今天我们来介绍下关于odoo10的提交:08ab28
改进结果:
这个提交是对销售费用中的exponse_policy字段的值增加了onchange方法以便动态的更改该字段的值
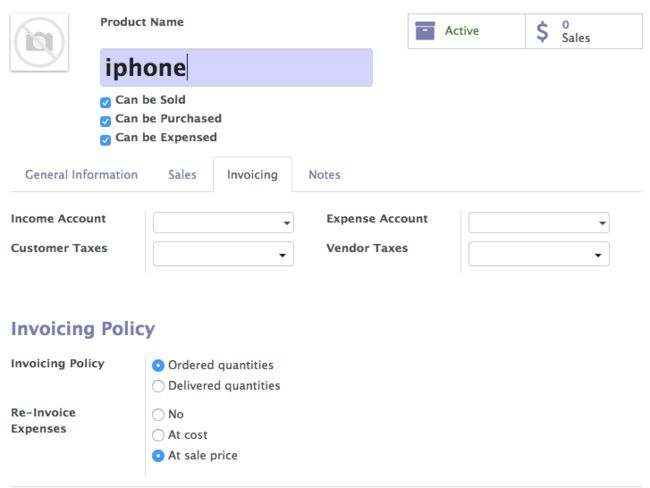
- 我们首先来看下销售模块中定义产品时可以选择的字段
上图是我们在安装销售费用后创建产品时新增的一个bool字段can_be_expensed。先进入sale_expense模块.我们在views文件夹中可以看到这个模块对product.template视图做的继承
product.template.expense.policy
product.template
上面的代码相信大家很容易看懂,无非就是在我们把该字段设置为True时。就能在开票策略下出现一个重新开票费用的选择框。这三个选项也很好理解,
- '否' 即表示不进行开票.
- '成本' 即使用成本价格进行开票.
- '销售价格' 即使用销售价格进行开票.
让我们来看看这次提交对该模块的更改:
。
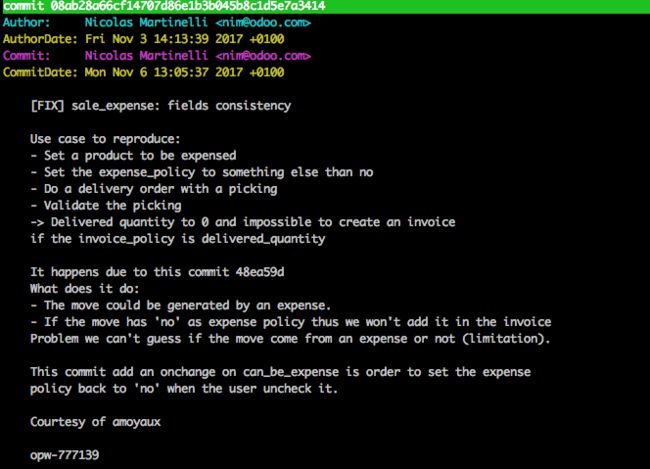
通过代码我们发现,这个提交在sale_expense模块中对project.template进行了继承,新增加了一个onchange方法.当产品的can_be_expense字段为False时,把expense_policy的值设置为'no'.(即'否'这个选项)
先上commit的说明内容:
为何要进行这个修改:
这就需要通过前一个xml文件来结合一起看,由于在xml中定义了'invisible'属性,我们把产品的can_be_expense属性取消时,重新开票费用这个选项会自动隐藏.但其中的expense_policy字段还保留以前选择的内容.
在实际生产过程中.操作者很容易忽视这个问题.这就会在销售订单完成后的开票操作产生bug.我们来演示下这个bug的产生。
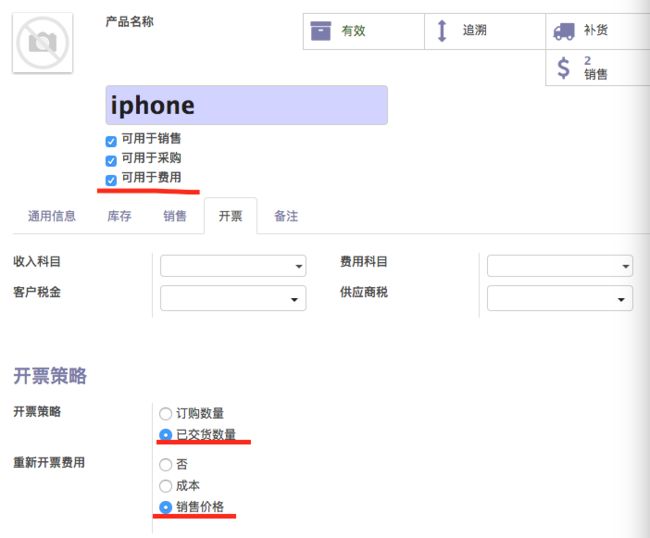
- 创建名为iphone的产品。勾选
可用于费用. 开票策略中选择已交货数量. 重新开票费用设置为销售价格.保存
- 编辑刚才创建的iphone产品。取消选择
可用于费用.点击保存.这时候这个iphone产品的expense_policy字段依然保存着销售价格这个选择. -
创建新的销售订单, 订单行中添加iphone这个产品。
保存后点击把该订单状态设为确认销售。此时,该订单已经确认销售,当我们交货后即可进行开票操作。让我们来试下
。
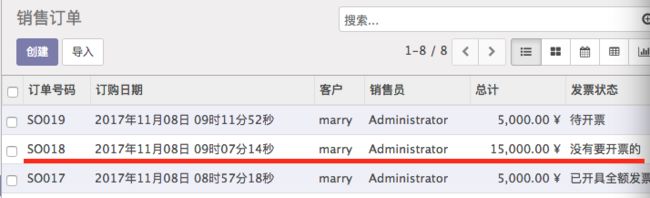
此时,我们在销售订单的发票状态中却发现该订单显示为没有要开票的。
这是为什么呢?让我们通过代码来进行解释。
首先,进入打开sale模块中的sale.py文件。
我们首先来看下发票状态的生成策略。
class SaleOrderLine(models.Model):
_name = 'sale.order.line'
_description = 'Sales Order Line'
_order = 'order_id, layout_category_id, sequence, id'
@api.depends('state', 'product_uom_qty', 'qty_delivered', 'qty_to_invoice', 'qty_invoiced')
def _compute_invoice_status(self):
"""
Compute the invoice status of a SO line. Possible statuses:
- no: if the SO is not in status 'sale' or 'done', we consider that there is nothing to
invoice. This is also hte default value if the conditions of no other status is met.
- to invoice: we refer to the quantity to invoice of the line. Refer to method
`_get_to_invoice_qty()` for more information on how this quantity is calculated.
- upselling: this is possible only for a product invoiced on ordered quantities for which
we delivered more than expected. The could arise if, for example, a project took more
time than expected but we decided not to invoice the extra cost to the client. This
occurs onyl in state 'sale', so that when a SO is set to done, the upselling opportunity
is removed from the list.
- invoiced: the quantity invoiced is larger or equal to the quantity ordered.
"""
precision = self.env['decimal.precision'].precision_get('Product Unit of Measure')
for line in self:
if line.state not in ('sale', 'done'):
line.invoice_status = 'no'
elif not float_is_zero(line.qty_to_invoice, precision_digits=precision):
line.invoice_status = 'to invoice'
elif line.state == 'sale' and line.product_id.invoice_policy == 'order' and\
float_compare(line.qty_delivered, line.product_uom_qty, precision_digits=precision) == 1:
line.invoice_status = 'upselling'
elif float_compare(line.qty_invoiced, line.product_uom_qty, precision_digits=precision) >= 0:
line.invoice_status = 'invoiced'
else:
line.invoice_status = 'no'
可以看到,首先通过对订单的状态进行判断,然后根据各个条件来决定开票的状态。那为什么我们的expense_policy属性会影响开票状态呢。继续往里走,来到第一个elif判断,这里的判断条件是当销售订单中产品的字段qty_to_invoice不为0时,开票状态处于可开票,我们来看qty_to_invoice这个字段。它是一个计算字段
@api.depends('qty_invoiced', 'qty_delivered', 'product_uom_qty', 'order_id.state')
def _get_to_invoice_qty(self):
"""
Compute the quantity to invoice. If the invoice policy is order, the quantity to invoice is
calculated from the ordered quantity. Otherwise, the quantity delivered is used.
"""
for line in self:
if line.order_id.state in ['sale', 'done']:
if line.product_id.invoice_policy == 'order':
line.qty_to_invoice = line.product_uom_qty - line.qty_invoiced
else:
line.qty_to_invoice = line.qty_delivered - line.qty_invoiced
else:
line.qty_to_invoice = 0
通过这个计算方法我们可以发现,由于我们的iphone产品使用的是已交货数量的开票策略,我们就需要qty_delivered这个字段。
这个字段是在sale模块中定义的
qty_delivered = fields.Float(string='Delivered', copy=False, digits=dp.get_precision('Product Unit of Measure'), default=0.0)
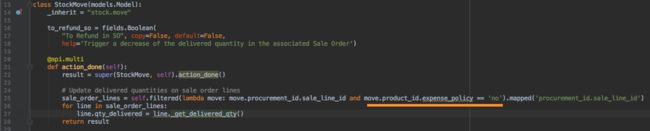
但是它的取值是通过sale_stock模块扩展的.进入sale_stock模块models文件夹中的stock.py文件.在13行
我们看到
qty_delivered字段的取值会在这里进行一次更新.注意这里的代码.首先会对产品的expense_policy字段进行过滤。
到这里
相信我们已经可以得出结论了。因为我们的iphone产品的expense_policy的默认值依然存在,即使发了货,在销售订单中该产品却还是被过滤了。销售订单的字段
qty_delivered始终是默认值
0.0。所以销售订单的开票状态始终为
没有要开票的。