第01章 Pandas基础
第02章 DataFrame运算
第03章 数据分析入门
第04章 选取数据子集
第05章 布尔索引
第06章 索引对齐
第07章 分组聚合、过滤、转换
第08章 数据清理
第09章 合并Pandas对象
第10章 时间序列分析
第11章 用Matplotlib、Pandas、Seaborn进行可视化
In[1]: import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
1. 检查索引
# 读取college数据集,提取所有的列
In[2]: college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv')
columns = college.columns
columns
Out[2]: Index(['INSTNM', 'CITY', 'STABBR', 'HBCU', 'MENONLY', 'WOMENONLY', 'RELAFFIL',
'SATVRMID', 'SATMTMID', 'DISTANCEONLY', 'UGDS', 'UGDS_WHITE',
'UGDS_BLACK', 'UGDS_HISP', 'UGDS_ASIAN', 'UGDS_AIAN', 'UGDS_NHPI',
'UGDS_2MOR', 'UGDS_NRA', 'UGDS_UNKN', 'PPTUG_EF', 'CURROPER', 'PCTPELL',
'PCTFLOAN', 'UG25ABV', 'MD_EARN_WNE_P10', 'GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP'], dtype='object')
# 用values属性,访问底层的NumPy数组
In[3]: columns.values
Out[3]: array(['INSTNM', 'CITY', 'STABBR', 'HBCU', 'MENONLY', 'WOMENONLY',
'RELAFFIL', 'SATVRMID', 'SATMTMID', 'DISTANCEONLY', 'UGDS',
'UGDS_WHITE', 'UGDS_BLACK', 'UGDS_HISP', 'UGDS_ASIAN', 'UGDS_AIAN',
'UGDS_NHPI', 'UGDS_2MOR', 'UGDS_NRA', 'UGDS_UNKN', 'PPTUG_EF',
'CURROPER', 'PCTPELL', 'PCTFLOAN', 'UG25ABV', 'MD_EARN_WNE_P10',
'GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP'], dtype=object)
# 取出该数组的第6个值
In[4]: columns[5]
Out[4]: 'WOMENONLY'
# 取出该数组的第2\9\11
In[5]: columns[[1,8,10]]
Out[5]: Index(['CITY', 'SATMTMID', 'UGDS'], dtype='object')
# 逆序切片选取
In[6]: columns[-7:-4]
Out[6]: Index(['PPTUG_EF', 'CURROPER', 'PCTPELL'], dtype='object')
# 索引有许多和Series和DataFrame相同的方法
In[7]: columns.min(), columns.max(), columns.isnull().sum()
Out[7]: ('CITY', 'WOMENONLY', 0)
# 索引对象可以直接通过字符串方法修改
In[8]: columns + '_A'
Out[8]: Index(['INSTNM_A', 'CITY_A', 'STABBR_A', 'HBCU_A', 'MENONLY_A', 'WOMENONLY_A',
'RELAFFIL_A', 'SATVRMID_A', 'SATMTMID_A', 'DISTANCEONLY_A', 'UGDS_A',
'UGDS_WHITE_A', 'UGDS_BLACK_A', 'UGDS_HISP_A', 'UGDS_ASIAN_A',
'UGDS_AIAN_A', 'UGDS_NHPI_A', 'UGDS_2MOR_A', 'UGDS_NRA_A',
'UGDS_UNKN_A', 'PPTUG_EF_A', 'CURROPER_A', 'PCTPELL_A', 'PCTFLOAN_A',
'UG25ABV_A', 'MD_EARN_WNE_P10_A', 'GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP_A'],
dtype='object')
# 索引对象也可以通过比较运算符,得到布尔索引
In[9]: columns > 'G'
Out[9]: array([ True, False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, False, True, True, True, True, True], dtype=bool)
# 尝试用赋值的方法,修改索引对象的一个值,会导致类型错误,因为索引对象是不可变类型
In[10]: columns[1] = 'city'
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
in ()
----> 1 columns[1] = 'city'
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/indexes/base.py in __setitem__(self, key, value)
1668
1669 def __setitem__(self, key, value):
-> 1670 raise TypeError("Index does not support mutable operations")
1671
1672 def __getitem__(self, key):
TypeError: Index does not support mutable operations
更多
