from sklearn import metrics
1.accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred, normalize=True, sample_weight=None)
参数分别为y实际类别、预测类别、返回值要求(True返回正确的样本占比,false返回的是正确分类的样本数量)
eg:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
>>> y_pred = [0, 2, 1, 3]
>>> y_true = [0, 1, 2, 3]
>>> accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
0.5
>>> accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred, normalize=False)
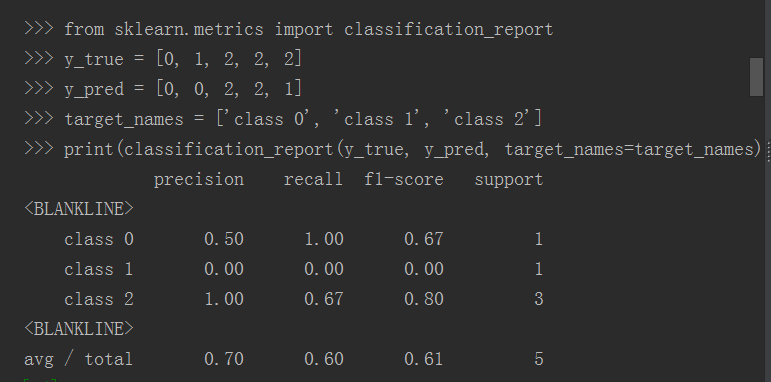
2.classification_report(y_true, y_pred, labels=None, target_names=None, sample_weight=None, digits=2)
参数:真是类别,预测类别,目标类别名称
eg:
3.confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, labels=None, sample_weight=None)
输出为混淆矩阵
eg:
太多了,写3个常用的吧,具体参考help(metrics)
文末惊喜在此:
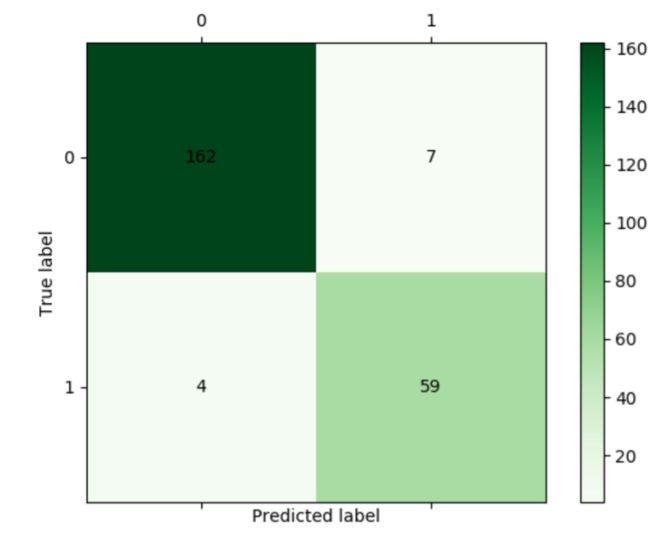
纯手工Python混淆矩阵作图代码案例
defcm_plot(y,yp):#参数为实际分类和预测分类
fromsklearn.metricsimportconfusion_matrix
#导入混淆矩阵函数
cm = confusion_matrix(y,yp)
#输出为混淆矩阵
importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt
#导入作图函数
plt.matshow(cm,cmap=plt.cm.Greens)
# 画混淆矩阵图,配色风格使用cm.Greens
plt.colorbar()
# 颜色标签
forxinrange(len(cm)):
foryinrange(len(cm)):
plt.annotate(cm[x,y],xy=(x,y),horizontalalignment='center',verticalalignment='center')
#annotate主要在图形中添加注释
# 第一个参数添加注释
# 第一个参数是注释的内容
# xy设置箭头尖的坐标
#horizontalalignment水平对齐
#verticalalignment垂直对齐
#其余常用参数如下:
# xytext设置注释内容显示的起始位置
# arrowprops 用来设置箭头
# facecolor 设置箭头的颜色
# headlength 箭头的头的长度
# headwidth 箭头的宽度
# width 箭身的宽度
plt.ylabel('True label')# 坐标轴标签
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')# 坐标轴标签
returnplt
#函数调用
cm_plot(train[:,3],tree.predict(train[:,:3])).show()
输出结果图: