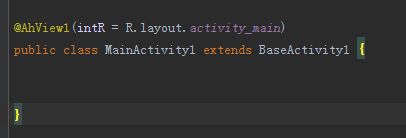
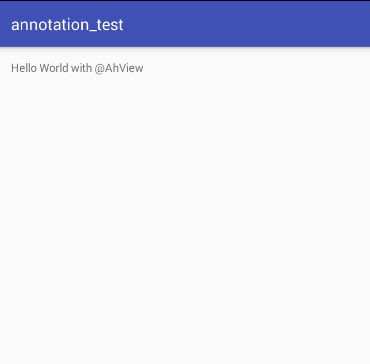
- SpringMVC-注解配置
zl979899
SSMjavaspring
代替web.xml在Servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果找到的话就用它来配置Servlet容器,这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成Spring3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基
- 电脑界面美化工具,让你的电脑C位出道!
学术裁缝李师傅
电脑windows软件构建github
在这个万物皆可定制的时代,怎么能不对你的电脑进行定制呢!今天李师傅向大家安利这款「枫の美化工具箱」,堪称电脑界的魔法化妆师,三秒让你的桌面从路人甲变身Superstar!【海量美化资源】壁纸库简直像百宝箱!想找梦幻星空?有!想要霸气山河图?马上安排!连萌萌的动漫壁纸都给你备齐了。每张都超高清,不管大屏小屏都能完美适配。还有超多图标套装,系统图标、软件图标都能整套换新,再也不用看千篇一律的默认图标啦
- ChatTTS-ui模型概述、安装及使用方法说明
醉心编码
人工智能基础技术类脚本基础TTS大模型人工智能
ChatTTS-ui模型概述、安装及使用方法说明一、ChatTTS-ui模型概述二、ChatTTS-ui的技术优势三、ChatTTS-ui的安装与配置1.安装Python和Git环境2.下载ChatTTS-ui源码3.创建并激活虚拟环境4.安装依赖5.启动应用四、ChatTTS-ui的高级功能1.API调用2.音色自定义3.细粒度控制4.GPU加速五、ChatTTS-ui的应用场景六、ChatTT
- Unity画面模糊抗锯齿解决方案
黑夜de骑士
U3D数字孪生Unity智慧城市数字孪生
一、背景小伙伴们在使用Unity时,是否会遇到画面模糊,有锯齿的情况呢?对于为何出现锯齿,这个原因,可以在图形学相关的教学中找到答案,这里就不赘述了。二、解决思路1.确保Game视图中的Scale为1x,因为如果不为1x会直接引起显示上的锯齿问题。2.在ProjectsSettings里面将AntiAliasing的Disable改为多重采样三、注意事项1.大家好,我是黑夜de骑士,欢迎大家关注我
- android手机自带浏览器无法识别apk文件
afslc17394
在项目中遇到安卓自带浏览器下载成功,但无法打开已下载的APK文件自动安装的问题,特别是三星系列的手机普遍存在这种问题,google后发现也有朋友遇到类似的问题:http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390262400引:写了一些android的应用放在网站上让人下载,在某些机型上,三星的android的4.0以上多款机型最普遍,用安卓自带浏览器下载程序,会提示"无法打开文件",导致
- Android操作系统详细目录结构
Zengyangtech
Androidandroid文件管理器systemgmail音乐测试
Android操作系统相信大家已经非常熟悉了。该系统没有内置文件管理器,经过安装第三方文件管理器后可以对主系统内存和SD卡上的文件管理。主内存中的文件目录都是由主系统自动生成,那么又有多少人他们目录结构的具体分工呢?下面是本站整理的Android操作系统详细目录结构,供大家交流使用。首先是/system/app文件夹,这里面主要存放的是常规下载的应用程序,可以看到都是以APK格式结尾的文件。在这个
- Android已死,备战三个月
2401_89224638
android
性,到公司之后就迫不及待的更新了3.0版本,嗯,还算顺利,只遇到了一个坑,一切都在happy的进行着。什么,你以为我想要写遇到的坑是什么,呵呵哒,我才不会告诉你,等等。。。手里的板砖先放下,一会说还不行吗,今天我们主要来聊聊如何在AndroidStudio3.0上分析内存泄漏,文章的内容很简单,但是自己摸索还是需要一些时间的,所以就在这里记录下来分享给大家。Android高级知识点一、Androi