索引对象支持集合运算:联合、交叉、求差、对称差
# 切片
In[11]: c1 = columns[:4]
c1
Out[11]: Index(['INSTNM', 'CITY', 'STABBR', 'HBCU'], dtype='object')
In[12]: c2 = columns[2:5]
c2
Out[12]: Index(['STABBR', 'HBCU', 'MENONLY'], dtype='object')
# 联合
In[13]: c1.union(c2)
Out[13]: Index(['CITY', 'HBCU', 'INSTNM', 'MENONLY', 'STABBR'], dtype='object')
In[14]: c1 | c2
Out[14]: Index(['CITY', 'HBCU', 'INSTNM', 'MENONLY', 'STABBR'], dtype='object')
# 对称差
In[15]: c1.symmetric_difference(c2)
Out[15]: Index(['CITY', 'INSTNM', 'MENONLY'], dtype='object')
In[16]: c1 ^ c2
Out[16]: Index(['CITY', 'INSTNM', 'MENONLY'], dtype='object')
2. 求笛卡尔积
# 创建两个有不同索引、但包含一些相同值的Series
In[17]: s1 = pd.Series(index=list('aaab'), data=np.arange(4))
s1
Out[17]: a 0
a 1
a 2
b 3
dtype: int64
In[18]: s2 = pd.Series(index=list('cababb'), data=np.arange(6))
s2
Out[18]: c 0
a 1
b 2
a 3
b 4
b 5
dtype: int64
# 二者相加,以产生一个笛卡尔积
In[19]: s1 + s2
Out[19]: a 1.0
a 3.0
a 2.0
a 4.0
a 3.0
a 5.0
b 5.0
b 7.0
b 8.0
c NaN
dtype: float64
更多
# 当两组索引元素完全相同、顺序也相同时,不会生成笛卡尔积;索引会按照它们的位置对齐。下面的例子,两个Series完全相同,结果也是整数
In[20]: s1 = pd.Series(index=list('aaabb'), data=np.arange(5))
s2 = pd.Series(index=list('aaabb'), data=np.arange(5))
s1 + s2
Out[20]: a 0
a 2
a 4
b 6
b 8
dtype: int64
# 如果索引元素相同,但顺序不同,是能产生笛卡尔积的
In[21]: s1 = pd.Series(index=list('aaabb'), data=np.arange(5))
s2 = pd.Series(index=list('bbaaa'), data=np.arange(5))
s1 + s2
Out[21]: a 2
a 3
a 4
a 3
a 4
a 5
a 4
a 5
a 6
b 3
b 4
b 4
b 5
dtype: int64
3. 索引爆炸
# 读取employee数据集,设定行索引是RACE
In[22]: employee = pd.read_csv('data/employee.csv', index_col='RACE')
employee.head()
Out[22]:
# 选取BASE_SALARY做成两个Series,判断二者是否相同
In[23]: salary1 = employee['BASE_SALARY']
salary2 = employee['BASE_SALARY']
salary1 is salary2
Out[23]: True
# 结果是True,表明二者指向的同一个对象。这意味着,如果修改一个,另一个也会去改变。为了收到一个全新的数据,使用copy方法:
In[24]: salary1 = employee['BASE_SALARY'].copy()
salary2 = employee['BASE_SALARY'].copy()
salary1 is salary2
Out[24]: False
# 对其中一个做索引排序,比较二者是否不同
In[25]: salary1 = salary1.sort_index()
salary1.head()
Out[25]: RACE
American Indian or Alaskan Native 78355.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native 26125.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native 98536.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native NaN
American Indian or Alaskan Native 55461.0
Name: BASE_SALARY, dtype: float64
In[26]: salary2.head()
Out[26]: RACE
Hispanic/Latino 121862.0
Hispanic/Latino 26125.0
White 45279.0
White 63166.0
White 56347.0
Name: BASE_SALARY, dtype: float64
# 将两个Series相加
In[27]: salary_add = salary1 + salary2
In[28]: salary_add.head()
Out[28]: RACE
American Indian or Alaskan Native 138702.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native 156710.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native 176891.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native 159594.0
