【原创文章,转载请注明原文章地址,谢谢!】
前提条件:
1,该网站需要进行微信OAuth2.0网页授权。
2,微信用户已绑定网站账号。
即为那种经过一次绑定后,直接点击公众号菜单就能进入到个人页面,无需再次登陆,这种绑定一般是利用openID实现,OpenID是微信唯一对应用户身份的标识,网站或应用可将此ID进行存储,便于用户下次登录时辨识其身份,或将其与用户在网站上或应用中的原有账号进行绑定。
流程:
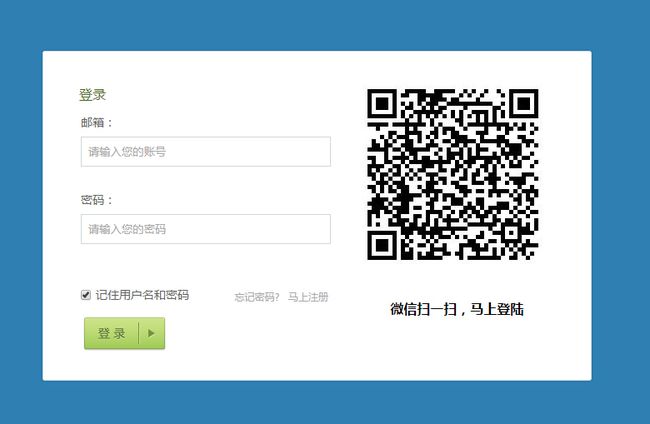
PC端—>打开登陆页面—>请求获取uuid及二维码图片—>服务器相应结果返回二维码相关信息—>页面轮询检查二维码是否被扫描—>服务器返回检查结果,若已扫描成功则跳转页面,否则继续轮询检查。
微信端—>扫一扫二维码—>微信浏览器自动打开二维码中的链接,并带上code参数,通过该参数可获取openID—>服务器检查uuid有效性,并查询该openID是否已经绑定账号,返回登陆结果。
注:如果用户在微信客户端中访问第三方网页,公众号可以通过微信网页授权机制,来获取用户基本信息,进而实现业务逻辑。 其流程为:当微信浏览器请求了授权页面,会带上code参数,通过该参数我们可以获取微信用户的openID,具体流程可查看微信开发官方文档:
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/wiki/9/01f711493b5a02f24b04365ac5d8fd95.html
文章内使用简单的Servlet容器,使用QRGen生成二维码,这是一款轻量级的QRCode二维码生成工具。
QRGen依赖包:
net.glxn.qrgen
javase
2.0
代码部分:
二维码生成工具:
public class QrGenUtil {
public static ByteArrayOutputStream createQrGen(String url) throws IOException {
//如果有中文,可使用withCharset("UTF-8")方法
//设置二维码url链接,图片宽度250*250,JPG类型
return QRCode.from(url).withSize(250, 250).to(ImageType.JPG).stream();
}
}
domain:
public class User {
/**
* 账号名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 密码
*/
private String password;
/**
* 微信账号唯一标识
*/
private String openID;
//省略get,set方法
}
页面:
页面重点代码:获取到图片后PC端页面轮询检测二维码是否被扫描
![]()
服务器需要生成一个二维码,并且使用UUID来保持唯一性,避免登陆信息混乱。
/**
* 获取uuid及二维码图片地址
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void showQrGen(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//生成UUID随机数
UUID randomUUID = UUID.randomUUID();
//通过应用获取共享的uuid集合
Map map = (Map) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("UUID_MAP");
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap();
req.getServletContext().setAttribute("UUID_MAP", map);
}
//把uuid放入map中
map.put(randomUUID.toString(), null);
//二维码图片扫描后的链接
String url = "http://192.168.1.104:8080/login?cmd=loginByQrGen&uuid="+ randomUUID;
//生成二维码图片
ByteArrayOutputStream qrOut = QrGenUtil.createQrGen(url);
String fileName = randomUUID+ ".jpg";
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File(req.getServletContext().getRealPath("/temp"),fileName));
os.write(qrOut.toByteArray());
os.flush();
os.close();
//返回页面json字符串,uuid用于轮询检查时所带的参数, img用于页面图片显示
String jsonStr = "{\"uuid\":\"" + randomUUID + "\",\"img\":\"" + "/temp/"+fileName + "\"}";
OutputStream outStream = resp.getOutputStream();
outStream.write(jsonStr.getBytes());
outStream.flush();
outStream.close();
}
}
二维码中的请求链接:
当用户使用与网站账号绑定后的微信号扫描二维码的时候,会将uuid和唯一标识openID的用户进行绑定,这个时候,浏览器通过轮询查询到uid扫描记录,得到相关响应信息,客户端由此也进入一个新的页面。
/**
* 手机端扫描二维码执行的方法
*
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void loginByQrGen(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取二维码链接中的uuid
String uuid = req.getParameter("uuid");
// 通过应用获取共享的uuid集合
Map uuidMap = (Map) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("UUID_MAP");
// 如果集合内没有这个uuid,则响应结果
if (uuidMap == null || !uuidMap.containsKey(uuid)) {
resp.getOutputStream().write("二维码不存在或已失效!".getBytes());
return;
}
// 根据微信传来的code来获取用户的openID
String code = req.getParameter("code");
try {
String url = "https://api.weixin.qq.com/sns/oauth2/access_token?appid=YOUR_APPID"
+ "&secret=YOUR_SECRTC"
+ "&grant_type=authorization_code" + "&code=" + code;
Gson gson = new Gson();
Map map = gson.fromJson(HttpUtil.get(url, "utf-8"),
new TypeTokenPC端进行轮询检查:
/**
* PC端不断进行轮询检查的方法
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void checkScan(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取页面的uuid参数
String uuid = req.getParameter("uuid");
//通过应用获取共享的uuid集合
Map map = (Map) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("UUID_MAP");
if (map != null) {
//查询该uuid是否存在,且二维码已经被扫描并匹配到账号
if(map.containsKey(uuid)){
User user = (User) map.get(uuid);
if (user != null) {
//从集合中移除
map.remove(uuid);
//设置登录信息
req.getSession().setAttribute("USER_IN_SESSION", user);
resp.getOutputStream().write("ok".getBytes());
}else{
resp.getOutputStream().write("native".getBytes());
}
}
}
}
无论是通过微信扫一扫还是网站自身的客户端扫码功能,都是需要一方登陆或绑定账号,在扫码的时候才可以获取到用户身份的唯一标识,并且所使用的二维码需要有唯一性,失效时并不是二维码图片失效,而是二维码对应的链接或uuid参数失效,二维码只是文字和超链接的图形化而已。只是在超时、网络断开、过期等情况,此前获得的uuid应失效,对检测过程形成有效的防护。