1.建造者模式
Builder Pattern使用多个简单的对象一步一步构建成一个复杂的对象。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
- Builder:给出一个抽象接口,以规范产品对象的各个组成成分的建造。这个接口规定要实现复杂对象的哪些部分的创建,并不涉及具体的对象部件的创建;
ConcreteBuilder:实现Builder接口,针对不同的商业逻辑,具体化复杂对象的各部分的创建。在建造过程完成后,提供产品的实例;
Director:调用具体建造者来创建复杂对象的各个部分,在指导者中不涉及具体产品的信息,只负责保证对象各部分完整创建或按某种顺序创建;
Product:要创建的复杂对象。
建造者模式使用场景:
- 需要生成的对象具有复杂的内部结构,实例化对象时要屏蔽掉对象内部细节,让上层代码与复杂对象的实例化过程解耦,可以使用建造者模式。简而言之,如果遇到多个构造器参数时要考虑用建造者模式。
- 一个对象的实例化是依赖各个组件的产生以及装配顺序,关注的是一步一步地组装出目标对象,可以使用建造者模式。
与工厂模式区别:
- 对象复杂度
建造者建造的对象更加负责,是一个复合产品,它由各个部件复合而成,部件不同产品对象不同,生成的产品粒度细;
在工厂方法模式里,关注的是一个产品整体,无须关心产品的各部分是如何创建出来的。 - 客户端参与程度
建造者模式,导演对象参与了产品的创建,决定了产品的类型和内容,参与度高,适合实例化对象时属性变化频繁的场景;
工厂模式,客户端对产品的创建过程参与度低,对象实例化时属性值相对比较固定。
2.建造者模式实例
建造者模式参考代码
2.1 Builder抽象接口
public interface RedPacketBuilder {
RedPacketBuilder setPublisherName(String publishName);
RedPacketBuilder setAcceptName(String acceptName);
RedPacketBuilder setPacketAmount(BigDecimal packetAmount);
RedPacketBuilder setPacketType(int packetType);
RedPacketBuilder setPulishPacketTime(Date pushlishPacketTime);
RedPacketBuilder setOpenPacketTime(Date openPacketTime);
RedPacket build();
}
2.2 实际的Builder
注意点:
1)RedPacketBuilderImpl包含RedPacket的所有域
2)set方法设置一个域,并且返回this,这是流式编程的关键
3)最后build调用一个完整包含所有域的RedPacket构造函数
public class RedPacketBuilderImpl implements RedPacketBuilder {
private String publisherName;
private String acceptName;
private BigDecimal packetAmount;
private int packetType;
private Date pulishPacketTime;
private Date openPacketTime;
public static RedPacketBuilderImpl getBulider(){
return new RedPacketBuilderImpl();
}
@Override
public RedPacketBuilder setPublisherName(String publishName) {
this.publisherName = publishName;
return this;
}
@Override
public RedPacketBuilder setAcceptName(String acceptName) {
this.acceptName = acceptName;
return this;
}
@Override
public RedPacketBuilder setPacketAmount(BigDecimal packetAmount) {
this.packetAmount = packetAmount;
return this;
}
@Override
public RedPacketBuilder setPacketType(int packetType) {
this.packetType = packetType;
return this;
}
@Override
public RedPacketBuilder setPulishPacketTime(Date pushlishPacketTime) {
this.pulishPacketTime = pushlishPacketTime;
return this;
}
@Override
public RedPacketBuilder setOpenPacketTime(Date openPacketTime) {
this.openPacketTime = openPacketTime;
return this;
}
public RedPacket build() {
return new RedPacket(publisherName,acceptName,packetAmount,packetType,pulishPacketTime,openPacketTime);
}
}
2.3 具体的对象类
public class RedPacket {
private String publisherName; //发包人
private String acceptName; //手包人
private BigDecimal packetAmount; //红包金额
private int packetType; //红包类型
private Date pulishPacketTime; //发包时间
private Date openPacketTime; //抢包时间
public RedPacket(String publisherName, String acceptName, BigDecimal packetAmount, int packetType, Date pulishPacketTime, Date openPacketTime) {
this.publisherName = publisherName;
this.acceptName = acceptName;
this.packetAmount = packetAmount;
this.packetType = packetType;
this.pulishPacketTime = pulishPacketTime;
this.openPacketTime = openPacketTime;
}
public String getPublisherName() {
return publisherName;
}
public void setPublisherName(String publisherName) {