American Indian or Alaskan Native 127734.0
Name: BASE_SALARY, dtype: float64
# 再将salary1与其自身相加;查看几个所得结果的长度,可以看到长度从2000到达了117万
In[29]: salary_add1 = salary1 + salary1
len(salary1), len(salary2), len(salary_add), len(salary_add1)
Out[29]: (2000, 2000, 1175424, 2000)
更多
# 验证salary_add值的个数。因为笛卡尔积是作用在相同索引元素上的,可以对其平方值求和
In[30]: index_vc = salary1.index.value_counts(dropna=False)
index_vc
Out[30]: Black or African American 700
White 665
Hispanic/Latino 480
Asian/Pacific Islander 107
NaN 35
American Indian or Alaskan Native 11
Others 2
Name: RACE, dtype: int64
In[31]: index_vc.pow(2).sum()
Out[31]: 1175424
4. 用不等索引填充数值
# 读取三个baseball数据集,行索引设为playerID
In[32]: baseball_14 = pd.read_csv('data/baseball14.csv', index_col='playerID')
baseball_15 = pd.read_csv('data/baseball15.csv', index_col='playerID')
baseball_16 = pd.read_csv('data/baseball16.csv', index_col='playerID')
baseball_14.head()
Out[32]:
# 用索引方法difference,找到哪些索引标签在baseball_14中,却不在baseball_15、baseball_16中
In[33]: baseball_14.index.difference(baseball_15.index)
Out[33]: Index(['corpoca01', 'dominma01', 'fowlede01', 'grossro01', 'guzmaje01',
'hoeslj01', 'krausma01', 'preslal01', 'singljo02'],
dtype='object', name='playerID')
In[34]: baseball_14.index.difference(baseball_16.index)
Out[34]: Index(['congeha01', 'correca01', 'gattiev01', 'gomezca01',
'lowrije01', 'rasmuco01', 'tuckepr01', 'valbulu01'],
dtype='object', name='playerID')
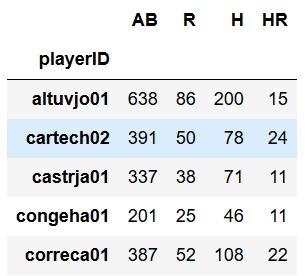
# 找到每名球员在过去三个赛季的击球数,H列包含了这个数据
In[35]: hits_14 = baseball_14['H']
hits_15 = baseball_15['H']
hits_16 = baseball_16['H']
hits_14.head()
Out[35]: Index(['corpoca01', 'dominma01', 'fowlede01', 'grossro01', 'guzmaje01',
'hoeslj01', 'krausma01', 'preslal01', 'singljo02'],
dtype='object', name='playerID')
# 将hits_14和hits_15两列相加
In[36]: (hits_14 + hits_15).head()
Out[36]: playerID
altuvjo01 425.0
cartech02 193.0
castrja01 174.0
congeha01 NaN
corpoca01 NaN
Name: H, dtype: float64
# congeha01 和 corpoca01 在2015年是有记录的,但是结果缺失了。使用add方法和参数fill_value,避免产生缺失值
In[37]: hits_14.add(hits_15, fill_value=0).head()
Out[37]: playerID
altuvjo01 425.0
cartech02 193.0
castrja01 174.0
congeha01 46.0
corpoca01 40.0
Name: H, dtype: float64
# 再将2016的数据也加上
In[38]: hits_total = hits_14.add(hits_15, fill_value=0).add(hits_16, fill_value=0)
hits_total.head()
Out[38]: playerID
altuvjo01 641.0
bregmal01 53.0
cartech02 193.0
castrja01 243.0
congeha01 46.0
Name: H, dtype: float64
# 检查结果中是否有缺失值
In[39]: hits_total.hasnans
Out[39]: False
原理
# 如果一个元素在两个Series都是缺失值,即便使用了fill_value,相加的结果也仍是缺失值
In[40]: s = pd.Series(index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], data=[np.nan, 3, np.nan, 1])
s
Out[40]: a NaN
b 3.0
c NaN
d 1.0
dtype: float64
In[41]: s1 = pd.Series(index=['a', 'b', 'c'], data=[np.nan, 6, 10])
