关键词:Python;循环技巧;map();filter();reduce()
1、循环技巧
在字典中循环时,关键字和对应的值可以使用 items() 方法同时解读出来:
>>> knights = {'gallahad': 'the pure', 'robin': 'the brave'}
>>> for k, v in knights.items():
... print(k, v)
...
gallahad the pure
robin the brave
在序列中循环时,索引位置和对应值可以使用enumerate() 函数同时得到:
>>> for i, v in enumerate(['tic', 'tac', 'toe']):
... print(i, v)
...
0 tic
1 tac
2 toe
同时循环两个或更多的序列,可以使用 zip() 整体打包:
>>> questions = ['name', 'quest', 'favorite color']
>>> answers = ['lancelot', 'the holy grail', 'blue']
>>> for q, a in zip(questions, answers):
... print('What is your {0}? It is {1}.'.format(q, a))
...
What is your name? It is lancelot.
What is your quest? It is the holy grail.
What is your favorite color? It is blue.
需要逆向循环序列的话,先正向定位序列,然后调用 reversed() 函数:
>>> for i in reversed(range(1, 10, 2)):
... print(i)
...
9
7
5
3
1
要按排序后的顺序循环序列的话,使用 sorted() 函数,它不改动原序列,而是生成一个新的已排序的序列:
>>> basket = ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'pear', 'orange', 'banana']
>>> for f in sorted(set(basket)):
... print(f)
...
apple
banana
orange
pear
若要在循环内部修改正在遍历的序列(例如复制某些元素),建议您首先制作副本。在序列上循环不会隐式地创建副本。切片表示法使这尤其方便,切片表示方法创建了words的复本。这个要求循环的列表要能够增加的。
>>> words = ['cat', 'window', 'defenestrate']
>>> for w in words[:]: # Loop over a slice copy of the entire list.
... if len(w) > 6:
... words.insert(0, w)
...
>>> words
['defenestrate', 'cat', 'window', 'defenestrate']
2、特殊高阶函数
map(func, list):
map 本身接收 2 个参数:一个函数、一个列表, 将 func 作用在 list 中的每一个元素上并返回一个新的 list
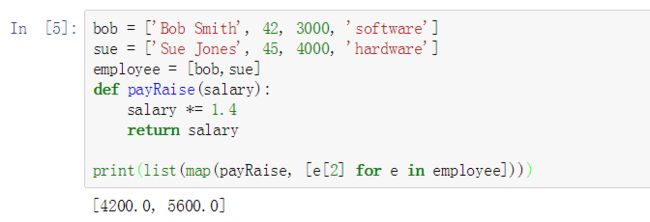
Ex: 我们要将公司每个人的薪水提高 40% 并打印出来,就可以这样完成
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
bob = ['Bob Smith', 42, 3000, 'software']
sue = ['Sue Jones', 45, 4000, 'hardware']
employee = [bob,sue]
def payRaise(salary):
salary *= 1.4
return salary
print(list(map(payRaise, [e[2] for e in employee]))) # 这里用到了列表解析器
# 打印结果为:[4200.0, 5600.0]
reduce(func, list):
reduce 本身接收 2 个参数:一个函数、一个列表,与 map 不同之处在于 map 接收的函数只能接收一个参数,而 reduce 接收的函数只能接收2个参数,reduce 依次反复对 list 中每一个元素进行 func 操作,并将最终结果返回
Ex:我们要将一个列表中所有的数求和,就可以这样完成
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from functools import reduce
# 在 Python 3 里,reduce()函数已经被从全局名字空间里移除了,它现在被放置在 fucntools 模块里,用的话要先导入
score = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
def mySum(a, b):
return a + b
print(reduce(mySum, score))
# 打印结果为:28
filter(func, list):
filter 本身也接受2个参数:一个函数,一个列表, 将 func 作用在 list 中的每一个元素上进行判断,将判断结果为 True 的元素返回,并生成一个生成器对象
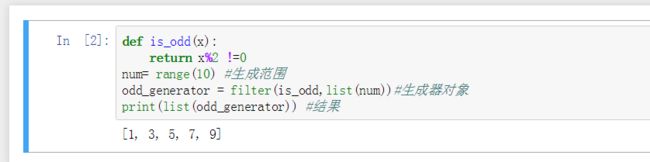
Ex:我们要得到 1-100 里面所有的奇数,就可以这样完成
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def is_odd(x):
return x % 2 != 0
num = range(10) # python 3 中 range 函数返回生成器对象
odd_generator = filter(is_odd, list(num)) # filter 函数然会生成器对象
print(list(odd_generator)) # 打印列表
# 打印结果为:0-10 所有奇数
Python学习资源:
W3C Python教程
Python中文学习大本营
Jupyter
参考出处: 谢烟客:说说那些我也不太懂的 Python 高阶函数