- android游戏开发引擎!妈妈再也不用担心我的面试,赶快收藏备战金九银十!_android 三元数组
2401_89224638
android面试职场和发展
8.树的深度优先搜索(TreeDFS)9.TwoHeaps10.子集11.经过修改的二叉搜索12.前K个元素13.K路合并14.拓扑排序我们开始吧!1.滑动窗口滑动窗口模式是用于在给定数组或链表的特定窗口大小上执行所需的操作,比如寻找包含所有1的最长子数组。从第一个元素开始滑动窗口并逐个元素地向右滑,并根据你所求解的问题调整窗口的长度。在某些情况下窗口大小会保持恒定,在其它情况下窗口大小会增大或减
- Android 串口通信
消失的旧时光-1943
android
引言在iot项目中,Android端总会有和硬件通信。通信这里:串口通信,蓝牙通信或者局域网通信。这里讲一下串口通信。什么是串口?“串口”(SerialPort)通常是指一种用于与外部设备进行串行通信的接口。如下是其中一种DB9的形式:更加简单的,还有这样的形式:只要有三条线,TX、RX和GND,或者A、B和GND,就可以去实现通讯。................................
- DeepSeek+Kimi生成高质量PPT
Ljw...
小知识点计算机知识点powerpoint数据库DeepSeekpptc++
DeepSeek与Kimi生成PPT全流程解析一、工具分工原理DeepSeek核心作用:生成结构化PPT大纲(擅长逻辑构建与内容优化)Kimi核心作用:将文本转换为视觉化PPT(提供模板库与排版引擎)二、操作步骤详解1.通过DeepSeek生成PPT大纲down输入提示词示例(需包含三要素)你是有10年经验的AI行业分析师,请为科技公司投资人制作一份30页的PPT,要求:首页包含主标题与3个核心论
- 23种设计模式之《外观模式(Facade)》在c#中的应用及理解
yuanpan
外观模式设计模式c#开发语言
程序设计中的主要设计模式通常分为三大类,共23种:1.创建型模式(CreationalPatterns)单例模式(Singleton):确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供全局访问点。工厂方法模式(FactoryMethod):定义创建对象的接口,由子类决定实例化哪个类。抽象工厂模式(AbstractFactory):提供一个创建一系列相关或依赖对象的接口,而无需指定具体类。建造者模式(Builder)
- python系列&deep_study系列:【Conda】自定义conda环境安装位置,三种解决方法
坦笑&&life
#pythonAI系列pythonconda开发语言
【Conda】自定义conda环境安装位置,三种解决方法【Conda】自定义conda环境安装位置,三种解决方法前言常用命令方法一方法二方法三【Conda】自定义conda环境安装位置,三种解决方法前言新建conda环境时,可能会出现默认在C盘创建环境,一般情况下,是不建议将conda环境放在C盘里,因此,我们需要对conda的环境位置进行配置。常用命令查看环境和环境所在的位置condainfo-
- 周末总结(2024/02/22)
全栈黎明
日记
工作人际关系核心实践:要学会随时回应别人的善意,执行时间控制在5分钟以内坚持每天早会打招呼遇到接不住的话题时拉低自己,抬高别人(无阴阳气息)朋友圈点赞控制在5min以内,职场社交不要放在5min以外职场的人际关系在面对利益冲突是直接质疑,要快准狠,不要内耗、回复消息要控制在30mins之内,一定要及时回复每周抽出10mins时间用来反思人际关系不能当面揭别人的短,这会显得自己情商很低三分假,七分真
- 掌握 ElasticSearch 组合查询:Bool Query 详解与实践
全端工程师
elasticsearchelasticsearchjenkins大数据