s1
Out[41]: a NaN
b 6.0
c 10.0
dtype: float64
In[42]: s.add(s1, fill_value=5)
Out[42]: a NaN
b 9.0
c 15.0
d 6.0
dtype: float64
In[43]: s1.add(s, fill_value=5)
Out[43]: a NaN
b 9.0
c 15.0
d 6.0
dtype: float64
更多
# 从baseball_14中选取一些列
In[44]: df_14 = baseball_14[['G','AB', 'R', 'H']]
df_14.head()
Out[44]:
# 再从baseball_15中选取一些列,有相同的、也有不同的
In[45]: df_15 = baseball_15[['AB', 'R', 'H', 'HR']]
df_15.head()
Out[45]:
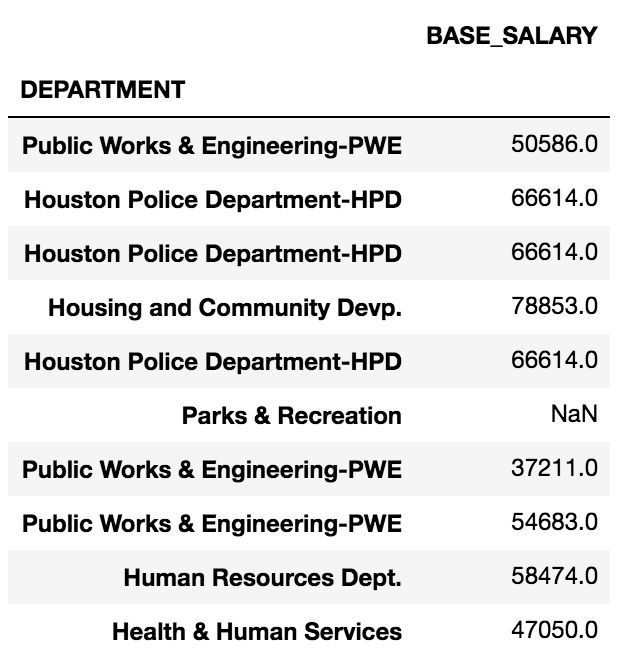
# 将二者相加的话,只要行或列不能对齐,就会产生缺失值。style属性的highlight_null方法可以高亮缺失值
In[46]: (df_14 + df_15).head(10).style.highlight_null('yellow')
Out[46]:
# 即便使用了fill_value=0,有些值也会是缺失值,这是因为一些行和列的组合根本不存在输入的数据中
In[47]: df_14.add(df_15, fill_value=0).head(10).style.highlight_null('yellow')
Out[47]:
5. 从不同的DataFrame追加列
# 读取employee数据,选取'DEPARTMENT', 'BASE_SALARY'这两列
In[48]: employee = pd.read_csv('data/employee.csv')
dept_sal = employee[['DEPARTMENT', 'BASE_SALARY']]
# 在每个部门内,对BASE_SALARY进行排序
In[49]: dept_sal = dept_sal.sort_values(['DEPARTMENT', 'BASE_SALARY'],
ascending=[True, False])
# 用drop_duplicates方法保留每个部门的第一行
In[50]: max_dept_sal = dept_sal.drop_duplicates(subset='DEPARTMENT')
max_dept_sal.head()
Out[50]:
# 使用DEPARTMENT作为行索引
In[51]: max_dept_sal = max_dept_sal.set_index('DEPARTMENT')
employee = employee.set_index('DEPARTMENT')
# 现在行索引包含匹配值了,可以向employee的DataFrame新增一列
In[52]: employee['MAX_DEPT_SALARY'] = max_dept_sal['BASE_SALARY']
In[53]: pd.options.display.max_columns = 6
Out[54]:
# 现在可以用query查看是否有BASE_SALARY大于MAX_DEPT_SALARY的
In[55]: employee.query('BASE_SALARY > MAX_DEPT_SALARY')
Out[55]:
原理
# 用random从dept_sal随机取10行,不做替换
In[56]: np.random.seed(1234)
random_salary = dept_sal.sample(n=10).set_index('DEPARTMENT')
random_salary
Out[56]:
# random_salary中是有重复索引的,employee DataFrame的标签要对应random_salary中的多个标签
In[57]: employee['RANDOM_SALARY'] = random_salary['BASE_SALARY']
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
in ()
----> 1 employee['RANDOM_SALARY'] = random_salary['BASE_SALARY']
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/frame.py in __setitem__(self, key, value)
2329 else:
2330 # set column
-> 2331 self._set_item(key, value)
2332
2333 def _setitem_slice(self, key, value):
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/frame.py in _set_item(self, key, value)
2395
2396 self._ensure_valid_index(value)
-> 2397 value = self._sanitize_column(key, value)
2398 NDFrame._set_item(self, key, value)
2399
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/frame.py in _sanitize_column(self, key, value, broadcast)
2545
2546 if isinstance(value, Series):
-> 2547 value = reindexer(value)
2548
2549 elif isinstance(value, DataFrame):
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/frame.py in reindexer(value)
2537 # duplicate axis
2538 if not value.index.is_unique:
