固定大小字节数组(Fixed-size byte arrays)之间的转换
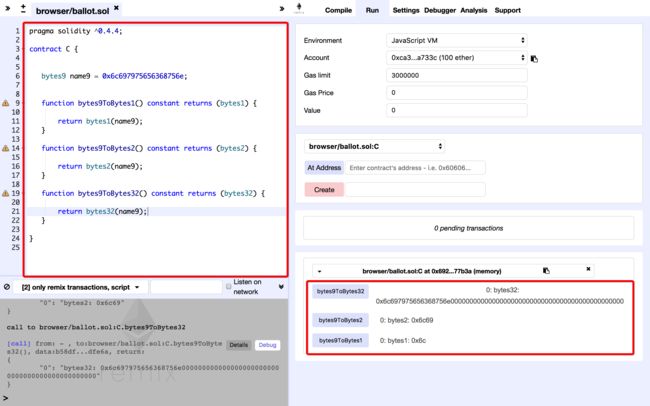
固定大小字节我们可以通过bytes0 ~ bytes32来进行声明,固定大小字节数组的长度不可变,内容不可修改。接下来我们通过下面的代码看看固定大小字节之间的转换关系。
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
bytes9 name9 = 0x6c697975656368756e;
function bytes9ToBytes1() constant returns (bytes1) {
return bytes1(name9);
}
function bytes9ToBytes2() constant returns (bytes2) {
return bytes2(name9);
}
function bytes9ToBytes32() constant returns (bytes32) {
return bytes32(name9);
}
}
结论:当bytes9转bytes1或者bytes2时,会进行低位截断,0x6c697975656368756e转换为bytes1,结果为0x6c,转换为bytes2时结果为0x6c69。当0x6c697975656368756e转换为bytes32时会进行低位补齐,结果为0x6c697975656368756e0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000。
固定大小字节数组(Fixed-size byte arrays)转动态大小字节数组(Dynamically-sized byte array)
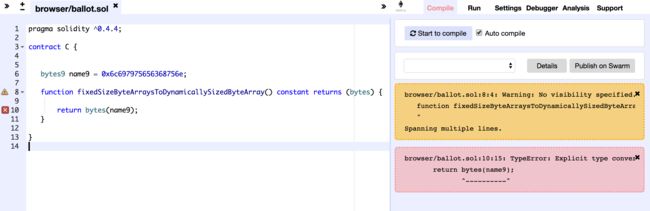
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
bytes9 name9 = 0x6c697975656368756e;
function fixedSizeByteArraysToDynamicallySizedByteArray() constant returns (bytes) {
return bytes(name9);
}
}
对于刚接触的童鞋,很多人都会用上面的方法进行转换,以为理所当然,殊不知编译运行时,代码报错,原因如下:
备注:简言之,固定大小字节数组和动态大小字节数组之间不能简单直接转换。
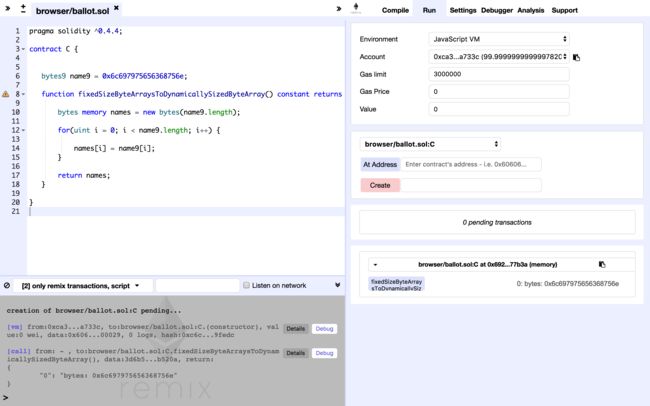
下面是固定大小字节数组转动态大小字节数组正确的姿势。
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
bytes9 name9 = 0x6c697975656368756e;
function fixedSizeByteArraysToDynamicallySizedByteArray() constant returns (bytes) {
bytes memory names = new bytes(name9.length);
for(uint i = 0; i < name9.length; i++) {
names[i] = name9[I];
}
return names;
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们根据固定字节大小数组的长度来创建一个memory类型的动态类型的字节数组,然后通过一个for循环将固定大小字节数组中的字节按照索引赋给动态大小字节数组即可。
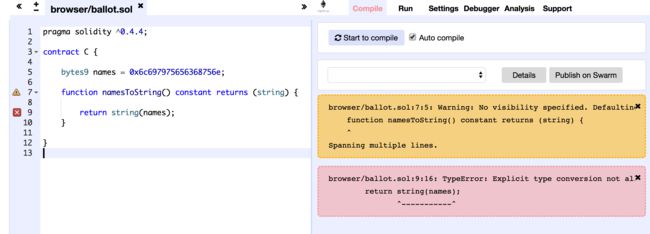
固定大小字节数组(Fixed-size byte arrays)不能直接转换为string
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
bytes9 names = 0x6c697975656368756e;
function namesToString() constant returns (string) {
return string(names);
}
}
动态大小字节数组(Dynamically-sized byte array)转string
重要:因为string是特殊的动态字节数组,所以string只能和动态大小字节数组(Dynamically-sized byte array)之间进行转换,不能和固定大小字节数组进行转行。
- 如果是现成的动态大小字节数组(Dynamically-sized byte array),如下:
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
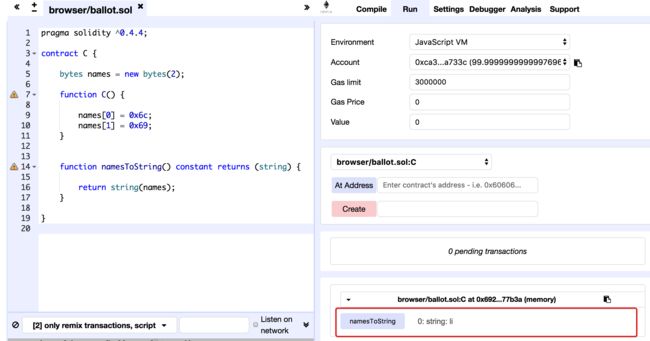
bytes names = new bytes(2);
function C() {
names[0] = 0x6c;
names[1] = 0x69;
}
function namesToString() constant returns (string) {
return string(names);
}
}
- 如果是固定大小字节数组转string,那么就需要先将字节数组转动态字节数组,再转字符串
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
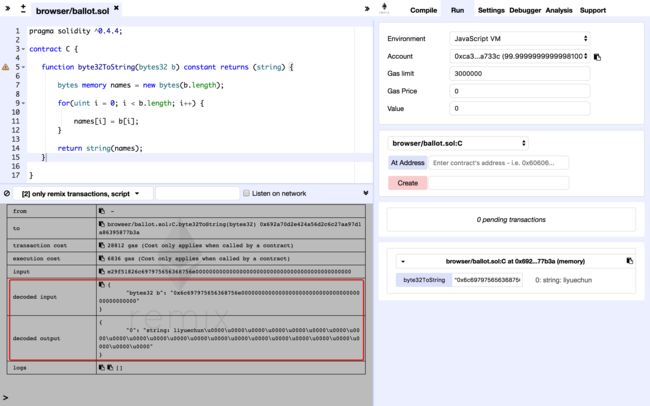
function byte32ToString(bytes32 b) constant returns (string) {
bytes memory names = new bytes(b.length);
for(uint i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
names[i] = b[I];
}
return string(names);
}
}
可以通过0x6c697975656368756e作为参数进行测试,右边的返回结果看似为liyuechun,它的实际内容为liyuechun\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000,所以在实际的操作中,我们应该将后面的一些列\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000去掉。
- 正确的固定大小字节数组转string的代码
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
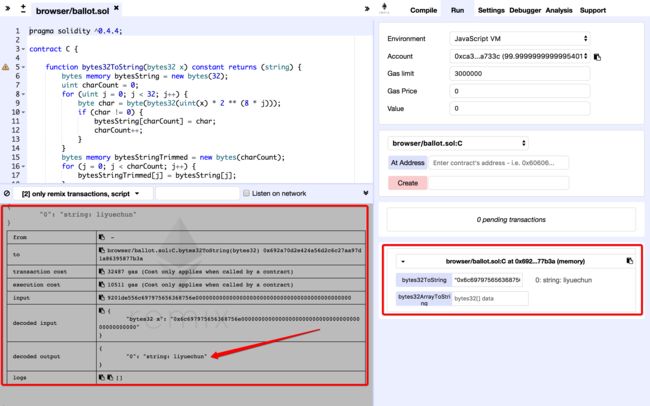
function bytes32ToString(bytes32 x) constant returns (string) {
bytes memory bytesString = new bytes(32);
uint charCount = 0;
for (uint j = 0; j < 32; j++) {
byte char = byte(bytes32(uint(x) * 2 ** (8 * j)));
if (char != 0) {
bytesString[charCount] = char;
charCount++;
}
}
bytes memory bytesStringTrimmed = new bytes(charCount);
for (j = 0; j < charCount; j++) {
bytesStringTrimmed[j] = bytesString[j];
}
return string(bytesStringTrimmed);
}
function bytes32ArrayToString(bytes32[] data) constant returns (string) {
bytes memory bytesString = new bytes(data.length * 32);
uint urlLength;
for (uint i = 0; i< data.length; i++) {
for (uint j = 0; j < 32; j++) {
byte char = byte(bytes32(uint(data[i]) * 2 ** (8 * j)));
if (char != 0) {
bytesString[urlLength] = char;
urlLength += 1;
}
}
}
bytes memory bytesStringTrimmed = new bytes(urlLength);
for (i = 0; i < urlLength; i++) {
bytesStringTrimmed[i] = bytesString[I];
}
return string(bytesStringTrimmed);
}
}
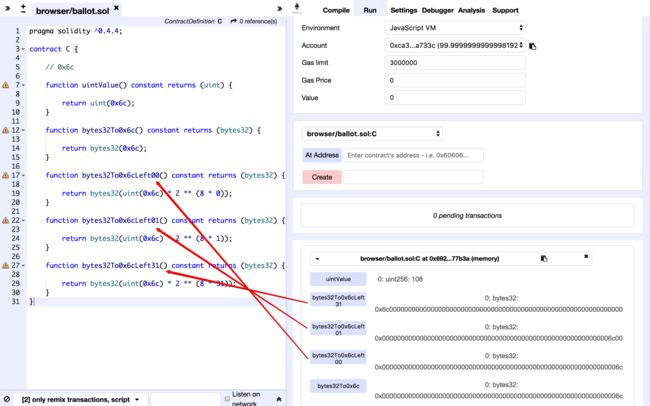
byte char = byte(bytes32(uint(x) * 2 ** (8 * j)))在上面的代码中,估计大家最难看懂的就是这一句代码,我们通过下面的案例给大家解析:
pragma solidity ^0.4.4;
contract C {
// 0x6c
function uintValue() constant returns (uint) {
return uint(0x6c);
}
function bytes32To0x6c() constant returns (bytes32) {
return bytes32(0x6c);
}
function bytes32To0x6cLeft00() constant returns (bytes32) {
return bytes32(uint(0x6c) * 2 ** (8 * 0));
}
function bytes32To0x6cLeft01() constant returns (bytes32) {
return bytes32(uint(0x6c) * 2 ** (8 * 1));
}
function bytes32To0x6cLeft31() constant returns (bytes32) {
return bytes32(uint(0x6c) * 2 ** (8 * 31));
}
}
bytes32(uint(0x6c) * 2 ** (8 * 31));左移31位bytes32(uint(0x6c) * 2 ** (8 * 1));左移1位
通过byte(bytes32(uint(x) * 2 ** (8 * j)))获取到的始终是第0个字节。
总结
string本身是一个特殊的动态字节数组,所以它只能和bytes之间进行转换,不能和固定大小字节数组进行直接转换,如果是固定字节大小数组,需要将其转换为动态字节大小数组才能进行转换。
原文:Solidity Types - 动态字节数组(Dynamically-sized byte array)、固定大小字节数组(Fixed-size byte arrays)、string之间的转换关系
作者:黎跃春