掌握ElasticSearch组合查询:BoolQuery详解与实践一、引言(Introduction)二、Bool查询基础2.1什么是Bool查询?2.2Bool查询的四种子句2.3语法结构三、Bool查询的四种子句详解与示例3.1`must`子句3.2`filter`子句3.3`should`子句3.4`must_not`子句四、`minimum_should_match`参数4.1什么是`m
- 前端大厂常见面试题目|react|5-reacr ajax,axios,消息订阅发布机制,react-routerdom的api,基本路由使用,rdirct,antd,navlink,switch,
学习记录wanxiaowan
前端八股文前端面试react.js
第4章:Reactajax4.1.理解4.1.1.前置说明React本身只关注于界面,并不包含发送ajax请求的代码前端应用需要通过ajax请求与后台进行交互(json数据)react应用中需要集成第三方ajax库(或自己封装)4.1.2.常用的ajax请求库jQuery:比较重,如果需要另外引入不建议使用axios:轻量级,建议使用封装XmlHttpRequest对象的ajaxpromise风格
- 英语场景(一)
山猪打不过家猪
En面试职场和发展
文章目录项目地址一、点餐二、美发三、健身项目地址教程作者:教程地址:代码仓库地址:一、点餐点东西i'dliketoordertwopizzas其他小料extraingredients回答anythingelseNo,that'sall.Thankyou!That'sit,thanks!我喜欢这里的装修llovethedecor我要…I'llhave...给你一些时间看菜单I'llgiveyouac
- 设计模式-adapter模式(适配器)
老菜鸟的每一天
设计模式设计模式适配器模式
解释适配器模式(AdapterPattern)用于将一个类的接口转换成客户端所期望的另一个接口,使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。该模式属于结构型设计模式。应用场景场景1:旧系统与新系统的整合当你有一个现有系统,并且想要集成一个第三方库或新的模块时,可能会遇到接口不匹配的问题。此时,适配器模式可以帮助你创建一个“桥梁”,使得旧代码能够调用新API,反之亦然。场景2:不同第三
- 蓝桥杯训练题(1)
wuhu_king
算法算法
幂ab的末3位数是多少?输入两个正整数a,b。1≤a≤100,1≤b≤10000。输出从高位到低位输出幂的末三位数字,中间无分隔符。若幂本身不足三位,在前面补零。样例输入72011样例输出743答案#includeintmain(){inta,b;intret=1;scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);inti;for(i=0;i
- 实时系统vxWorks - zynq7020移植vxWorks
不只会拍照的程序猿
实时vxWorks听说ZYNQ嵌入式vxWorksZynq实时系统操作系统
概述关于zynq的启动方式,网上百度有一大堆,这里就不详细阐述了,小编整理了一下主要流程大致为:上电->bootRom->FSBL->操作系统。BootRom:硬件固化,用户无需更改,类似bios。FSBL(BOOT.bin):由fsbl.elf、bitstream和SSBL三部分组成。fsbl.elf用于完成PS初始化工作,加载PLbitstream文件,运行SSBL(bootrom)。操作系统
- Hot100 动态规划
Coco_9264
动态规划算法
动态规划动规五部曲:确定dp数组以及下标的含义确定递推公式dp数组如何初始化确定遍历顺序举例推导dp数组70.爬楼梯-力扣(LeetCode)爬到第一层楼梯有一种方法,爬到二层楼梯有两种方法。那么第一层楼梯再跨两步就到第三层,第二层楼梯再跨一步就到第三层。所以到第三层楼梯的状态可以由第二层楼梯和到第一层楼梯状态推导出来,那么就可以想到动态规划了。我们来分析一下,动规五部曲:定义一个一维数组来记录不
- RAG驱动的健康信息检索,三阶段破解健康谣言
Debroon
医疗大模型研发:慢病停药逆转人工智能
