决策树
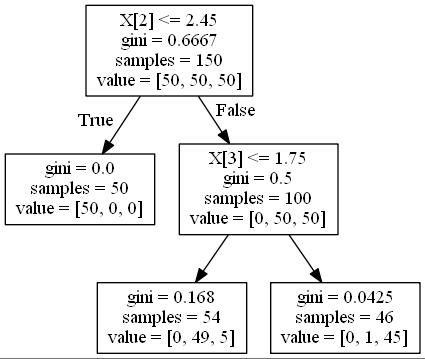
1、画决策树
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris #使用iris数据集
from sklearn import tree
#iris.data #iris的分类依据
#iris.target #iris的分类结果
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2) #设置最大深度为2层
clf.fit(iris.data,iris.target)
clf.predict(iris.data)
# 将决策树输出到图片
from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
import pydotplus
dot_data = StringIO()
tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=dot_data)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data.getvalue())
graph.write_jpg('tree.jpg') # 生成tree.jpg
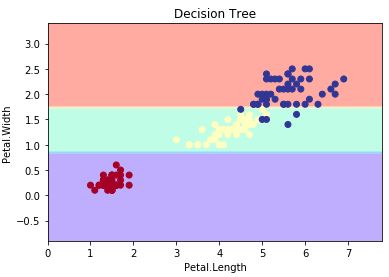
2、画决策边界
只能使用2个变量
第一步,建立模型
from itertools import product
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn import tree
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data[:,[2,3]] #选取iris.data中第三、第四个变量
y = iris.target
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = 2)
clf.fit(X,y)
x_min ,x_max = X[:,0].min()-1,X[:,0].max()+1 #边界图横坐标
y_min ,y_max = X[:,1].min()-1,X[:,1].max()+1 #边界图纵坐标
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min,x_max,0.1),np.arange(y_min,y_max,0.1))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.plot()
plt.contourf(xx,yy,Z,alpha=0.4,cmap=plt.cm.rainbow) #边界图背景
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,alpha=1,cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
plt.title('Decision Tree')
plt.xlabel('Petal.Length')
plt.ylabel('Petal.Width')
plt.show()
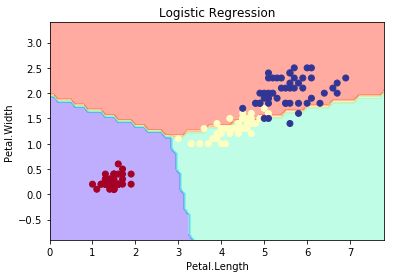
逻辑回归分析
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
iris = load_iris()
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(iris.data,iris.target)
clf.predict(iris.data)
逻辑回归画决策边界图
x_min ,x_max = X[:,0].min()-1,X[:,0].max()+1
y_min ,y_max = X[:,1].min()-1,X[:,1].max()+1
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min,x_max,0.1),np.arange(y_min,y_max,0.1))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.plot()
plt.contourf(xx,yy,Z,alpha=0.4,cmap=plt.cm.rainbow) #alpha 透明度,cmap 配色
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,alpha=1,cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
plt.title('Logistic Regression')
plt.xlabel('Petal.Length')
plt.ylabel('Petal.Width')
plt.show()
SVM
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
iris = load_iris()
clf = SVC(C=100,kernel='linear') #kernel 可选,参考函数说明;C 正则项,C数值小,margin大,允许数据跨界
clf.fit(iris.data,iris.target)
clf.predict(iris.data)
SVM 与逻辑回归对比
from itertools import product
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_estimator(estimator,X,y):
x_min ,x_max = X[:,0].min()-1,X[:,0].max()+1
y_min ,y_max = X[:,1].min()-1,X[:,1].max()+1
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min,x_max,0.1),np.arange(y_min,y_max,0.1))
Z = estimator.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.plot()
plt.contourf(xx,yy,Z,alpha=0.4,cmap=plt.cm.rainbow)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,alpha=1,cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
plt.xlabel('Petal.Length')
plt.ylabel('Petal.Width')
plt.show()
X = iris.data[0:100,[2,3]]
y = iris.target[0:100]
clf1 = SVC(kernel='linear')
clf1.fit(X,y)
clf2 = LogisticRegression()
clf2.fit(X,y)
plot_estimator(clf1,X,y)
plot_estimator(clf2,X,y)
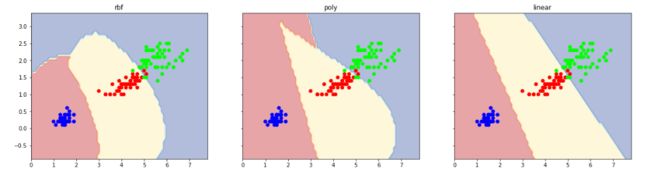
SVM不同kernel对比
from itertools import product
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.svm import SVC
iris = load_iris()
