这是Mach-O系列的第三篇
阅读 FishHook源码之前,你可能需要对以下知识有个简单的了解
- Mach-O文件格式:趣探 Mach-O:文件格式分析
- 动态链接相关知识:Mach-O 的动态链接过程 、 趣探 Mach-O:加载过程
- 对操作系统、编译原理的理解:深入解析Mac OS X & iOS操作系统 、 程序员的自我修养
本文的阐述顺序按照函数调用过程来进行
Fishhook 可以做什么
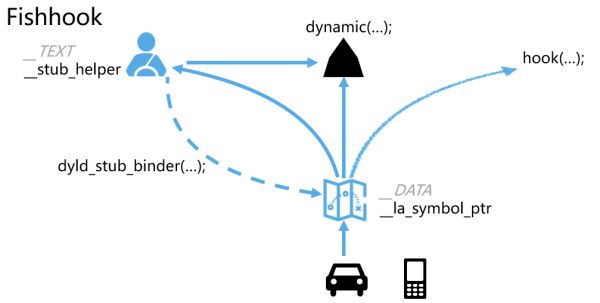
在此借用阿里百川的一张分析图,可以比较清晰的了解FishHook发挥了哪些作用
FishHook在这里是对动态链接库起作用,修改对应的函数实现
对于动态链接库里面的C函数,第一次调用的时候,我们会得到函数和实现地址的对应关系,函数的实现地址存放在一个叫la_symbol_ptr的地方,第二次调用的时候,直接通过la_symbol_ptr找到函数地址就可以,不再需要繁琐的获取函数地址的过程。(具体通过哪些过程,可以参考刚才的链接:Mach-O 的动态链接过程)
那么,上图的含义就很明了了
在程序运行时,动态链接的 C 函数
dynamic(...)地址记录在DATA segment下的la_symbol_ptr中;初始时,程序只知道dynamic函数的符号名而不知道函数的实现地址;首次调用时,程序通过TEXT segment中的stub_helper取得绑定信息,通过dyld_stub_binder来更新la_symbol_ptr中的符号实现地址;这样,再次调用时,就可以通过la_symbol_ptr直接找到dynamic函数的实现;如果我们需要替换dynamic函数的实现,只需要修改__la_symbol_ptr即可,也就是我们要谈的Fishhook
Fishhook 的实现
通过fishhook的官方文档可以知道,Fishhook的使用方法大致如下:
static int (*original_open)(const char *, int, ...);
int new_open(const char *path, int oflag, ...) {
va_list ap = {0};
mode_t mode = 0;
if ((oflag & O_CREAT) != 0) {
// mode only applies to O_CREAT
va_start(ap, oflag);
mode = va_arg(ap, int);
va_end(ap);
printf("Calling real open('%s', %d, %d)\n", path, oflag, mode);
return original_open(path, oflag, mode);
} else {
printf("Calling real open('%s', %d)\n", path, oflag);
return original_open(path, oflag, mode);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
struct rebinding open_rebinding = { "open", new_open, (void *)&original_open };
rebind_symbols((struct rebinding[1]){open_rebinding}, 1);
__unused int fd = open(argv[0], O_RDONLY);
}
return 0;
}
先从函数的入口,rebind_symbols开始谈起吧,rebind_symbols主要是使用_dyld_register_func_for_add_image来注册回调函数,在加载动态库的时候执行一些操作
int rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel) {
// 调用 prepend_rebindings 的函数,将整个 rebindings 数组添加到 _rebindings_head 这个私有链表的头部
int retval = prepend_rebindings(&_rebindings_head, rebindings, rebindings_nel);
if (retval < 0) {
return retval;
}
// 判断 _rebindings_head->next 的值来判断是否为第一次调用
// If this was the first call, register callback for image additions (which is also invoked for
// existing images, otherwise, just run on existing images
if (!_rebindings_head->next) {
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image(_rebind_symbols_for_image);
} else {
uint32_t c = _dyld_image_count();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < c; i++) {
_rebind_symbols_for_image(_dyld_get_image_header(i), _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(i));
}
}
return retval;
}
对于prepend_rebindings的代码如下
// 链表的数组结构
struct rebindings_entry {
struct rebinding *rebindings;
size_t rebindings_nel;
struct rebindings_entry *next;
};
static struct rebindings_entry *_rebindings_head;
static int prepend_rebindings(struct rebindings_entry **rebindings_head,
struct rebinding rebindings[],
size_t nel) {
struct rebindings_entry *new_entry = malloc(sizeof(struct rebindings_entry));
if (!new_entry) {
return -1;
}
new_entry->rebindings = malloc(sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel);
if (!new_entry->rebindings) {
free(new_entry);
return -1;
}
// 将 rebindings 插入到链表头部
memcpy(new_entry->rebindings, rebindings, sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel);
new_entry->rebindings_nel = nel;
new_entry->next = *rebindings_head;
*rebindings_head = new_entry;
return 0;
}
基础结构解释
Dl_info
/*
* Structure filled in by dladdr().