RAG驱动的健康信息检索,三阶段破解健康谣言论文大纲1.Why:这个研究要解决什么现实问题2.What:核心发现或论点是什么3.How3.1前人研究的局限性3.2你的创新方法/视角3.3关键数据支持3.4可能的反驳及应对4.HowGood:研究的理论贡献和实践意义解法拆解一、总体解法的拆解逻辑二、逐层拆解:子解法与特征的对应关系1)特征与子解法对应情况三、分析是否存在“隐性方法”四、分析是否有隐性
- 便携式动平衡仪Qt应用层详细设计说明书
m0_55576290
工作一二三qt开发语言
便携式动平衡仪Qt应用层详细设计说明书(DDD)版本:1.1日期:2023年10月一、文档目录系统概述应用层架构设计模块详细设计接口定义与数据流关键数据结构代码框架与实现测试计划附录二、系统概述2.1功能需求开机流程:长按电源键启动,全屏显示商标动画(快闪3~4次)。主界面:三栏布局(状态栏、工作区图标、导航栏),支持点击图标跳转。模板系统:保存/加载动平衡参数模板(.tpl文件),点击模板直接跳
- 点云从入门到精通技术详解100篇-基于多线激光雷达的点云数据处理与导航(续)
格图素书
人工智能算法
目录三维点云建图与定位算法研究§3.1激光SLAM技术§3.2基于特征的建图算法§3.2.1三维点云建图算法简述§3.2.3LeGO-LOAM建图算法§3.3基于点云配准的定位算法§3.3.1点云配准§3.3.2基于ICP的配准定位算法§3.3.3基于NDT的配准定位算法§3.4基于LM法优化的NDT配准定位算法§3.4.1列文伯格-马夸尔特法原理§3.4.2LM-NDT算法配准原理及流程§3.5
- SOC模式控制下的电池充放电研究(Simulink仿真实现)
程序猿鑫
数学建模
欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️博主优势:博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。本文目录如下:目录1概述SOC模式控制下的电池充放电研究一、SOC模式控制的定义及分类二、SOC控制策略的设计方法三、电池性能评估指标四、研究文档撰写规范五、未来研究方向2运行结果3参考文献4Simulink仿真实现1概述SOC模式控制下的电池充放电研究一、SOC模式控制的定义及分类S
- 多维度多级数据查询sql语句
luvianfu
sql数据库
数据结构实体A配置权限时,有以下维度:产品线数据有:查询接口测试一级产品类别、查询接口测试二级产品类别、查询接口测试三级产品类别服务网点数据有:查询接口测试网点1、查询接口测试网点2、查询接口测试网点3部门数据有(负责人维度):查询接口测试上级部门、查询接口测试下级部门以上数据都有上下级关系用户“张三”的基础信息中,部门是查询接口测试上级部门,服务网点是查询接口测试网点2,产品线是查询接口测试一级
- Linux系统——Nginx常见面试题
一坨小橙子ovo
linuxnginx服务器
目录一、Nginx使用场景二、Nginx的发展历史三、Nginx没出现之前都存在过什么问题四、Nginx的优点五、正向代理和反向代理分别是什么六、Nginx限流问题七、Nginx动静分离八、什么是负载均衡九、Nginx负载均衡的策略有哪些十、Nginx多进程模型十一、为什么Nginx不使用多线程十二、Nginx高可用性十三、Nginx压缩十四、总结Nginx是一种高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,
- Python:FastAPI开发从入门到精通
赵梓宇
Python权威教程合集Python
想用Python写API快到飞起?FastAPI就是你的“代码瑞士军刀”!这本书不讲玄学,只教真功夫——从零搭建高性能API,到微服务、分布式事务、熔断限流,连异步编程都能玩成魔法!小白也能变大神:路由、依赖注入、数据库集成手把手教学;老鸟直呼内行:服务网格、Saga模式、K8s部署实战全覆盖。附赠三个硬核项目:任务管理、在线商城、实时聊天系统,代码跑起来比老裁缝织毛衣还丝滑!别说我没提醒你:翻开
- 【2025年】全国CTF夺旗赛-从零基础入门到竞赛,看这一篇就稳了!
网安詹姆斯
web安全CTF网络安全大赛pythonlinux
【2025年】全国CTF夺旗赛-从零基础入门到竞赛,看这一篇就稳了!基于入门网络安全/黑客打造的:黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包目录一、CTF简介二、CTF竞赛模式三、CTF各大题型简介四、CTF学习路线4.1、初期1、html+css+js(2-3天)2、apache+php(4-5天)3、mysql(2-3天)4、python(2-3天)5、burpsuite(1-2天)4.2、中期1、S
- 冬训周报(四)
HL0614SC
算法蓝桥杯
一、补题天梯赛训练补题-CSDN博客蓝桥杯训练补题-CSDN博客二、算法本周主要是蓝桥杯的一个训练,这其中对于搜索和二分的算法居多,对于搜索而言,简单的搜索可能还不成问题,但稍微一复杂写起来还是有些吃力的;另外还有二分,二分的关键就在于check函数,这要求对题目理解足够透彻,同时二分还要注意左右端点的值以及答案记录。三、小结本周是寒假训练的最后一周,这周进行了三次的蓝桥杯训练,对于OI的赛制感觉
- 暑期集训周报(第一周)
HL0614SC
算法
第☝️周训练内容个人赛为主,加上题单的练习,主要的算法包括二分,三分,栈,队列,01分数规划等等。存在的问题①英文题面这几次个人赛的大多题面都是英文,四级还不知道过没过的我属实觉得读题有点困难了,大多时候都是靠翻译解决的读题问题,而这也可能导致一些题没读准的情况,就类似于这道题一样,没仔细读题,结果白磕的很长时间,导致后面更简单的G题没写。所以还是要提升读英文题面的能力才行;②作息问题之前的训练大
- HQL之投影查询
归来朝歌
HQLHibernate查询语句投影查询
在HQL查询中,常常面临这样一个场景,对于多表查询,是要将一个表的对象查出来还是要只需要每个表中的几个字段,最后放在一起显示?
针对上面的场景,如果需要将一个对象查出来:
HQL语句写“from 对象”即可
Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession();
- Spring整合redis
bylijinnan
redis
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Data - Redis Library -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redi
- org.hibernate.NonUniqueResultException: query did not return a unique result: 2
0624chenhong
Hibernate
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/qingfeilee/article/details/7052736
org.hibernate.NonUniqueResultException: query did not return a unique result: 2
在项目中出现了org.hiber
- android动画效果
不懂事的小屁孩
android动画
前几天弄alertdialog和popupwindow的时候,用到了android的动画效果,今天专门研究了一下关于android的动画效果,列出来,方便以后使用。
Android 平台提供了两类动画。 一类是Tween动画,就是对场景里的对象不断的进行图像变化来产生动画效果(旋转、平移、放缩和渐变)。
第二类就是 Frame动画,即顺序的播放事先做好的图像,与gif图片原理类似。
- js delete 删除机理以及它的内存泄露问题的解决方案
换个号韩国红果果
JavaScript
delete删除属性时只是解除了属性与对象的绑定,故当属性值为一个对象时,删除时会造成内存泄露 (其实还未删除)
举例:
var person={name:{firstname:'bob'}}
var p=person.name
delete person.name
p.firstname -->'bob'
// 依然可以访问p.firstname,存在内存泄露
- Oracle将零干预分析加入网络即服务计划
蓝儿唯美
oracle
由Oracle通信技术部门主导的演示项目并没有在本月较早前法国南斯举行的行业集团TM论坛大会中获得嘉奖。但是,Oracle通信官员解雇致力于打造一个支持零干预分配和编制功能的网络即服务(NaaS)平台,帮助企业以更灵活和更适合云的方式实现通信服务提供商(CSP)的连接产品。这个Oracle主导的项目属于TM Forum Live!活动上展示的Catalyst计划的19个项目之一。Catalyst计
- spring学习——springmvc(二)
a-john
springMVC
Spring MVC提供了非常方便的文件上传功能。
1,配置Spring支持文件上传:
DispatcherServlet本身并不知道如何处理multipart的表单数据,需要一个multipart解析器把POST请求的multipart数据中抽取出来,这样DispatcherServlet就能将其传递给我们的控制器了。为了在Spring中注册multipart解析器,需要声明一个实现了Mul
- POJ-2828-Buy Tickets
aijuans
