转载请标注出处: http://www.jianshu.com/p/8facd77fac09
Android DisplayList 构建过程 写了DisplayList的构建,接下来要做的事情就是开始渲染DisplayList了,具体的函数是nSyncAndDrawFrame , UI线程通过RenderProxy请求RenderThread执行一个DrawFrameTask, 然后阻塞式等着RenderThread的通知
void DrawFrameTask::postAndWait() {
AutoMutex _lock(mLock);
mRenderThread->queue(this);
mSignal.wait(mLock); //UI线程blocking等着 RenderThread的回应
}
当RenderThread调度到DrawFrameTask时会执行DrawFrameTask::run()函数。
void DrawFrameTask::run() {
bool canUnblockUiThread;
bool canDrawThisFrame;
{
TreeInfo info(TreeInfo::MODE_FULL, *mContext);
info.observer = mObserver;
canUnblockUiThread = syncFrameState(info); //同步DisplayList信息
canDrawThisFrame = info.out.canDrawThisFrame;
}
// Grab a copy of everything we need
CanvasContext* context = mContext;
if (canUnblockUiThread) {
//是否unblock ui线程, 有可能需要RenderThread在这一帧画完后才unblock ui thread
unblockUiThread();
}
if (CC_LIKELY(canDrawThisFrame)) {
context->draw();
}
if (!canUnblockUiThread) { //与上面的 if(canUnblockUiThread)相反,肯定最后都会unblock ui的,否则就会发生ANR了
unblockUiThread();
}
}
上面的run函数包含两个动作,一是sync DisplayList的动作,一个是渲染DisplayList的动作,这篇blog仅分析 DisplayList同步的过程
注意: 这里并不考虑Texture, Layer相关, 那么syncFrameState简化后的代码如下,
bool DrawFrameTask::syncFrameState(TreeInfo& info) {
// mFrameInfo是一个int形数组,它主要记录事件发生的各种时刻,
// 比如接收到vsync时间, draw start时间等等
int64_t vsync = mFrameInfo[static_cast(FrameInfoIndex::Vsync)];
mRenderThread->timeLord().vsyncReceived(vsync);
bool canDraw = mContext->makeCurrent();
mContext->prepareTree(info, mFrameInfo, mSyncQueued, mTargetNode);
// If prepareTextures is false, we ran out of texture cache space
return info.prepareTextures;
}
其中 makeCurrent()函数直接调用了eglMakeCurrent,
eglMakeCurrent(mEglDisplay, mEglSurface, mEglSurface, mEglContext)
该接口将申请到的display,draw(surface)和 egl context进行了绑定。也就是说,在egl context下的OpenGL API指令将draw(surface)作为其渲染最终目的地, 而display作为draw(surface)的前端显示。调用后,当前线程使用的EGLContex为mEglContext. 参考这篇文章
而参数 TreeInfo是个临时变量,它的初始化在 DrawFrameTask::run()
TreeInfo info(TreeInfo::MODE_FULL, *mContext);
如果传入的就 MODE_FULL, TreeInfo里的成员prepareTextures将会置为true, 因为本例代码并不涉及到Texture相关,所以返回值 info.prepareTextures始终为true.