this.publisherName = publisherName;
}
public String getAcceptName() {
return acceptName;
}
public void setAcceptName(String acceptName) {
this.acceptName = acceptName;
}
public BigDecimal getPacketAmount() {
return packetAmount;
}
public void setPacketAmount(BigDecimal packetAmount) {
this.packetAmount = packetAmount;
}
public int getPacketType() {
return packetType;
}
public void setPacketType(int packetType) {
this.packetType = packetType;
}
public Date getPulishPacketTime() {
return pulishPacketTime;
}
public void setPulishPacketTime(Date pulishPacketTime) {
this.pulishPacketTime = pulishPacketTime;
}
public Date getOpenPacketTime() {
return openPacketTime;
}
public void setOpenPacketTime(Date openPacketTime) {
this.openPacketTime = openPacketTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RedPacket [publisherName=" + publisherName + ", acceptName="
+ acceptName + ", packetAmount=" + packetAmount
+ ", packetType=" + packetType + ", pulishPacketTime="
+ pulishPacketTime + ", openPacketTime=" + openPacketTime + "]";
}
}
2.4 导演
public class Director {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedPacket redPacket = RedPacketBuilderImpl.getBulider().setPublisherName("lison")
.setAcceptName("vip群")
.setPacketAmount(new BigDecimal("888"))
.setPacketType(1)
.setOpenPacketTime(new Date())
.setPulishPacketTime(new Date()).build();
System.out.println(redPacket);
}
}
结果:
RedPacket [publisherName=lison, acceptName=vip群, packetAmount=888, packetType=1, pulishPacketTime=Thu Sep 27 16:44:44 CST 2018, openPacketTime=Thu Sep 27 16:44:44 CST 2018]
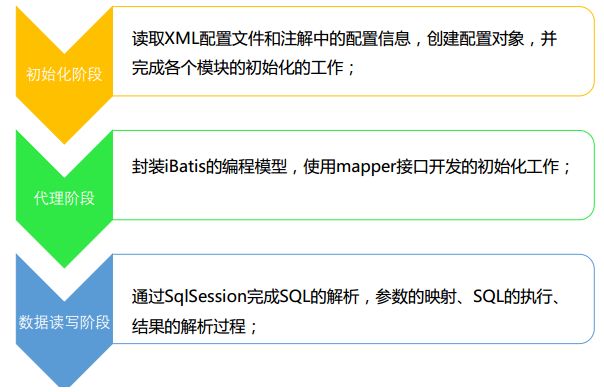
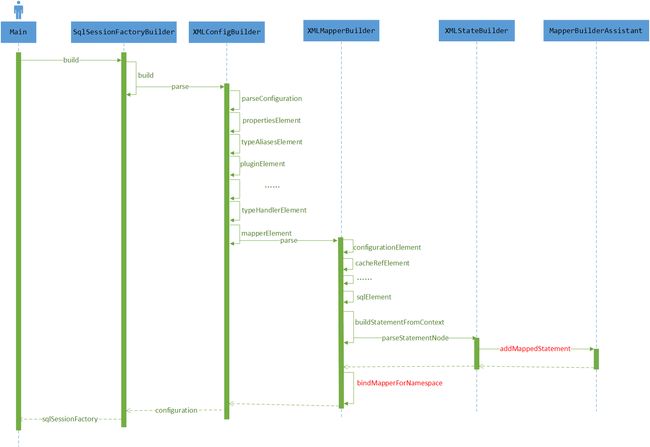
3.MyBatis的初始化
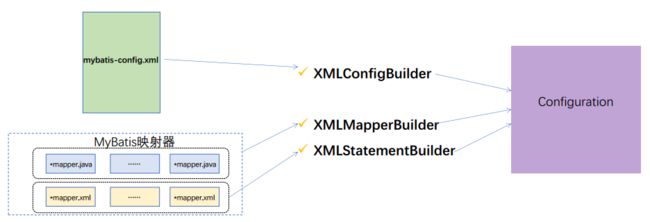
- XMLConfigBuilder:主要负责解释mybatis-config.xml
XMLMapperBuilder:负责解析映射配置文件
XMLStatementBuilder:负责解析映射配置文件中的SQL结点
3.1 映射器的关键类
- Configuration:Mybatis启动初始化的核心就是将所有xml配置文件信息加载到Configuration对象中,Configuration是单例的,生命周期是应用级的
- MapperRegistry:mapper接口动态代理工厂类的注册中心。在Mybatis中,通过mapperProxy实现InvocationHandler接口,MapperProxyFactory用于生成动态代理的实例对象
- ResultMap:用于解析mapper.xml文件中的resultMap节点,使用ResultMapping来封装id、result等子元素
- MappedStatement:用于存储mapper.xml文件中的select、insert、update和delete节点,同时还包含了这些节点很多重要属性
- SqlSource:mapper.xml文件中sql语句会被解析成SqlSource对象,经过解析SqlSource包含的语句最终仅仅包含?占位符,可以直接交给数据库执行。
3.2 Configuration的域对应mybatis-config.xml中相应的配置项
public class Configuration {
protected Environment environment;
/* 是否启用数据组A_column自动映射到Java类中的驼峰命名的属性**/
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
/*当对象使用延迟加载时 属性的加载取决于能被引用到的那些延迟属性,否则,按需加载(需要的是时候才去加载)**/
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
/*是否允许单条sql 返回多个数据集 (取决于驱动的兼容性) default:true **/
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
/*-允许JDBC 生成主键。需要驱动器支持。如果设为了true,这个设置将强制使用被生成的主键,有一些驱动器不兼容不过仍然可以执行。 default:false**/
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
/*配置全局性的cache开关,默认为true**/
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
/*指定 MyBatis 应如何自动映射列到字段或属性*/
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
/*MyBatis每次创建结果对象的新实例时,它都会使用对象工厂(ObjectFactory)去构建POJO*/
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
/*延迟加载的全局开关*/
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