X =iris.data[:,[2,3]]
y = iris.target
clf1 = SVC(kernel = 'rbf')
clf1.fit(X,y)
clf2 = SVC(kernel = 'poly')
clf2.fit(X,y)
clf3 = SVC(kernel = 'linear')
clf3.fit(X,y)
#rbf 和poly 非线性kernel,耗时久
x_min ,x_max = X[:,0].min()-1,X[:,0].max()+1
y_min ,y_max = X[:,1].min()-1,X[:,1].max()+1
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min,x_max,0.1),np.arange(y_min,y_max,0.1))
f,axarr = plt.subplots(1,3,sharex='col',sharey='row',figsize=(20,5))
for idx,clf,title in zip([0,1,2],[clf1,clf2,clf3],['rbf','poly','linear']):
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
axarr[idx].contourf(xx,yy,Z,alpha=0.4,cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
axarr[idx].scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,cmap=plt.cm.brg)
axarr[idx].set_title(title)
类神经网络
import itertools
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import numpy as np
digits = load_digits() #使用自带dataset,辨别手写数字
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0,right=1,bottom=0,top=1,hspace=0.05,wspace=0.05)
for i in range(36):
ax = fig.add_subplot(6,6,i+1,xticks=[],yticks=[])
ax.imshow(digits.images[i],cmap=plt.cm.binary,interpolation='nearest')
ax.text(0,7,str(digits.target[i]),color='red',fontsize=20)
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(digits.data)
X_scaled = scaler.transform(digits.data)
# 对数据进行标准话
mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes =(30,30,30),activation='logistic',max_iter= 100)
# 查看函数帮助
mlp.fit(X_scaled,digits.target)
predicted = mlp.predict(X_scaled)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0,right=1,bottom=0,top=1,hspace=0.05,wspace=0.05)
for i in range(36):
ax = fig.add_subplot(6,6,i+1,xticks=[],yticks=[])
ax.imshow(digits.images[i],cmap=plt.cm.binary,interpolation='nearest')
ax.text(0,7,str('{}-{}'.format(digits.target[i],predicted[i])),color='red',fontsize=20)
# 查看准确率
res = [i==j for i,j in zip(digits.target,predicted)]
print(sum(res)/len(digits.target)) # max_iter = 100时准确率94.5%,max_iter=1000时准确率达到100%
随机森林
def plot_estimator(estimator,X,y,title):
x_min ,x_max = X[:,0].min()-1,X[:,0].max()+1
y_min ,y_max = X[:,1].min()-1,X[:,1].max()+1
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min,x_max,0.1),np.arange(y_min,y_max,0.1))
Z = estimator.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.plot()
plt.contourf(xx,yy,Z,alpha=0.4,cmap=plt.cm.rainbow)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,alpha=1,cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel('Sepal.Length')
plt.ylabel('Sepal.Width')
plt.show()
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data[:,[0,1]]
y = iris.target
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100,criterion='gini',random_state=None)
# n_estimators 树的数量,n越大,分类越准确
clf.fit(X,y)
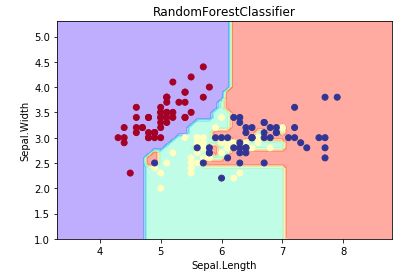
plot_estimator(clf,X,y,'RandomForestClassifier') # 画决策边界图
各种分类方法对比
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
x = iris.data[:,[0,1]]
y = iris.target
clf1 = SVC(kernel='rbf')
clf1.fit(x,y)
clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf2.fit(x,y)
clf3 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10,criterion='entropy')
clf3.fit(x,y)
clf4 = LogisticRegression()
clf4.fit(x,y)
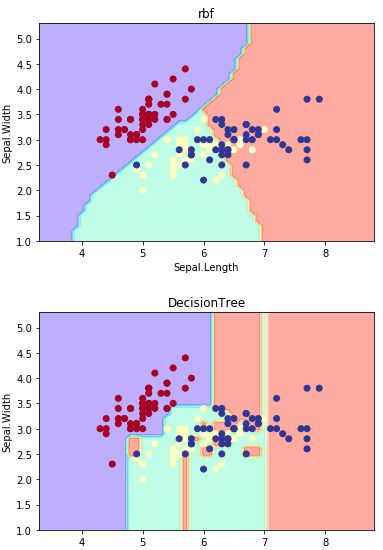
plot_estimator(clf1,x,y,'rbf')
plot_estimator(clf2,x,y,'DecisionTree')
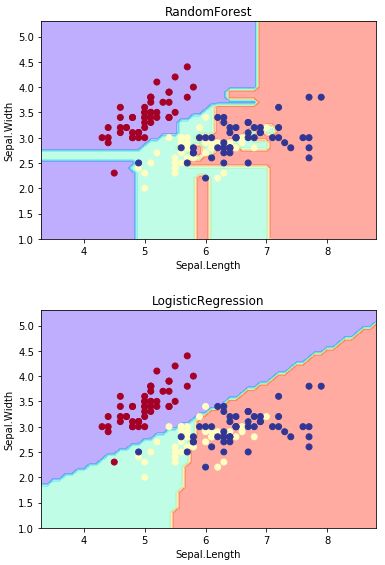
plot_estimator(clf3,x,y,'RandomForest')
plot_estimator(clf4,x,y,'LogisticRegression')