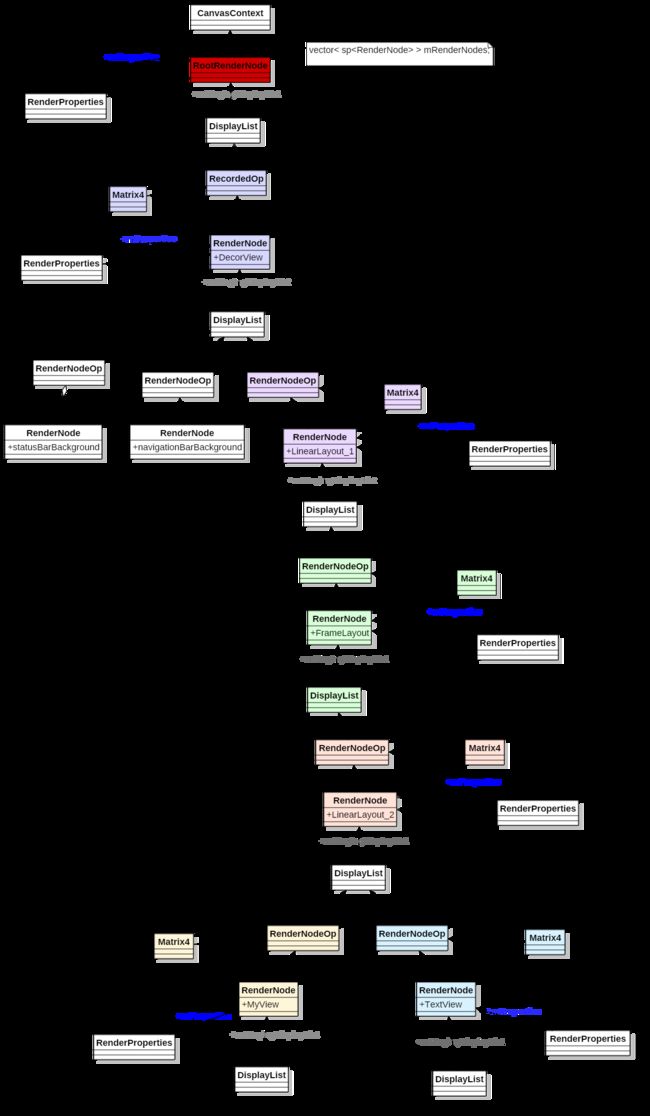
syncFrameState接着开始 prepareTree, 它从CanvasContext开始调用. 如图所示, 就是递归遍历整个Tree.
void CanvasContext::prepareTree(TreeInfo& info, int64_t* uiFrameInfo,
int64_t syncQueued, RenderNode* target) {
info.damageAccumulator = &mDamageAccumulator;
for (const sp& node : mRenderNodes) {
// info.mode 依然是MODE_FULL
info.mode = (node.get() == target ? TreeInfo::MODE_FULL : TreeInfo::MODE_RT_ONLY);
node->prepareTree(info);
}
}
CanvasContext里的mRenderNodes是一个Vector,也就是它储存了一系列的RenderNode, 但是这个盒子只有一个RenderNode, 也就是整个UI的RootRenderNode.
void RenderNode::prepareTree(TreeInfo& info) {
prepareTreeImpl(info, functorsNeedLayer);
}
void RenderNode::prepareTreeImpl(TreeInfo& info, bool functorsNeedLayer) {
info.damageAccumulator->pushTransform(this);
if (info.mode == TreeInfo::MODE_FULL) {
pushStagingPropertiesChanges(info);
}
...
if (info.mode == TreeInfo::MODE_FULL) {
pushStagingDisplayListChanges(info);
}
prepareSubTree(info, childFunctorsNeedLayer, mDisplayList);
info.damageAccumulator->popTransform();
}
由prepareTreeImpl的实现看出,先同步 当前的 RenderNode, 然后再递归同步子RenderNode.
一、同步RenderProperties和DisplayList
1.1 pushStagingPropertiesChanges
void RenderNode::pushStagingPropertiesChanges(TreeInfo& info) {
if (mDirtyPropertyFields) {
mDirtyPropertyFields = 0;
damageSelf(info);
info.damageAccumulator->popTransform();
syncProperties();
info.damageAccumulator->pushTransform(this);
damageSelf(info);
}
}
mDirtyPropertyFields是一个int变量,它的每一位都表示一种Dirty的类型, 只要RenderNode中 RenderProperties(mStagingProperties表示,该值由UI线程维护)发生变化时,mDirtyPropertyFields就不为0,就表示要同步该Properties.
而同步的方法就是 mProperties = mStagingProperties
其中 mProperites由RenderThread线程维护, 而mStagingProperties由 UI线程维护.
1.2 pushStagingDisplayListChanges
void RenderNode::pushStagingDisplayListChanges(TreeInfo& info) {
mNeedsDisplayListSync = false;
damageSelf(info);
syncDisplayList(&info);
damageSelf(info);
}
}
当Java层调用RenderNode.end()后,就会将Canvas中的DisplayList更新到RenderNode中的mStagingDisplayList中,具体参考 Android DisplayList 构建过程第三节。
同时会将 mNeedDisplayListSync置为true, 这样,在sync的时候就会去同步DisplayList, 同步过程如下所示.
void RenderNode::syncDisplayList(TreeInfo* info) {
// Make sure we inc first so that we don't fluctuate between 0 and 1,
// which would thrash the layer cache
if (mStagingDisplayList) {
for (auto&& child : mStagingDisplayList->getChildren()) {
child->renderNode->incParentRefCount(); //增加parent的引用计数
}
}
deleteDisplayList(info ? info->observer : nullptr, info);
mDisplayList = mStagingDisplayList; //重新赋值
mStagingDisplayList = nullptr;
...
}
从代码中看出,在同步DisplayList后,UI线程维护的mStagingDisplayList就被重新置为null了。而 RenderThread 维护的mDisplayList指向了UI线程的mStagingDisplayList.
二、递归同步子RenderNode
void RenderNode::prepareSubTree(TreeInfo& info, bool functorsNeedLayer, DisplayList* subtree) {
if (subtree) {
for (auto&& op : subtree->getChildren()) {
RenderNode* childNode = op->renderNode;
info.damageAccumulator->pushTransform(&op->localMatrix);
childNode->prepareTreeImpl(info, childFunctorsNeedLayer);
info.damageAccumulator->popTransform();
}
}
}
RenderNode在同步完自己的RenderProperties和DisplayList后,开始递归同步子RenderNode信息。
就这样就把整个DisplayTree的信息从UI thread同步到了RenderThread.
三、计算脏区域
3.1 damageSelf()
damageSelf在同步Properties和DisplayList时被调用了两次。
damageSelf这个函数从字面上理解就是"自毁",那自毁什么呢?从函数定义来看
void RenderNode::damageSelf(TreeInfo& info) {
if (isRenderable()) {
if (properties().getClipDamageToBounds()) {
info.damageAccumulator->dirty(0, 0, properties().getWidth(), properties().getHeight());
} else {
info.damageAccumulator->dirty(DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MAX, DIRTY_MAX);
}
}
}
damageSelf()是RenderNode里面的函数,猜想这个自毁应该是和RenderNode相关。
- 自毁的前提
damageSelf要工作的一个前提就是 RenderNode是可Renderable (isRenderable())的,从 isRenderable函数定义可以看出,也就是当前的RenderNode已经同步过DisplayList(pushStagingDisplayListChanges),并且这个DisplayList里有绘制命令。
- 自毁什么?
从if else可以看出,自毁是调用DamageAccumulator->dirty
void DamageAccumulator::dirty(float left, float top, float right, float bottom) {
mHead->pendingDirty.join(left, top, right, bottom);
}
原来是将mHead的pendingDirty与自毁的区域求并集(具体可以查看 join函数),
DirtyStack* mHead
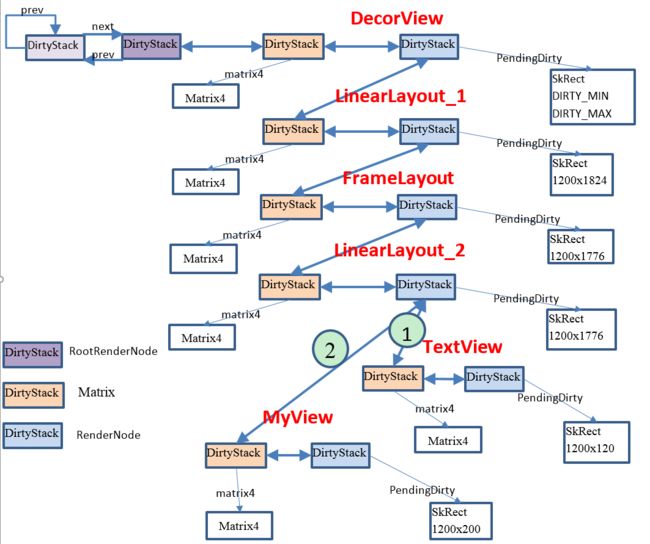
mHead是在DamageAccumulator里定义的,DamageAccumulator里维护着一个栈,栈顶由mHead指定。
整个DamageAccumulator的栈图如下所示
damageSelf()函数会计算出 图中浅蓝色背景方块的 pendingDirty, 也就是脏区域. 注意这幅图是针对第一次同步时的栈图。
- 为什么damageSelf都调用两次呢?
从 1.2 的pushStagingPropertiesChanges和 1.3 的 pushStagingDisplayListChanges可以看出,这两个函数都分别调用了两次 damageSelf(), 为什么呢?
pushStagingPropertiesChanges和pushStagingDisplayListChanges都是从UI线程同步相应的信息到RenderThread线程,那说明RenderThread的线程里保存的是旧数据,而UI线程是新数据,
既然是求脏区域,那么不能只求新数据的脏区域啊,比如,如果一个操作是将View从 1200x300(旧数据) 缩小到1200x150(新数据), 那么这块脏区域是多少呢? 1200x150?这显然不对了吧,数据从1200x300变换到1200x150, 那么整个脏区域就应该是它们的并集,1200x300.
所以调用两次damageSelf,第一次是针对旧数据,得到一个脏区域,第二次是针对新数据,然后再计算它们的并集也就是整个脏区域。
- 脏区域的大小
这个就具体参考 getClipDamageToBounds了,它的意思是说是否可以裁剪脏区域到固定的区域, 如果可以的话,那么就将脏区域裁剪到 View的 Width和Height.
3.2 push/pop Transform
pushTransform与popTransform都是成对出现的,它们是DamageAccumulator里的成员函数,
pushTransform有两种定义
pushTransform(const RenderNode* transform)
这种函数形式在prepareTreeImpl中调用,主要是将当前的RenderNode push进栈pushTransform(const Matrix4* transform)
这种函数形式在prepareSubTree中调用,主要是将RenderNodeOp中的localMatrix进栈popTransform()
这个就是出栈的操作
通过pushTransform操作就形成了图2 DamageAccumulator的栈图
图中1和2是子view, 它们本就没有子children,所以栈的操作是先对TextView入栈,待TextView的DisplayList与RenderProperties更新完后就会依次对TextView的RenderNode pop,然后对TextView的matrix4 pop.
那么popTransform的操作是干什么的呢?
void DamageAccumulator::popTransform() {
DirtyStack* dirtyFrame = mHead;
mHead = mHead->prev;
switch (dirtyFrame->type) {
case TransformRenderNode:
applyRenderNodeTransform(dirtyFrame);
break;
case TransformMatrix4:
applyMatrix4Transform(dirtyFrame);
break;
case TransformNone:
mHead->pendingDirty.join(dirtyFrame->pendingDirty);
break;
default:
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("Tried to pop an invalid type: %d", dirtyFrame->type);
}
}
从代码可以看出来,先将栈顶元素出栈得到 dirtyFrame, 然后再重新assign 栈顶, 接着针对dirtyFrame的类型再作具体的变换。
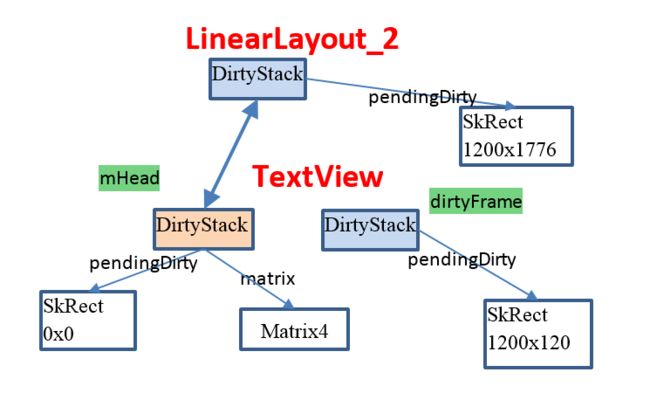
以TextView为例
TransformRenderNode
void DamageAccumulator::applyRenderNodeTransform(DirtyStack* frame) {
if (frame->pendingDirty.isEmpty()) { //此时的frame为图中的dirtyFrame, 可以看出它的pendingDirty不为空
return;
}
const RenderProperties& props = frame->renderNode->properties();
if (props.getAlpha() <= 0) { //如果 alpha是透明的,那么就没必要继续计算脏区域了,
return;
}
// Perform clipping
if (props.getClipDamageToBounds() && !frame->pendingDirty.isEmpty()) {
//进入分支,
if (!frame->pendingDirty.intersect(0, 0, props.getWidth(), props.getHeight())) {
frame->pendingDirty.setEmpty();
}
}
// apply all transforms
mapRect(props, frame->pendingDirty, &mHead->pendingDirty);
...