ACM_POJ
POJ-2828-Buy Tickets
http://poj.org/problem?id=2828
线段树,逆序插入
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<cstdlib>using namespace std;#define N 200010struct
- Java Ant build.xml详解
asia007
build.xml
1,什么是antant是构建工具2,什么是构建概念到处可查到,形象来说,你要把代码从某个地方拿来,编译,再拷贝到某个地方去等等操作,当然不仅与此,但是主要用来干这个3,ant的好处跨平台 --因为ant是使用java实现的,所以它跨平台使用简单--与ant的兄弟make比起来语法清晰--同样是和make相比功能强大--ant能做的事情很多,可能你用了很久,你仍然不知道它能有
- android按钮监听器的四种技术
百合不是茶
androidxml配置监听器实现接口
android开发中经常会用到各种各样的监听器,android监听器的写法与java又有不同的地方;
1,activity中使用内部类实现接口 ,创建内部类实例 使用add方法 与java类似
创建监听器的实例
myLis lis = new myLis();
使用add方法给按钮添加监听器
- 软件架构师不等同于资深程序员
bijian1013
程序员架构师架构设计
本文的作者Armel Nene是ETAPIX Global公司的首席架构师,他居住在伦敦,他参与过的开源项目包括 Apache Lucene,,Apache Nutch, Liferay 和 Pentaho等。
如今很多的公司
- TeamForge Wiki Syntax & CollabNet User Information Center
sunjing
TeamForgeHow doAttachementAnchorWiki Syntax
the CollabNet user information center http://help.collab.net/
How do I create a new Wiki page?
A CollabNet TeamForge project can have any number of Wiki pages. All Wiki pages are linked, and
- 【Redis四】Redis数据类型
bit1129
redis
概述
Redis是一个高性能的数据结构服务器,称之为数据结构服务器的原因是,它提供了丰富的数据类型以满足不同的应用场景,本文对Redis的数据类型以及对这些类型可能的操作进行总结。
Redis常用的数据类型包括string、set、list、hash以及sorted set.Redis本身是K/V系统,这里的数据类型指的是value的类型,而不是key的类型,key的类型只有一种即string
- SSH2整合-附源码
白糖_
eclipsespringtomcatHibernateGoogle
今天用eclipse终于整合出了struts2+hibernate+spring框架。
我创建的是tomcat项目,需要有tomcat插件。导入项目以后,鼠标右键选择属性,然后再找到“tomcat”项,勾选一下“Is a tomcat project”即可。具体方法见源码里的jsp图片,sql也在源码里。
补充1:项目中部分jar包不是最新版的,可能导
- [转]开源项目代码的学习方法
braveCS
学习方法
转自:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_693458530100lk5m.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/west-link/archive/2011/06/07/2074466.html
1)阅读features。以此来搞清楚该项目有哪些特性2)思考。想想如果自己来做有这些features的项目该如何构架3)下载并安装d
- 编程之美-子数组的最大和(二维)
bylijinnan
编程之美
package beautyOfCoding;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class MaxSubArraySum2 {
/**
* 编程之美 子数组之和的最大值(二维)
*/
private static final int ROW = 5;
private stat
- 读书笔记-3
chengxuyuancsdn
jquery笔记resultMap配置ibatis一对多配置
1、resultMap配置
2、ibatis一对多配置
3、jquery笔记
1、resultMap配置
当<select resultMap="topic_data">
<resultMap id="topic_data">必须一一对应。
(1)<resultMap class="tblTopic&q
- [物理与天文]物理学新进展
comsci
如果我们必须获得某种地球上没有的矿石,才能够进行某些能量输出装置的设计和建造,而要获得这种矿石,又必须首先进行深空探测,而要进行深空探测,又必须获得这种能量输出装置,这个矛盾的循环,会导致地球联盟在与宇宙文明建立关系的时候,陷入困境
怎么办呢?
