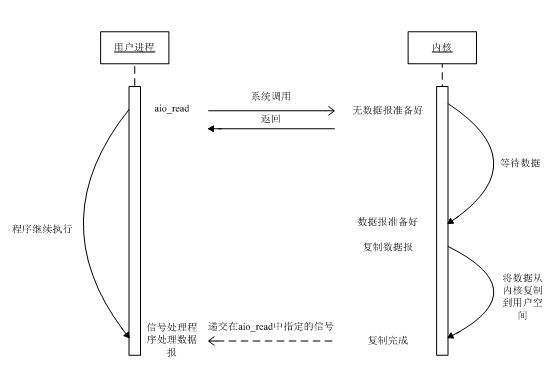
异步非阻塞 I/O 模型
告知内核启动某个操作,并让内核在整个操作完成后通知我们。这种模型与信号驱动模型的区别是:信号驱动 I/O 由内核告知我们何时可以开始一个 I/O 操作,而异步 I/O 模型由内核通知我们操作何时已经完成。
下面我们总结一下,各种不同的 I/O 模型下,用户进程都需要做什么呢?
| 模型 | 阻塞 | 除了发起请求,用户进程还参与了哪些步骤? |
|---|---|---|
| 同步阻塞 I/O | 是 | 阻塞于全部过程 |
| 同步非阻塞 I/O | 否 | 轮询状态,复制数据 |
| I/O 复用 | 否 | 阻塞于多路复用系统调用,但可监听多个事件。但是 I/O 读写本身是非阻塞的 |
| 信号驱动 I/O | 否 | 复制数据 |
| 异步非阻塞 I/O | 否 | 用户进程只需要处理数据。完全无阻塞,内核负责 I/O 读写操作并复制数据 |
Java I/O
和 Linux 的诸多网络 I/O 模型相对应,Java 也有多种 I/O 相关的 API:
| Linux 网络 I/O 模型 | Java I/O API |
|---|---|
| 同步阻塞 I/O | Socket、ServerSocket |
| I/O 复用 | NIO: Selector、SocketChannel、ServerSocketChannel |
| 异步非阻塞 I/O | AIO: AsynchronousSocketChannel、AsynchronousServerSocketChannel |
Java NIO 代码示例
服务器端
端口监听类:
public class SelectorTest {
private static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1000, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES, new ArrayBlockingQueue(1), new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println("reject ...");
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9078));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
selectionKey.attach("accept_channel");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true) {
int readyNum = selector.select();
System.out.println("\nready num: " + readyNum + ", time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey next = iterator.next();
String tag = (String) next.attachment();
if (next.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) next.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = channel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
String socketName = "socket_" + atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketName);
System.out.println(tag + " new SocketChannel: " + socketName);
} else if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
executor.submit(new SocketServerRunnable(socketChannel, tag));
next.cancel();
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
SocketServerRunnable 业务处理类:
public class SocketServerRunnable implements Runnable {
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String tag;
public SocketServerRunnable(SocketChannel serverSocketChannel, String tag) {
this.socketChannel = serverSocketChannel;
this.tag = tag;
}
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
buffer.clear();
int readNum = socketChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(tag + " receive: " + ConvertUtil.convertByteBufferToString(buffer));
buffer.rewind();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(tag + " time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
}
客户端
public class SocketChannelRunnable implements Runnable {
private String tag = "default";
public SocketChannelRunnable(){}
public SocketChannelRunnable(String tag) {
this.tag = tag;
}
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9078));
System.out.println(tag + " connect success ......");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = helloString();
while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
}
byteBuffer.clear();
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(tag + " receive: " + ConvertUtil.convertByteBufferToString(byteBuffer));
socketChannel.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(tag + " time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new SocketChannelRunnable().run();
}
}
总结,是为了强化学习效果。