}
- getAlpha() <=0
那说明这个是透明的属性, 透明的意思就是不显示? 就不需要应用这些矩阵变换了 - frame->pendingDirty.intersect()
这个是求交集的意思,pendingDirty的区域是 (0, 0, 1200, 120), 而props,getWidth(), props.getHeight()分别也是1200, 120
接下来看mapRect, frame->pendingDrity这块区域是(0, 0, 1200, 120), 而mHead->pendingDirty是图3中浅黄色的pendingDirty (0, 0, 0, 0)
static inline void mapRect(const RenderProperties& props, const SkRect& in, SkRect* out) {
if (in.isEmpty()) return;
const SkMatrix* transform = props.getTransformMatrix();
SkRect temp(in);
if (transform && !transform->isIdentity()) { //不会进入该分支
if (CC_LIKELY(!transform->hasPerspective())) {
transform->mapRect(&temp);
} else {
// Don't attempt to calculate damage for a perspective transform
// as the numbers this works with can break the perspective
// calculations. Just give up and expand to DIRTY_MIN/DIRTY_MAX
temp.set(DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MAX, DIRTY_MAX);
}
}
temp.offset(props.getLeft(), props.getTop());
out->join(temp);
}
- isIdentity()
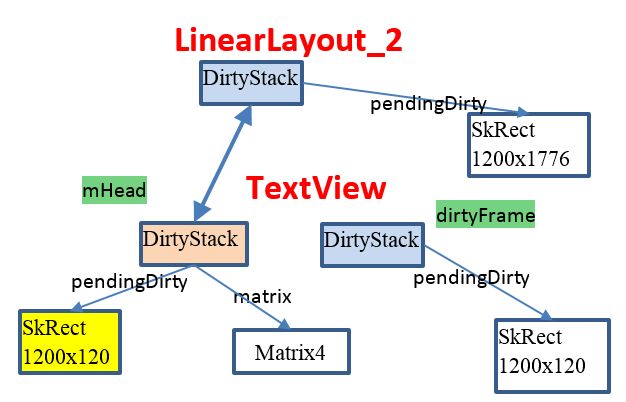
这个判断是否是单位矩阵,一般都是单位矩阵, 所以并不会进入 if分支. 所以最后out的区域大小为(0, 0, 1200, 120). 也就是mHead->pendingDirty,也就是下图黄色块区域
TransformMatrix4
void DamageAccumulator::applyMatrix4Transform(DirtyStack* frame) {
mapRect(frame->matrix4, frame->pendingDirty, &mHead->pendingDirty);
}
static inline void mapRect(const Matrix4* matrix, const SkRect& in, SkRect* out) {
if (in.isEmpty()) return;
Rect temp(in);
if (CC_LIKELY(!matrix->isPerspective())) {
matrix->mapRect(temp);
} else {
// Don't attempt to calculate damage for a perspective transform
// as the numbers this works with can break the perspective
// calculations. Just give up and expand to DIRTY_MIN/DIRTY_MAX
temp.set(DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MAX, DIRTY_MAX);
}
out->join(RECT_ARGS(temp));
}
那么现在TextView相关的栈图如下所示
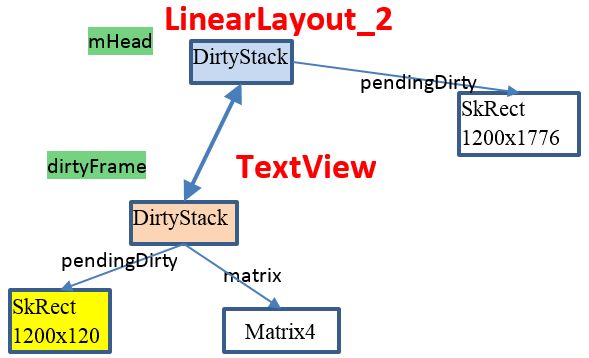
此时 mHead指向LinearLayout_2, dirtyFrame指向浅黄色的DirtyStack.
即 frame->pendingDirty 区域是(0, 0, 1200, 120), mHead->pendingDirty (0, 0, 1200, 1776),
代码中 isPerspective() 这个意思是判断矩阵是否是投影矩阵。在一般的矩阵都不是投影矩阵,所以一般会进入 if分支 matrix->mapRect(temp), 最后再和out( mHead->pendingDirty)求并集, 最后的out(mHead->pendingDirty)的pendingDirty依然还是 (0, 0, 1200, 1776)
四、小结
经过1, 2小节后,整个DisplayList tree都同步更新了,并且经过3 算出来整张画布的脏区域, 因为是第一次同步,所以这里算出来的脏区域为默认的最大画布(DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MIN, DIRTY_MAX, DIRTY_MAX), 且它的值保存在DamageAccumulator.mHead->pendingDirty中.
可以看出, syncFrameState就完成两件事,一件是从UI线程同步 RenderProperties和DisplayList 到RenderThread线程,第二件事就是计算出画面的脏区域。