*/
typedef struct dl_info {
const char *dli_fname; /* Pathname of shared object */
void *dli_fbase; /* Base address of shared object */
const char *dli_sname; /* Name of nearest symbol */
void *dli_saddr; /* Address of nearest symbol */
} Dl_info;
我们一会经过 dladdr()处理后的有效信息都会放进这个结构体中
-
fname:路径名,例如
/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneSimulator.platform/Developer/SDKs/iPhoneSimulator.sdk/System/Library/Frameworks/CoreFoundation.framework/CoreFoundation
-
dli_fbase:镜像的的起始地址(Base address of shared object,比如上面的 CoreFoundation) -
dli_saddr :符号的地址 -
dli_sname:符号的名字,即下面的第四列的函数信息
Thread 0:
0 libsystem_kernel.dylib 0x11135810a __semwait_signal + 94474
1 libsystem_c.dylib 0x1110dab0b sleep + 518923
2 QYPerformanceMonitor 0x10dda4f1b -[ViewController tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:] + 7963
3 UIKit 0x10ed4d4f4 -[UITableView _createPreparedCellForGlobalRow:withIndexPath:willDisplay:] + 1586420
LC_SYMTAB
struct symtab_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SYMTAB */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* sizeof(struct symtab_command) */
uint32_t symoff; /* symbol table offset */
uint32_t nsyms; /* number of symbol table entries */
uint32_t stroff; /* string table offset */
uint32_t strsize; /* string table size in bytes */
};
主要是提供符号表的偏移量,以及元素个数,还有字符串表的偏移和其长度。符号表在 Mach-O目标文件中的地址可以通过LC_SYMTAB加载命令指定的 symoff找到,对应的符号名称在stroff,总共有nsyms条符号信息
LC_DYSYMTAB
这个数组结构有些复杂,有兴趣的可以阅读loader.h文件,内部标示了动态符号表的偏移量和符号个数
struct dysymtab_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_DYSYMTAB */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* sizeof(struct dysymtab_command) */
uint32_t indirectsymoff; /* file offset to the indirect symbol table */
uint32_t nindirectsyms; /* number of indirect symbol table entries */
.......