/*指定 Mybatis 创建具有延迟加载能力的对象所用到的代理工具*/
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); // #224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL
/*插件集合*/
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
/*TypeHandler注册中心*/
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry();
/*TypeAlias注册中心*/
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
//-------------------------------------------------------------
/*mapper接口的动态代理注册中心*/
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
/*mapper文件中增删改查操作的注册中心*/
protected final Map mappedStatements = new StrictMap<>("Mapped Statements collection");
/*mapper文件中配置的所有resultMap对象 key为命名空间+ID*/
protected final Map resultMaps = new StrictMap<>("Result Maps collection");
protected final Map parameterMaps = new StrictMap<>("Parameter Maps collection");
/*加载到的所有*mapper.xml文件*/
protected final Set loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
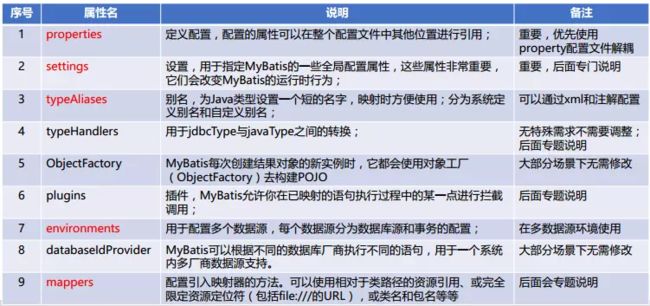
3.3 XMLConfigBuilder解析mybatis-config.xml,将解析出的相关的值加入到Configuration对象中
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.读取mybatis配置文件创SqlSessionFactory
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
具体的解析方法:
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
//解析节点
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//解析节点
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
//解析节点
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//解析节点
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//解析节点
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
//解析节点
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
//解析节点
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);//将settings填充到configuration
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//解析节点
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//解析节点
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
//解析节点
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//解析节点
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
3.4 XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper.xml映射文件
解析方法:
//解析节点
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件:
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {//处理mapper子节点
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {//package子节点
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {//获取节点的resource、url或mClass属性这三个属性互斥
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {//如果resource不为空
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);//加载mapper文件
//实例化XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {//如果url不为空
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);//加载mapper文件
//实例化XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {//如果class不为空
Class mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);//加载class对象
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);//向代理中心注册mapper
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
public void parse() {
//判断是否已经加载该配置文件
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));//处理mapper节点
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);//将mapper文件添加到configuration.loadedResources中
bindMapperForNamespace();//注册mapper接口
}
//处理解析失败的ResultMap节点
parsePendingResultMaps();
//处理解析失败的CacheRef节点
parsePendingCacheRefs();
//处理解析失败的Sql语句节点
parsePendingStatements();
}
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
//获取mapper节点的namespace属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
//设置builderAssistant的namespace属性
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
//解析cache-ref节点
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
//重点分析 :解析cache节点----------------1-------------------
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//解析parameterMap节点(已废弃)
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//重点分析 :解析resultMap节点(基于数据结果去理解)----------------2-------------------
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析sql节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//重点分析 :解析select、insert、update、delete节点 ----------------3-------------------
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
解析mapper.xml文件,例如TUserMapper.xml:
3.4.1 解析缓存节点cache
//重点分析 :解析cache节点----------------1-------------------
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//获取cache节点的type属性,默认为PERPETUAL
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
//找到type对应的cache接口的实现
Class typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
//读取eviction属性,既缓存的淘汰策略,默认LRU
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
//根据eviction属性,找到装饰器
Class evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
//读取flushInterval属性,既缓存的刷新周期
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
//读取size属性,既缓存的容量大小
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
//读取readOnly属性,既缓存的是否只读
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
//读取blocking属性,既缓存的是否阻塞
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//通过builderAssistant创建缓存对象,并添加至configuration
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
//通过builderAssistant创建缓存对象,并添加至configuration
public Cache useNewCache(Class typeClass,
Class evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
//经典的建造起模式,创建一个cache对象
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
//将缓存添加至configuration,注意二级缓存以命名空间为单位进行划分
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
3.4.2 解析resultMap(整体思路都是一样的)
//重点分析 :解析resultMap节点(基于数据结果去理解)----------------2-------------------
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析resultMap节点,实际就是解析sql查询的字段与pojo属性之间的转化规则
private void resultMapElements(List list) throws Exception {
//遍历所有的resultmap节点
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
try {
//解析具体某一个resultMap节点
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ignore, it will be retried
}
}
}
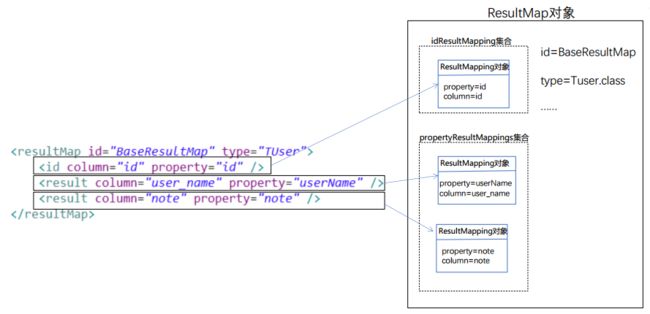
用来存储resultMap节点的ResultMap对象:
public class Configuration {
/*mapper文件中配置的所有resultMap对象 key为命名空间+ID*/
protected final Map resultMaps = new StrictMap<>("Result Maps collection");
public class ResultMap {
private Configuration configuration;//configuration对象
private String id;//resultMap的id属性
private Class type;//resultMap的type属性
private List resultMappings;//除discriminator节点之外的映射关系
private List idResultMappings;//记录ID或者中idArg的映射关系
private List constructorResultMappings;////记录标志的映射关系
private List propertyResultMappings;//记录非标志的映射关系
private Set mappedColumns;//记录所有有映射关系的columns字段
private Set mappedProperties;//记录所有有映射关系的property字段
private Discriminator discriminator;//鉴别器,对应discriminator节点
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;//是否有嵌套结果映射
private boolean hasNestedQueries;////是否有嵌套查询
private Boolean autoMapping;//是否开启了自动映射
public class ResultMapping {
private Configuration configuration;//引用的configuration对象
private String property;//对应节点的property属性
private String column;//对应节点的column属性
private Class javaType;//对应节点的javaType属性
private JdbcType jdbcType;//对应节点的jdbcType属性
private TypeHandler typeHandler;//对应节点的typeHandler属性
private String nestedResultMapId;////对应节点的resultMap属性,嵌套结果时使用
private String nestedQueryId;////对应节点的select属性,嵌套查询时使用
private Set notNullColumns;//对应节点的notNullColumn属性
private String columnPrefix;//对应节点的columnPrefix属性
private List flags;//标志,id 或者 constructor
private List composites;
private String resultSet;//对应节点的resultSet属性
private String foreignColumn;//对应节点的foreignColumn属性
private boolean lazy;//对应节点的fetchType属性,是否延迟加载
3.4.3 XMLStatementBuilder解析SQL语句
//重点分析 :解析select、insert、update、delete节点 ----------------3-------------------
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
//解析select、insert、update、delete节点
private void buildStatementFromContext(List list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
//处理所有的sql语句节点并注册至configuration对象
private void buildStatementFromContext(List list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
//创建XMLStatementBuilder 专门用于解析sql语句节点
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
//解析sql语句节点
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
增删改查sql语句对应的对象MappedStatement:
4.Configuration建造过程的总结
4.1 建造者模式的灵魂
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
//实例化XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
XMLConfigBuilder,XMLMapperBuilder和XMLStatementBuilder整体层次上并没有采用建造者的流式编程风格,但是采用了建造者模式的灵魂,因为这三个建造者分别构建了Configuration对象的不同部分。
4.2 MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant调用经典的建造者模式
//通过builderAssistant创建缓存对象,并添加至configuration
public Cache useNewCache(Class typeClass,
Class evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
//经典的建造起模式,创建一个cache对象
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
//将缓存添加至configuration,注意二级缓存以命名空间为单位进行划分
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
经典建造者模式CacheBuilder:
public class CacheBuilder {
public Cache build() {
//设置缓存的主实现类为PerpetualCache
setDefaultImplementations();
//通过反射实例化PerpetualCache对象
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);//根据cache节点下的信息,初始化cache
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {//如果cache是PerpetualCache的实现,则为其添加标准的装饰器
for (Class decorator : decorators) {//为cache对象添加装饰器,这里主要处理缓存清空策略的装饰器
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
//通过一些属性为cache对象添加装饰器
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
//如果cache不是PerpetualCache的实现,则为其添加日志的能力
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}
4.3 各个节点的构造思路
- step1.解析XML节点的值
- step2.通过MapperBuilder调用相应节点对象建造者
- step3.加入到Configuration对象中
4.4 源码分析的核心思路
- step1.搞清楚XML各节点解析出来的对象类结构
也即XML结点与相关类的对应关系 - step2.知道了源点(XML节点)和目标(对象类),然后找到从源点到目标对象之间调用的方法,搞清楚方法是怎么建造的即可
参考
- 1)享学课堂Lison老师笔记