1. rensorboard的网络结构
- 首先定义命名空间,运行代码,生成log文件
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist import read_data_sets
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
mnist = read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
batch_size = 100
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
# 添加命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784], name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('wights'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]), name='W')
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), name='b')
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x, W) + b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - prediction))
with tf.name_scope('train_step'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.arg_max(prediction, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
sess.run(init)
# 输出graph
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/', sess.graph)
for epoch in range(1):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter " + str(epoch) + ",Testing Accuracy " + str(acc))
- 打开 anaconda prompt,运行
tensorboard --logdir=D:\python\demo\logs
- 运行成功后在chrome浏览器打开
http://localhost:6006
2. 查看网络运行时的数据
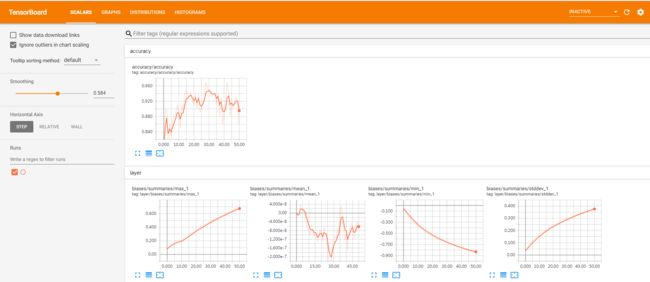
TensorBoard是TensorFlow自带的一个强大的可视化工具,也是一个Web应用程序套件。TensorBoard目前支持7种可视化,Scalars,Images,Audio,Graphs,Distributions,Histograms和Embeddings。其中可视化的主要功能如下。
(1)Scalars:展示训练过程中的准确率、损失值、权重/偏置的变化情况。
(2)Images:展示训练过程中记录的图像。
(3)Audio:展示训练过程中记录的音频。
(4)Graphs:展示模型的数据流图,以及训练在各个设备上消耗的内存和时间。
(5)Distributions:展示训练过程中记录的数据的分部图。
(6)Histograms:展示训练过程中记录的数据的柱状图。
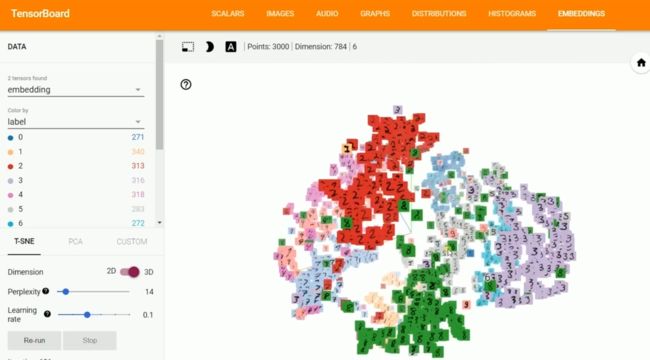
(7)Embeddings:展示词向量后的投影分部。
TensorBoard通过运行一个本地服务器,来监听6006端口。在浏览器发出请求时,分析训练时记录的数据,绘制训练过程中的图像。
wights和biases打印参数概要函数(variable_summaries),loss和accuracy打印数据变化,合并所有的summary,每次运行train_step同时运行merged输出一次summary,每次epoch写入summary到文件
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist import read_data_sets
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
mnist = read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
batch_size = 100
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
# 参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean) # 平均值
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) # 标准差
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var)) # 最大值
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var)) # 最小值
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) # 直方图
# 添加命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784], name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('wights'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]), name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), name='b')
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x, W) + b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - prediction))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss)
with tf.name_scope('train_step'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.arg_max(prediction, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
# 合并所有的summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
sess.run(init)
# 输出graph
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/', sess.graph)
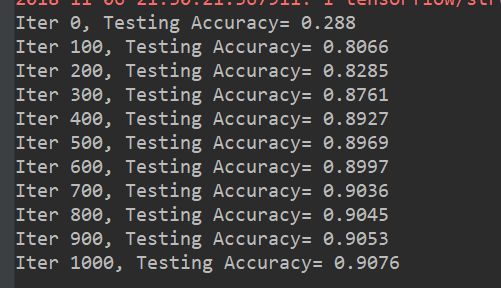
for epoch in range(51):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step], feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
writer.add_summary(summary, epoch)
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter " + str(epoch) + ",Testing Accuracy " + str(acc))
3. tensorboard的高维可视化
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from tensorflow.contrib.tensorboard.plugins import projector
# 载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# 运行次数
max_steps = 1001
# 图片数量
image_num = 3000
# 文件路径
DIR = "D:/python/demo/"
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
# 定义会话
sess = tf.Session(config=config)
# 载入图片
# stack函数 打包图片
embedding = tf.Variable(tf.stack(mnist.test.images[:image_num]), trainable=False, name='embedding')
# 参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean) # 平均值
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) # 标准差
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var)) # 最大值
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var)) # 最小值
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) # 直方图
# 命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
# 这里的none表示第一个维度可以是任意的长度
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784], name='x-input')
# 正确的标签
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name='y-input')
# 显示图片
with tf.name_scope('input_reshape'):
# -1代表个数不限,28,28代表把784转成28行28列,1代表黑白照片维度为1,3彩色照片维度为3
image_shaped_input = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
tf.summary.image('input', image_shaped_input, 10)
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
# 创建一个简单神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]), name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), name='b')
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x, W) + b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# 交叉熵代价函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
# 使用梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(loss)
# 初始化变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
# 结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1)) # argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
# 求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) # 把correct_prediction变为float32类型
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
# 产生metadata文件
# 如果文件存在,创建文件,如果不存在,删除文件
if tf.gfile.Exists(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv'):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv')
with open(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv', 'w') as f:
labels = sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[:], 1))
for i in range(image_num):
f.write(str(labels[i]) + '\n')
# 合并所有的summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 定义图的结构
projector_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(DIR + 'projector/projector', sess.graph)
# 保存网络的模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# 定义配置文件
config = projector.ProjectorConfig()
embed = config.embeddings.add()
embed.tensor_name = embedding.name
embed.metadata_path = DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv'
embed.sprite.image_path = DIR + 'projector/data/mnist_10k_sprite.png'
# 把图片切分,每一个大小28*28
embed.sprite.single_image_dim.extend([28, 28])
projector.visualize_embeddings(projector_writer, config)
for i in range(max_steps):
# 每个批次100个样本
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step], feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}, options=run_options,
run_metadata=run_metadata)
projector_writer.add_run_metadata(run_metadata, 'step%03d' % i)
projector_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
if i % 100 == 0:
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter " + str(i) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(acc))
saver.save(sess, DIR + 'projector/projector/a_model.ckpt', global_step=max_steps)
projector_writer.close()
sess.close()
mnist_10k_sprite.png