DMCplus控制计算负责维护斜坡变量在控制范围内。稳态优化解决方案只提供了能平衡斜坡的MV稳态值。
然而为了有效地控制斜坡,控制动作计算必须暂时产生失衡以驱动斜坡变量朝设定值动作。如果控制器的MV被过度抑制,控制器将不能充分实现上述要求。
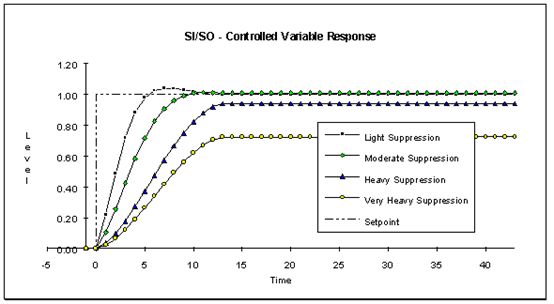
这一点通过考虑图18中控制计算主题所示简单例子进行说明。在t=0时,液位设定值增加。图32显示了不同动作抑制因子值下设定值变化的液位响应情况。
图33显示了这些不同动作抑制因子时对应的出料流量动作。显然,如果动作抑制过大,MV将不能充分移动以使液位到达其新设定值。因此,MV的过度抑制将导致难以控制斜坡变量。
在实践中,过度抑制可通过比较液位预测向量中最后一个元素与设定点接近值来诊断,如图32所示。如果在控制时域终点未来动作预测值不接近设定点,那么系统就有可能是过度抑制。斜坡的动作抑制因子往往比稳态变量小。
图32:不同动作抑制时设定点变化的液位响应
图33:不同动作抑制情况下液位设定点变化时出料流量动作
在设定误差重要度时,注意允许的最大值为10,000。这可以防止斜坡在问题的动态部分被丢弃。
附原文:
The DMCplus control calculation is responsible for maintaining the ramp variables within control range. The steady-state optimization solution only provides steady-state values for the manipulated variables which will balance the ramp.
However, in order to control the ramp effectively, the control moves calculation must temporarily create an imbalance to move the ramp variable toward the setpoint. If the manipulated variables for the controller are over-suppressed, the controller will not be able to achieve this adequately.
This point is illustrated by considering the simple example shown in Figure 18 in the Control Calculation topic. At time=0, the level setpoint is increased. Figure 32 shows the level response to this setpoint change at several different values of the move suppression factor.
Figure 33 shows how the out-flow moved at these different move suppression factors. Clearly, if the move suppression is too high, the manipulated variable cannot move sufficiently to allow the level to achieve its new setpoint. Thus, excessive suppression of manipulated variables can lead to difficulty in controlling ramp variables.
In practice, over-suppression canbe diagnosed by comparing the last element in the prediction vector for the level against its setpoint, as seen in Figure 32. If the prediction with future moves does not approach the setpoint towards the end of the control horizon,then the system is probably over-suppressed. Move suppression factors for ramps tend to be smaller than for steady-state variables.
In setting Equal Concern Errors,note that the largest value possible is 10,000. This prevents the ramp from being dropped from the dynamic portion of the problem.
2015.10.8