_rebind_symbols_for_image
对于关键的代码 _rebind_symbols_for_image 如下
static void rebind_symbols_for_image(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide) {
Dl_info info;
if (dladdr(header, &info) == 0) {
return;
}
// segment_command_64
segment_command_t *cur_seg_cmd;
segment_command_t *linkedit_segment = NULL;
// LC_SYMTAB
struct symtab_command* symtab_cmd = NULL;
// LC_DYSYMTAB
struct dysymtab_command* dysymtab_cmd = NULL;
// 下面是要寻找load_command,所以越过mach_header_t
uintptr_t cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) {
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) {
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_LINKEDIT) == 0) {
//遍历寻找__LINKEDIT
linkedit_segment = cur_seg_cmd;
}
} else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SYMTAB) {
//遍历寻找lc_symtab
symtab_cmd = (struct symtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd;
} else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_DYSYMTAB) {
//遍历寻找lc_dysymtab
dysymtab_cmd = (struct dysymtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd;
}
}
为什么要寻找这个几个LoadCommand的信息呢?就如上面介绍的__LINKEDIT、LC_DYSYMTAB、LC_SYMTAB都提供了重要的信息。
__LINKEDIT段 含有为动态链接库使用的原始数据,比如符号,字符串,重定位表条目等等
阅读下面的代码之前,先来看一个计算公式
链接时程序的基址 = __LINKEDIT.VM_Address -__LINKEDIT.File_Offset + silde的改变值
这里出现了一个 slide,那么slide是啥呢?先看一下ASLR
ASLR:Address space layout randomization,将可执行程序随机装载到内存中,这里的随机只是偏移,而不是打乱,具体做法就是通过内核将 Mach-O的段“平移”某个随机系数。slide 正是ASLR引入的偏移
也就是说程序的基址等于__LINKEDIT的地址减去偏移量,然后再加上ASLR造成的偏移
// 链接时程序的基址
uintptr_t linkedit_base = (uintptr_t)slide + linkedit_segment->vmaddr - linkedit_segment->fileoff;
// 符号表的地址 = 基址 + 符号表偏移量
nlist_t *symtab = (nlist_t *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->symoff);
// 字符串表的地址 = 基址 + 字符串表偏移量
char *strtab = (char *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->stroff);
// 动态符号表地址 = 基址 + 动态符号表偏移量
uint32_t *indirect_symtab = (uint32_t *)(linkedit_base + dysymtab_cmd->indirectsymoff);
符号表中的元素都是nlist_t结构体,nlist_t中有很多学问,这里先看一下他的基础结构
/*
* This is the symbol table entry structure for 32-bit architectures.
*/
struct nlist {
union {
uint32_t n_strx; /* index into the string table */
} n_un;
uint8_t n_type; /* type flag, see below */
uint8_t n_sect; /* section number or NO_SECT */
int16_t n_desc; /* see */
uint32_t n_value; /* value of this symbol (or stab offset) */
};
然后再次遍历loadcommands,寻找__DATA和__DATA_CONST的section,并对对__nl_symbol_ptr以及__la_symbol_ptr进行rebind
cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) {
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) {
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA) != 0 &&
strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA_CONST) != 0) {
continue;
}
//找到__DATA和__DATA_CONST的section,对__nl_symbol_ptr以及__la_symbol_ptr进行rebind
for (uint j = 0; j < cur_seg_cmd->nsects; j++) {
section_t *sect =
(section_t *)(cur + sizeof(segment_command_t)) + j;
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) {
// sect为Section,symtab为符号表,strtab字符串表,indirect_symtab动态符号表(indirect symbol table)
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) {
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
}
}
perform_rebinding_with_section
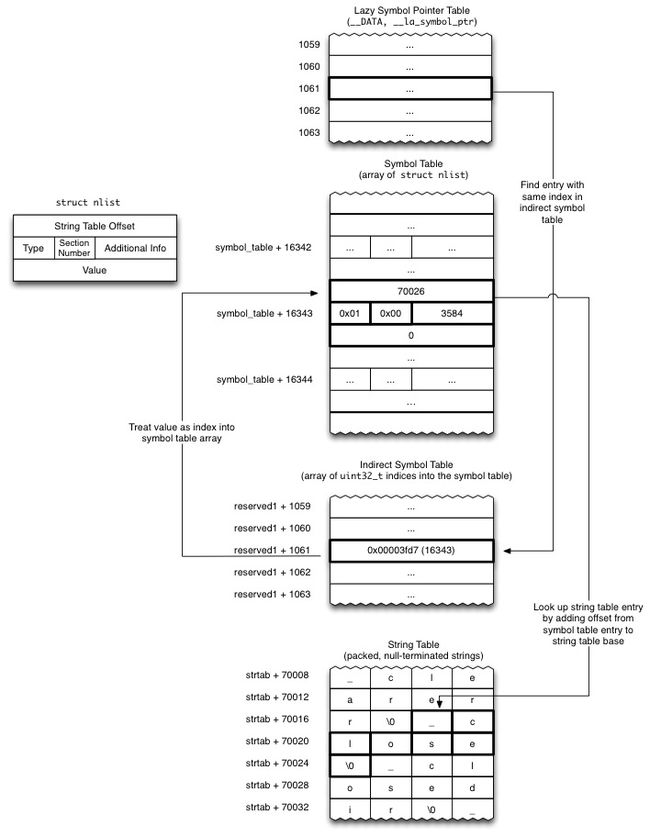
nl_symbol_ptr和la_symbol_ptrsection中的reserved1字段指明对应的indirect symbol table起始的index,
For the two relevant sections, the section headers (struct sections from
) provide an offset (in the reserved1 field) into what is known as the indirect symbol table. The indirect symbol table, which is located in the __LINKEDIT segment of the binary, is just an array of indexes into the symbol table (also in __LINKEDIT) whose order is identical to that of the pointers in the non-lazy and lazy symbol sections So, given struct section nl_symbol_ptr, the corresponding index in the symbol table of the first address in that section is indirect_symbol_table[nl_symbol_ptr->reserved1]. The symbol table itself is an array of struct nlists (see
), and each nlist contains an index into the string table in __LINKEDIT which where the actual symbol names are stored. So, for each pointer __nl_symbol_ptr and __la_symbol_ptr, we are able to find the corresponding symbol and then the corresponding string to compare against the requested symbol names, and if there is a match, we replace the pointer in the section with the replacement.
结合英文,看下面的代码就很容易理解
// sect为Section,symtab为符号表,strtab字符串表,indirect_symtab动态符号表(indirect symbol table)
static void perform_rebinding_with_section(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
section_t *section,
intptr_t slide,
nlist_t *symtab,
char *strtab,
uint32_t *indirect_symtab) {
// `nl_symbol_ptr`和`la_symbol_ptr`section中的`reserved1`字段指明对应的`indirect symbol table`起始的index
//动态符号表中第一个解析的符号的起始地址
uint32_t *indirect_symbol_indices = indirect_symtab + section->reserved1;
void **indirect_symbol_bindings = (void **)((uintptr_t)slide + section->addr);
for (uint i = 0; i < section->size / sizeof(void *); i++) {
// 符号表的index
uint32_t symtab_index = indirect_symbol_indices[i];
if (symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS || symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL ||
symtab_index == (INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL | INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS)) {
continue;
}
//获取每一个需要动态解析的符号在符号表中的偏移量
uint32_t strtab_offset = symtab[symtab_index].n_un.n_strx;
//通过字符串表偏移量获取符号对应的字符串(符号的名字)
char *symbol_name = strtab + strtab_offset;
上面的代码其实就可以用官方的一个图片很直观的表示
走到这里是找到了字符串表对应的符号(字符串)
如何替换实现
遍历 rebindings 数组,符号进行比较,相同的符号就进行实现替换,这里的代码比较清晰,直接贴出
struct rebindings_entry *cur = rebindings;
while (cur) {
for (uint j = 0; j < cur->rebindings_nel; j++) {
if (strcmp(&symbol_name[1], cur->rebindings[j].name) == 0) {
if (cur->rebindings[j].replaced != NULL &&
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] != cur->rebindings[j].replacement) {
*(cur->rebindings[j].replaced) = indirect_symbol_bindings[i];
}
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] = cur->rebindings[j].replacement;
goto symbol_loop;
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
symbol_loop:;
}
参考链接
- 动态修改 C 语言函数的实现
- mrh的Fihshook源码分析
- fishhook
- 深入解析Mac OS X & iOS操作系统
- 程序员的自我修养
- 编译体系漫游