在详解SpringMVC处理流程之前,首先我们要做好准备工作,比如初始化SpringMVC容器,如果SpringMVC和SpringMVC集成话,同样也需要初始化Spring容器。
容器初始化
web.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
contextConfigLocation
classpath*:applicationContext-*.xml
dispatcher
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath*:dispatcher-servlet.xml
0
dispatcher
/
从web.xml中可以看出通过ContextLoaderListener初始化Spring容器,通过DispatcherServlet初始化SpringMVC容器,SpringMVC容器作为Spring容器的子容器设置在Spring容器。
ContextLoaderListener的作用
初始ApplicationContext(默认的是XmlWebApplicationContext)然后将其放在ServletContext中。
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
currentContextPerThread.put(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), this.context);
ServletContext作用
每一个web应用都有一个 ServletContext与之相关联。
ServletContext对象在应用启动的被创建,在应用关闭的时候被销毁。
ServletContext在全局范围内有效,类似于应用中的一个全局变量。
DispatcherServlet作用
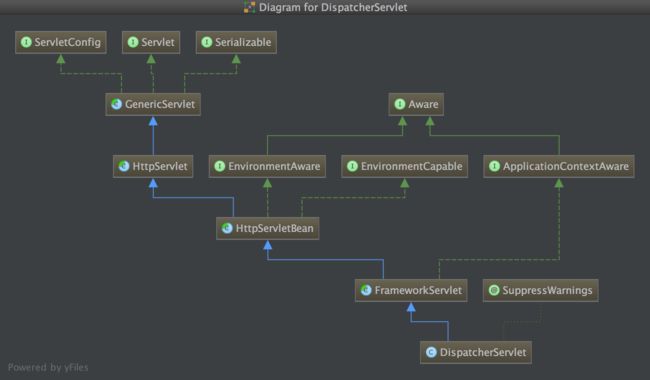
DispatcherServlet类图
通过类图可以看出,DispatcherServlet继承了FrameworkServlet和HttpServletBean。
HttpServletBean作用
HttpServletBean的作用主要是做一些初始化,将web.xml中配置的参数设置到Servlet中
//比如初始化init-param中的参数
contextConfigLocation classpath*:dispatcher-servlet.xml
//源码片段
HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues ex = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ServletContextResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(ex, true);
FrameworkServlet作用
FrameworkServlet的作用讲Servlet和Spring容器关联。其实也就是初始化FrameworkServlet的属性webApplicationContext,这个属性代表SpringMVC上下文,它有个父类上下文,既web.xml中配置的ContextLoaderListener监听器初始化的容器上下文。
//源码片段
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//这个设置springMVC的父类上下文为ContextLoaderListener初始化的容器上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if(this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if(wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext attrName = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac;
if(!attrName.isActive()) {
if(attrName.getParent() == null) {
attrName.setParent(rootContext);
}
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(attrName);
}
}
}
if(wac == null) {
wac = this.findWebApplicationContext();//一般返回的都是null
//具体实现,获取DispatcherServlet的applicationContext
//WebApplicationContext wac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext(), attrName);
}
if(wac == null) {
wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if(!this.refreshEventReceived) {
this.onRefresh(wac);
}
if(this.publishContext) {
//attrName1=org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT.dispatcher
String attrName1 = this.getServletContextAttributeName();
//新创建的容器上下文设置到ServletContext中
this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName1, wac);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet \'" + this.getServletName() + "\' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName1 + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
DispatcherServlet主要组建
DispatcherServlet覆写了FrameworkServlet中的onRefresh()方法,onRefresh()方法是钩子方法,子类可以重写自己特有的方法。
//初始化DispatcherServlet使用的策略
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
SpringMVC处理流程
简单的Demo
public class HelloWorldController implements Controller {
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
//1、收集参数、验证参数
//2、绑定参数到命令对象
//3、将命令对象传入业务对象进行业务处理
//4、选择下一个页面
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
//添加模型数据 可以是任意的POJO对象
mv.addObject("message", "Hello World!");
//设置逻辑视图名,视图解析器会根据该名字解析到具体的视图页面
mv.setViewName("hello");
return mv;
}
}
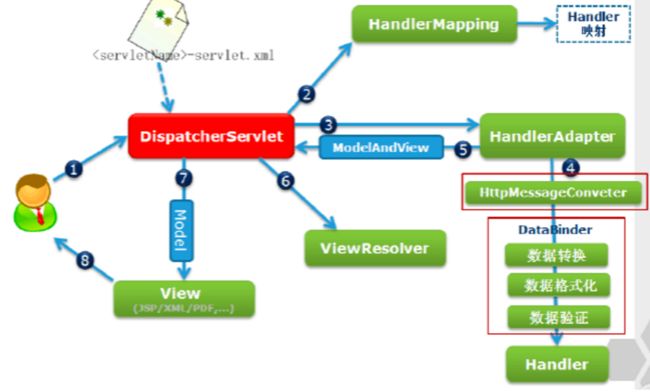
处理流程
处理流程图
用户将发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
处理器映射器找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView
HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器
ViewReslover解析后返回具体View
DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
DispatcherServlet响应用户
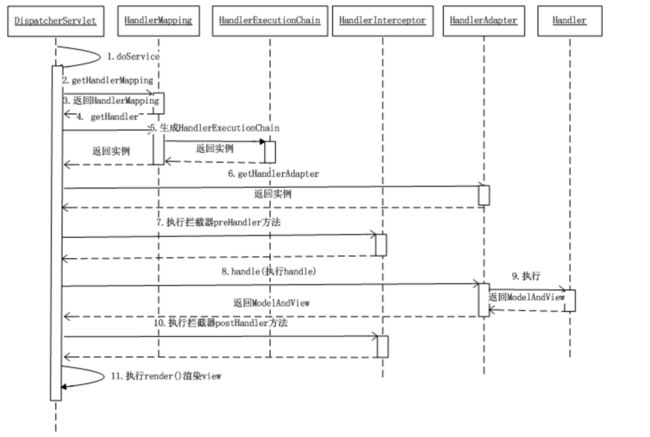
DispatcherServlet源码
DispatcherServlet中最主要的核心功能是由doService()和doDispatch()实现,接下来看一下他们的源码
//doService()
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = new UrlPathHelper().getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' processing request for [" + requestUri + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
logger.debug("Taking snapshot of request attributes before include");
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
//doDispatch()
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
int interceptorIndex = -1;
// Expose current LocaleResolver and request as LocaleContext.