-> 2539 raise e
2540
2541 # other
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/frame.py in reindexer(value)
2532 # GH 4107
2533 try:
-> 2534 value = value.reindex(self.index)._values
2535 except Exception as e:
2536
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/series.py in reindex(self, index, **kwargs)
2424 @Appender(generic._shared_docs['reindex'] % _shared_doc_kwargs)
2425 def reindex(self, index=None, **kwargs):
-> 2426 return super(Series, self).reindex(index=index, **kwargs)
2427
2428 @Appender(generic._shared_docs['fillna'] % _shared_doc_kwargs)
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.py in reindex(self, *args, **kwargs)
2513 # perform the reindex on the axes
2514 return self._reindex_axes(axes, level, limit, tolerance, method,
-> 2515 fill_value, copy).__finalize__(self)
2516
2517 def _reindex_axes(self, axes, level, limit, tolerance, method, fill_value,
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.py in _reindex_axes(self, axes, level, limit, tolerance, method, fill_value, copy)
2531 obj = obj._reindex_with_indexers({axis: [new_index, indexer]},
2532 fill_value=fill_value,
-> 2533 copy=copy, allow_dups=False)
2534
2535 return obj
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.py in _reindex_with_indexers(self, reindexers, fill_value, copy, allow_dups)
2625 fill_value=fill_value,
2626 allow_dups=allow_dups,
-> 2627 copy=copy)
2628
2629 if copy and new_data is self._data:
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/internals.py in reindex_indexer(self, new_axis, indexer, axis, fill_value, allow_dups, copy)
3884 # some axes don't allow reindexing with dups
3885 if not allow_dups:
-> 3886 self.axes[axis]._can_reindex(indexer)
3887
3888 if axis >= self.ndim:
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/indexes/base.py in _can_reindex(self, indexer)
2834 # trying to reindex on an axis with duplicates
2835 if not self.is_unique and len(indexer):
-> 2836 raise ValueError("cannot reindex from a duplicate axis")
2837
2838 def reindex(self, target, method=None, level=None, limit=None,
ValueError: cannot reindex from a duplicate axis
更多
# 选取max_dept_sal['BASE_SALARY']的前三行,赋值给employee['MAX_SALARY2']
In[58]: employee['MAX_SALARY2'] = max_dept_sal['BASE_SALARY'].head(3)
# 对MAX_SALARY2统计
In[59]: employee.MAX_SALARY2.value_counts()
Out[59]: 140416.0 29
100000.0 11
64251.0 5
Name: MAX_SALARY2, dtype: int64
# 因为只填充了三个部门的值,所有其它部门在结果中都是缺失值
In[60]: employee.MAX_SALARY2.isnull().mean()
Out[60]: 0.97750000000000004
6. 高亮每列的最大值
In[61]: pd.options.display.max_rows = 8
# 读取college数据集,INSTNM作为列
In[62]: college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv', index_col='INSTNM')
college.dtypes
Out[62]: CITY object
STABBR object
HBCU float64
MENONLY float64
...
PCTFLOAN float64
UG25ABV float64
MD_EARN_WNE_P10 object
GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP object
Length: 26, dtype: object
# MD_EARN_WNE_P10 和 GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP 两列是对象类型,对其进行检查,发现含有字符串
In[63]: college.MD_EARN_WNE_P10.iloc[0]
Out[63]: '30300'
In[64]: college.MD_EARN_WNE_P10.iloc[0]
Out[64]: '30300'
# 降序检查
In[65]: college.MD_EARN_WNE_P10.sort_values(ascending=False).head()
Out[65]: INSTNM
Sharon Regional Health System School of Nursing PrivacySuppressed
Northcoast Medical Training Academy PrivacySuppressed
Success Schools PrivacySuppressed
Louisiana Culinary Institute PrivacySuppressed
Bais Medrash Toras Chesed PrivacySuppressed
Name: MD_EARN_WNE_P10, dtype: object
# 可以用to_numeric,将某列的值做强制转换
In[66]: cols = ['MD_EARN_WNE_P10', 'GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP']
for col in cols:
college[col] = pd.to_numeric(college[col], errors='coerce')
college.dtypes.loc[cols]
Out[66]: MD_EARN_WNE_P10 float64
GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP float64
dtype: object
# 用select_dtypes方法过滤出数值列
In[67]: college_n = college.select_dtypes(include=[np.number])
college_n.head()
Out[67]:
# 有的列只含有两个值,用nunique()方法挑出这些列
In[68]: criteria = college_n.nunique() == 2
criteria.head()
Out[68]: HBCU True
MENONLY True
WOMENONLY True
RELAFFIL True
SATVRMID False
dtype: bool
# 将布尔Series传给索引运算符,生成二元列的列表
In[69]: binary_cols = college_n.columns[criteria].tolist()
binary_cols
Out[69]: ['HBCU', 'MENONLY', 'WOMENONLY', 'RELAFFIL', 'DISTANCEONLY', 'CURROPER']
# 用drop方法删除这些列
In[70]: college_n2 = college_n.drop(labels=binary_cols, axis='columns')
college_n2.head()
Out[70]:
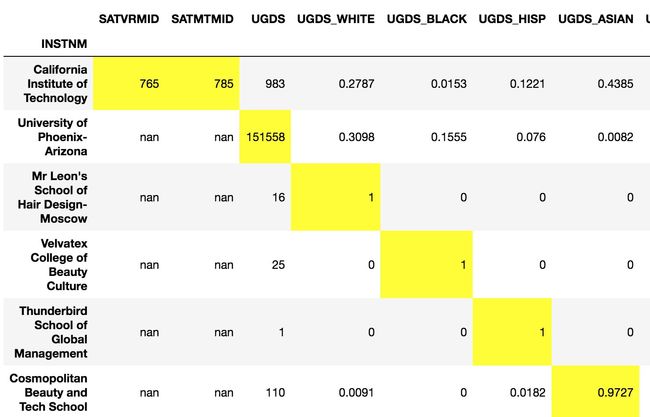
# 用idxmax方法选出每列最大值的行索引标签
In[71]: max_cols = college_n2.idxmax()
max_cols
Out[71]: SATVRMID California Institute of Technology
SATMTMID California Institute of Technology
UGDS University of Phoenix-Arizona
UGDS_WHITE Mr Leon's School of Hair Design-Moscow
...
PCTFLOAN ABC Beauty College Inc
UG25ABV Dongguk University-Los Angeles
MD_EARN_WNE_P10 Medical College of Wisconsin
GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP Southwest University of Visual Arts-Tucson
Length: 18, dtype: object
# 用unique()方法选出所有不重复的列名
In[72]: unique_max_cols = max_cols.unique()
unique_max_cols[:5]
Out[72]: array(['California Institute of Technology',
'University of Phoenix-Arizona',
"Mr Leon's School of Hair Design-Moscow",
'Velvatex College of Beauty Culture',
'Thunderbird School of Global Management'], dtype=object)
# 用max_cols选出只包含最大值的行,用style的highlight_max()高亮
In[73]: college_n2.loc[unique_max_cols].style.highlight_max()
Out[73]:
更多
# 用axis参数可以高亮每行的最大值
In[74]: college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv', index_col='INSTNM')
college_ugds = college.filter(like='UGDS_').head()
college_ugds.style.highlight_max(axis='columns')
Out[74]:
In[75]: pd.Timedelta(1, unit='Y')
Out[75]: Timedelta('365 days 05:49:12')
7. 用链式方法重现idxmax
# 和前面一样,只选出数值列
In[76]: college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv', index_col='INSTNM')
cols = ['MD_EARN_WNE_P10', 'GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP']
for col in cols:
college[col] = pd.to_numeric(college[col], errors='coerce')
college_n = college.select_dtypes(include=[np.number])
criteria = college_n.nunique() == 2
binary_cols = college_n.columns[criteria].tolist()
college_n = college_n.drop(labels=binary_cols, axis='columns')
In[77]: college_n.max().head()
Out[77]: SATVRMID 765.0
SATMTMID 785.0
UGDS 151558.0
UGDS_WHITE 1.0
UGDS_BLACK 1.0
dtype: float64
# college_n.max()可以选出每列的最大值,用eq方法比较DataFrame的每个值和该列的最大值
In[78]: college_n.eq(college_n.max()).head()
Out[78]:
# 用any方法,选出至少包含一个True值的行
In[79]: has_row_max = college_n.eq(college_n.max()).any(axis='columns')
has_row_max.head()
Out[79]: INSTNM
Alabama A & M University False
University of Alabama at Birmingham False
Amridge University False
University of Alabama in Huntsville False
Alabama State University False
dtype: bool
# 因为只有18列,has_row_max最多只能有18个True,来看下实际共有多少个
In[80]: college_n.shape
Out[80]: (7535, 18)
In[81]: has_row_max.sum()
Out[81]: 401
# 结果很奇怪,这是因为许多百分比的列的最大值是1。转而使用cumsum()累积求和
In[82]: has_row_max.sum()
In[83]: college_n.eq(college_n.max()).cumsum()
Out[83]:
# 一些列只有一个最大值,比如SATVRMID和SATMTMID,UGDS_WHITE列却有许多最大值。有109所学校的学生100%是白人。如果再使用一次cunsum,1在每列中就只出现一次,而且会是最大值首次出现的位置:
>>> college_n.eq(college_n.max()).cumsum().cumsum()
# 现在就可以用eq方法去和1进行比较,然后用any方法,选出所有至少包含一个True值的行
In[84]: has_row_max2 = college_n.eq(college_n.max())\
.cumsum()\
.cumsum()\
.eq(1)\
.any(axis='columns')
has_row_max2.head()
Out[84]: INSTNM
Alabama A & M University False
University of Alabama at Birmingham False
Amridge University False
University of Alabama in Huntsville False
Alabama State University False
dtype: bool
# 查看有多少True值
In[85]: has_row_max2.sum()
Out[85]: 16
# 直接通过布尔索引选出这些学校
In[86]: idxmax_cols = has_row_max2[has_row_max2].index
idxmax_cols
Out[86]: Index(['Thunderbird School of Global Management',
'Southwest University of Visual Arts-Tucson', 'ABC Beauty College Inc',
'Velvatex College of Beauty Culture',
'California Institute of Technology',
'Le Cordon Bleu College of Culinary Arts-San Francisco',
'MTI Business College Inc', 'Dongguk University-Los Angeles',
'Mr Leon's School of Hair Design-Moscow',
'Haskell Indian Nations University', 'LIU Brentwood',
'Medical College of Wisconsin', 'Palau Community College',
'California University of Management and Sciences',
'Cosmopolitan Beauty and Tech School', 'University of Phoenix-Arizona'],
dtype='object', name='INSTNM')
# 和idxmax方法的结果比较
In[87]: set(college_n.idxmax().unique()) == set(idxmax_cols)
Out[87]: True
更多
# 耗时比较
In[88]: %timeit college_n.idxmax().values
1.11 ms ± 50.9 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
Out[89]: %timeit college_n.eq(college_n.max())\
.cumsum()\
.cumsum()\
.eq(1)\
.any(axis='columns')\
[lambda x: x].index
5.26 ms ± 35.6 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
8. 找到最常见的最大值
# 读取college,过滤出只包含本科生种族比例信息的列
In[90]: pd.options.display.max_rows= 40
In[91]: college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv', index_col='INSTNM')
college_ugds = college.filter(like='UGDS_')
college_ugds.head()
Out[91]:
# 用idxmax方法选出每行种族比例最高的列名
In[92]: highest_percentage_race = college_ugds.idxmax(axis='columns')
highest_percentage_race.head()
Out[92]: INSTNM
Alabama A & M University UGDS_BLACK
University of Alabama at Birmingham UGDS_WHITE
Amridge University UGDS_BLACK
University of Alabama in Huntsville UGDS_WHITE
Alabama State University UGDS_BLACK
dtype: object
# 用value_counts,查看最大值的分布
In[93]: highest_percentage_race.value_counts(normalize=True)
Out[93]: UGDS_WHITE 0.670352
UGDS_BLACK 0.151586
UGDS_HISP 0.129473
UGDS_UNKN 0.023422
UGDS_ASIAN 0.012074
UGDS_AIAN 0.006110
UGDS_NRA 0.004073
UGDS_NHPI 0.001746
UGDS_2MOR 0.001164
dtype: float64
更多
# 对于黑人比例最高的学校,排名第二的种族的分布情况
In[94]: college_black = college_ugds[highest_percentage_race == 'UGDS_BLACK']
college_black = college_black.drop('UGDS_BLACK', axis='columns')
college_black.idxmax(axis='columns').value_counts(normalize=True)
Out[94]: UGDS_WHITE 0.670352
UGDS_BLACK 0.151586
UGDS_HISP 0.129473
UGDS_UNKN 0.023422
UGDS_ASIAN 0.012074
UGDS_AIAN 0.006110
UGDS_NRA 0.004073
UGDS_NHPI 0.001746
UGDS_2MOR 0.001164
dtype: float64
第01章 Pandas基础
第02章 DataFrame运算
第03章 数据分析入门
第04章 选取数据子集
第05章 布尔索引
第06章 索引对齐
第07章 分组聚合、过滤、转换
第08章 数据清理
第09章 合并Pandas对象
第10章 时间序列分析
第11章 用Matplotlib、Pandas、Seaborn进行可视化