- Oracle 11g新特性:Automatic Diagnostic Repository
daizj
oracleADR
Oracle Database 11g的FDI(Fault Diagnosability Infrastructure)是自动化诊断方面的又一增强。
FDI的一个关键组件是自动诊断库(Automatic Diagnostic Repository-ADR)。
在oracle 11g中,alert文件的信息是以xml的文件格式存在的,另外提供了普通文本格式的alert文件。
这两份log文
- 简单排序:选择排序
dieslrae
选择排序
public void selectSort(int[] array){
int select;
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
select = i;
for(int k=i+1;k<array.leng
- C语言学习六指针的经典程序,互换两个数字
dcj3sjt126com
c
示例程序,swap_1和swap_2都是错误的,推理从1开始推到2,2没完成,推到3就完成了
# include <stdio.h>
void swap_1(int, int);
void swap_2(int *, int *);
void swap_3(int *, int *);
int main(void)
{
int a = 3;
int b =
- php 5.4中php-fpm 的重启、终止操作命令
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
php 5.4中php-fpm 的重启、终止操作命令:
查看php运行目录命令:which php/usr/bin/php
查看php-fpm进程数:ps aux | grep -c php-fpm
查看运行内存/usr/bin/php -i|grep mem
重启php-fpm/etc/init.d/php-fpm restart
在phpinfo()输出内容可以看到php
- 线程同步工具类
shuizhaosi888
同步工具类
同步工具类包括信号量(Semaphore)、栅栏(barrier)、闭锁(CountDownLatch)
闭锁(CountDownLatch)
public class RunMain {
public long timeTasks(int nThreads, final Runnable task) throws InterruptedException {
fin
- bleeding edge是什么意思
haojinghua
DI
不止一次,看到很多讲技术的文章里面出现过这个词语。今天终于弄懂了——通过朋友给的浏览软件,上了wiki。
我再一次感到,没有辞典能像WiKi一样,给出这样体贴人心、一清二楚的解释了。为了表达我对WiKi的喜爱,只好在此一一中英对照,给大家上次课。
In computer science, bleeding edge is a term that
- c中实现utf8和gbk的互转
jimmee
ciconvutf8&gbk编码
#include <iconv.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int code_c
- 大型分布式网站架构设计与实践
lilin530
应用服务器搜索引擎
1.大型网站软件系统的特点?
a.高并发,大流量。
b.高可用。
c.海量数据。
d.用户分布广泛,网络情况复杂。
e.安全环境恶劣。
f.需求快速变更,发布频繁。
g.渐进式发展。
2.大型网站架构演化发展历程?
a.初始阶段的网站架构。
应用程序,数据库,文件等所有的资源都在一台服务器上。
b.应用服务器和数据服务器分离。
c.使用缓存改善网站性能。
d.使用应用
- 在代码中获取Android theme中的attr属性值
OliveExcel
androidtheme
Android的Theme是由各种attr组合而成, 每个attr对应了这个属性的一个引用, 这个引用又可以是各种东西.
在某些情况下, 我们需要获取非自定义的主题下某个属性的内容 (比如拿到系统默认的配色colorAccent), 操作方式举例一则:
int defaultColor = 0xFF000000;
int[] attrsArray = { andorid.r.
- 基于Zookeeper的分布式共享锁
roadrunners
zookeeper分布式共享锁
首先,说说我们的场景,订单服务是做成集群的,当两个以上结点同时收到一个相同订单的创建指令,这时并发就产生了,系统就会重复创建订单。等等......场景。这时,分布式共享锁就闪亮登场了。
共享锁在同一个进程中是很容易实现的,但在跨进程或者在不同Server之间就不好实现了。Zookeeper就很容易实现。具体的实现原理官网和其它网站也有翻译,这里就不在赘述了。
官
- 两个容易被忽略的MySQL知识
tomcat_oracle
mysql
1、varchar(5)可以存储多少个汉字,多少个字母数字? 相信有好多人应该跟我一样,对这个已经很熟悉了,根据经验我们能很快的做出决定,比如说用varchar(200)去存储url等等,但是,即使你用了很多次也很熟悉了,也有可能对上面的问题做出错误的回答。 这个问题我查了好多资料,有的人说是可以存储5个字符,2.5个汉字(每个汉字占用两个字节的话),有的人说这个要区分版本,5.0
- zoj 3827 Information Entropy(水题)
阿尔萨斯
format
题目链接:zoj 3827 Information Entropy
题目大意:三种底,计算和。
解题思路:调用库函数就可以直接算了,不过要注意Pi = 0的时候,不过它题目里居然也讲了。。。limp→0+plogb(p)=0,因为p是logp的高阶。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath&