大家都知道如果想让UIImageView显示动态图片,可以设置animationImages赋值一个图片数组,然后设置一下动画时间,再开启动画。总感觉使用很麻烦,而且如果是一个gif格式或者其他格式的动态图,直接就无法使用了。后来在github上发现了YYImage,发现使用起来很方便,但同时也很好奇是怎么做到的,现在就以YYAnimatedImageView为主介绍一下这个库是怎么实现显示动态图的。废话不多说,上图
先写两句代码,运行一下,然后打断点进去看看是怎么加载的
YYAnimatedImageView* animatedView = [[YYAnimatedImageView alloc] init];
animatedView.frame=CGRectMake(0,0,200,150);
animatedView.center=self.view.center;
[self.view addSubview:animatedView];
YYImage* image = [YYImage imageNamed:@"test.gif"];
animatedView.image= image;
这样就能显示动态图了。
- 首先从YYImage说起
A YYImage object is a high-level way to display animated image data
作者继承UIImage类写了YYImage,他自己的介绍是这是可以高效的展示动态图的类,我们从imageNamed:方法看起,这个方法主要是去遍历工程文件中是否有匹配的文件,如果找到路径然后直接获取图片的二进制文件,YYImage重写了initWithData:scale:方法,在这个里面使用了YYImageDecoder对图片进行界面,这就是YYImage为什么比较快的原因了
- 从
YYImageDecoder *decoder = [YYImageDecoder decoderWithData:datascale:scale]进入YYImagecoder去看看是怎么处理的
根据方法调用和参数传递,来到如上图所示方法,是yyImageCoder第一个做实事的方法,YYImageDetectType先得到这个图片的格式(比如PNG,JPEG,GIF等),具体怎么得出来的可以点进去仔细看看,大概就是获得这个二进制文件的前16字节,然后进行匹配,得到图片的格式,得到了图片格式之后进入下一步
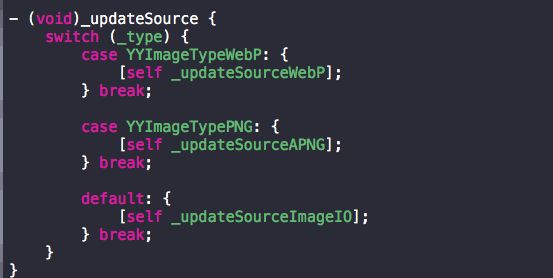
[self _updateSource]
在这里作者对webp和apng格式的动画进行了专门的解码优化所以进入不同方法,总之这个方法就是对不同格式的图片进行解码路由,我们点进去_updateSourceImageIO看看怎么做的,看下主要代码(去除了一些条件判断)
//使用ImageIO框架去获得图片
//使用CGImageSourceCreateWithData获得图片类型是CGImageSourceRef
_source=CGImageSourceCreateWithData((__bridgeCFDataRef)_data,NULL);
//这里frameCount代表图片的数量,比如GIF其实就是一组图片
//下面是一些不同类型的判断
_frameCount = CGImageSourceGetCount(_source);
if (_type == YYImageTypeGIF) {
//这字典打印出来是
//FileSize = 487202;
//"{GIF}" = {
// HasGlobalColorMap = 1;
// LoopCount = 0;
//};
// loopCount = 0 表示会无线循环当前的gif
CFDictionaryRef properties = CGImageSourceCopyProperties(_source, NULL);
if (properties) {
CFTypeRef loop = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyGIFLoopCount);
if (loop) CFNumberGetValue(loop, kCFNumberNSIntegerType, &_loopCount);
CFRelease(properties);
}
}
//建立一个数组,把每个图片的索引,延迟时间等封装成_YYImageDecoderFrame类
//加入到数组中
NSMutableArray *frames = [NSMutableArray new];
for (NSUInteger i = 0; i < _frameCount; i++) {
_YYImageDecoderFrame *frame = [_YYImageDecoderFrame new];
frame.index = i;
frame.blendFromIndex = i;
frame.hasAlpha = YES;
frame.isFullSize = YES;
[frames addObject:frame];
//得到每一帧图片的属性
//包括图片的 宽 高 延迟时间 颜色空间等
CFDictionaryRef properties = CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(_source, i, NULL);
if (properties) {
NSTimeInterval duration = 0;
NSInteger orientationValue = 0, width = 0, height = 0;
CFTypeRef value = NULL;
value = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyPixelWidth);
if (value) CFNumberGetValue(value, kCFNumberNSIntegerType, &width);
value = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyPixelHeight);
if (value) CFNumberGetValue(value, kCFNumberNSIntegerType, &height);
if (_type == YYImageTypeGIF) {
CFDictionaryRef gif = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyGIFDictionary);
//此处打断点 输出
// {
// DelayTime = "0.07";
// UnclampedDelayTime = "0.07";
// }
//表示每一帧图片的延迟时间,也就是需要显示的时间
if (gif) {
value = CFDictionaryGetValue(gif, kCGImagePropertyGIFUnclampedDelayTime);
if (!value) {
value = CFDictionaryGetValue(gif, kCGImagePropertyGIFDelayTime);
}
if (value) CFNumberGetValue(value, kCFNumberDoubleType, &duration);
}
}
//对动画中需要到的关键属性进行赋值
frame.width = width;
frame.height = height;
frame.duration = duration;
然后把每一帧图片加入到frames数组中,这基本上是YYImageCoder完成的大部分工作了
- 我们再回到YYImage中
YYImageCoder还是之前那个initWithData:scale方法,我加了注释,看一下
YYImageDecoder *decoder = [YYImageDecoder decoderWithData:data scale:scale];
YYImageFrame *frame = [decoder frameAtIndex:0 decodeForDisplay:YES];
UIImage *image = frame.image;
if (!image) return nil;
//这里返回的是第一帧的图片
self = [self initWithCGImage:image.CGImage scale:decoder.scale orientation:image.imageOrientation];
if (!self) return nil;
_animatedImageType = decoder.type;
//当frameCount >1 也就是 当图片是动态图的时候
if (decoder.frameCount > 1) {
//注意看这里,这里把decoder 当做自己成员变量了
//为什么要这样做? 因为当时上面返回的是第一帧的图片,但是对于frameCount > 1的动态图,
//当然返回一张是不够的,这里保留decoder,在需要使用YYAnimatedImageView代理方法的时候可以通过decoder来返回不同索引的图片
_decoder = decoder;
_bytesPerFrame = CGImageGetBytesPerRow(image.CGImage) * CGImageGetHeight(image.CGImage);
_animatedImageMemorySize = _bytesPerFrame * decoder.frameCount;
}
- 好了,
YYImage所做的工作已经完成了,我们现在来看看YYAnimatedImageView是怎么做最后的舞台的
从setImage:withType:方法出发,来到- (void)imageChanged方法,同样我也添加了注释
YYAnimatedImageType newType = [self currentImageType];
id newVisibleImage = [self imageForType:newType];
NSUInteger newImageFrameCount = 0;
BOOL hasContentsRect = NO;
if ([newVisibleImage isKindOfClass:[UIImage class]] &&
//这句话其实就是把newVisibleImage当做代理对象使用
//因为这里用的都是YYImage类型,YYImage已经实现了代理方法
[newVisibleImage conformsToProtocol:@protocol(YYAnimatedImage)]) {
//得到图片的个数
newImageFrameCount = ((UIImage *) newVisibleImage).animatedImageFrameCount;
if (newImageFrameCount > 1) {
hasContentsRect = [((UIImage *) newVisibleImage) respondsToSelector:@selector(animatedImageContentsRectAtIndex:)];
}
}
if (!hasContentsRect && _curImageHasContentsRect) {
//这个是关闭默认的隐式动画,防止对自己的动画播放产生影响,
//有兴趣的可以看看 core animation
if (!CGRectEqualToRect(self.layer.contentsRect, CGRectMake(0, 0, 1, 1)) ) {
[CATransaction begin];
[CATransaction setDisableActions:YES];
//设置layer的显示范围是整个寄宿图片
self.layer.contentsRect = CGRectMake(0, 0, 1, 1);
[CATransaction commit];
}
}
_curImageHasContentsRect = hasContentsRect;
if (hasContentsRect) {
CGRect rect = [((UIImage *) newVisibleImage) animatedImageContentsRectAtIndex:0];
[self setContentsRect:rect forImage:newVisibleImage];
}
if (newImageFrameCount > 1) {
//如果是 图片数量>1 针对动态图
//resetAnimated就是创建了一个CADisplayLink定时器去刷新图片显示
[self resetAnimated];
_curAnimatedImage = newVisibleImage;
_curFrame = newVisibleImage;
_totalLoop = _curAnimatedImage.animatedImageLoopCount;
_totalFrameCount = _curAnimatedImage.animatedImageFrameCount;
[self calcMaxBufferCount];
}
[self setNeedsDisplay];
//开始播放动画
[self didMoved];
在[self resetAnimated]方法中,使用dispatch_once来保证这个imageView中只起一次定时器,同时把这个定时器加到mainRunLoop,模式默认为NSRunLoopCommonModes,也就是说在你滑动的时候不会影响到动态图的播放,同时添加进通知中心,对于关于内存警告的通知,和后台的通知进行相应的一些处理,定时器定时调起step:方法,这个方法主要是做什么呢,
_time += link.duration;
//拿到当前索引图片的延迟时间,也就是需要显示的时间
delay = [image animatedImageDurationAtIndex:_curIndex];
//如果当前的link.duration还没到,直接返回等到下一次调起
//就拿文章头部的那个动态图来说,每张图显示的时间大约在0.07秒左右
//而CADisplayLink每次任务执行的时间大约是0.016秒
//所以不会用每次都刷新图片显示
if (_time < delay) return;
//如果调用了就用当前的时间减去 当前图片需要显示的时间
_time -= delay;
if (nextIndex == 0) {
_curLoop++;
if (_curLoop >= _totalLoop && _totalLoop != 0) {
_loopEnd = YES;
[self stopAnimating];
//主动调起刷新layer,系统会调用displayLayer
[self.layer setNeedsDisplay];
return;
}
}
_curFrame就是当前要显示的图片,_curFrame的赋值也在step中,具体就不解释了,然后就通过下面这句代码完成了imageview的layer的寄宿图的设置
layer.contents = (__bridge id)_curFrame.CGImage;
好了到这,YYAnimatedImageView就开始播放动态图了。