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(buildLocaleContext(request), this.threadContextInheritable);
// Expose current RequestAttributes to current thread.
RequestAttributes previousRequestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request);
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Bound request context to thread: " + request);
}
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
boolean errorView = false;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Apply preHandle methods of registered interceptors.
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = mappedHandler.getInterceptors();
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())) {
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
return;
}
interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Do we need view name translation?
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
// Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler(), mv);
}
}
}
catch (ModelAndViewDefiningException ex) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", ex);
mv = ex.getModelAndView();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(processedRequest, response, handler, ex);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, processedRequest, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" +
getServletName() + "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
// Trigger after-completion for successful outcome.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Trigger after-completion for thrown exception.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
ServletException ex = new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err);
// Trigger after-completion for thrown exception.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (processedRequest != request) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
// Reset thread-bound context.
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(previousRequestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(previousLocaleContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
// Clear request attributes.
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Cleared thread-bound request context: " + request);
}
}
}
再说DispatcherServlet
- 从上面的处理流程可以看出DispatcherServlet主要负责流程的控制,它的主要职责如下:
- 文件上传解析,如果请求类型是multipart将通过MultipartResolver进行文件上传解析;
通过HandlerMapping,将请求映射到处理器(返回一个HandlerExecutionChain,它包括一个处理器、多个HandlerInterceptor拦截器);
通过HandlerAdapter支持多种类型的处理器(HandlerExecutionChain中的处理器);
通过ViewResolver解析逻辑视图名到具体视图实现;
本地化解析;
渲染具体的视图等;
如果执行过程中遇到异常将交给HandlerExceptionResolver来解析。
DispatcherServlet特殊中的Bean:
- Controller:处理器/页面控制器,做的是MVC中的C的事情,但控制逻辑转移到前端控制器了,用于对请求进行处理;
HandlerMapping:请求到处理器的映射,如果映射成功返回一个HandlerExecutionChain对象(包含一个Handler处理器(页面控制器)对象、多个HandlerInterceptor拦截器)对象;如BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping将URL与Bean名字映射,映射成功的Bean就是此处的处理器;
HandlerAdapter:HandlerAdapter将会把处理器包装为适配器,从而支持多种类型的处理器,即适配器设计模式的应用,从而很容易支持很多类型的处理器;如SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter将对实现了Controller接口的Bean进行适配,并且diao处理器的handleRequest方法进行功能处理;
ViewResolver:ViewResolver将把逻辑视图名解析为具体的View,通过这种策略模式,很容易更换其他视图技术;如InternalResourceViewResolver将逻辑视图名映射为jsp视图;
LocalResover:本地化解析,因为Spring支持国际化,因此LocalResover解析客户端的Locale信息从而方便进行国际化;
ThemeResovler:主题解析,通过它来实现一个页面多套风格,即常见的类似于软件皮肤效果;
MultipartResolver:文件上传解析,用于支持文件上传;
HandlerExceptionResolver:处理器异常解析,可以将异常映射到相应的统一错误界面,从而显示用户友好的界面(而不是给用户看到具体的错误信息);
RequestToViewNameTranslator:当处理器没有返回逻辑视图名等相关信息时,自动将请求URL映射为逻辑视图名;
FlashMapManager:用于管理FlashMap的策略接口,FlashMap用于存储一个请求的输出,当进入另一个请求时作为该请求的输入,通常用于重定向场景,后边会细述。
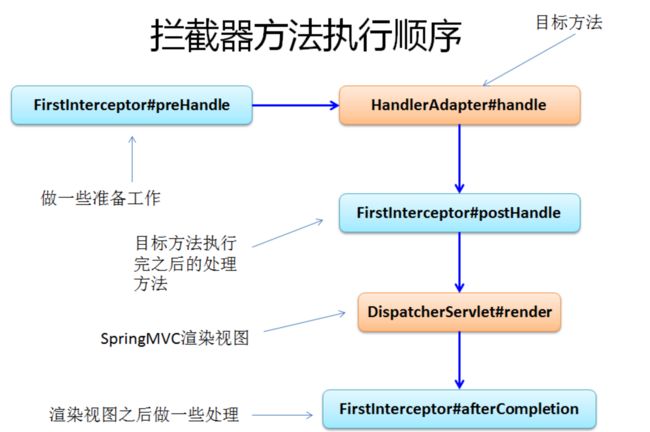
-
拦截器的处理流程