一、进程的含义
进程是运行中的程序,进程是操作系统资源分配的基本单位/最小单位。
- 进程在内存,程序在硬盘(程序代码在硬盘,运行时转存到内存)
- 同时运行2个程序时,它们是运行在物理内存的2个互不相关的地址上
例1:
// 001.c
#include
#include
int a;
int main()
{
int b;
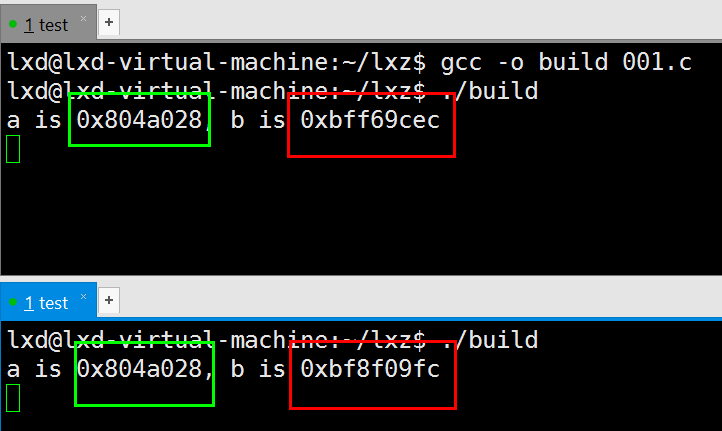
printf("a is %p, b is %p\n", &a, &b); // 查看a和b的地址
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
说明:
Q1:2个程序运行时,为何a的地址是一样的?
显示的地址都是虚拟地址,而非物理地址。
CPU中的MMU(内存管理单元)会根据不同的进程(进程号),将虚拟地址映射到不同的物理地址上。
Q2:2个程序运行时,为何a的地址一样,而b的地址是不一样的?
a是全局变量,存放在数据段;b是局部变量,存放在栈段。
编译完后,数据段的全局变量的地址是固定好的;栈是运行时才会分配地址的,是动态的,因此每次运行时地址都是不同的。
二、进程终止方式
1、return
2、exit
// return与exit基本是等价的
return 0;
exit(0);
// 程序结束的时候,既可以用return 0; 也可以用exit(0)。
// 二者唯一的区别:
// return 0; 返回时,会将程序控制权先交给程序(返回给函数)
// exit(0); 退出时,会将程序控制权直接交给内核
3、_exit
exit与_exit的区别:
1、在不同的头文件中定义的。
// man exit
#include
void exit(int status);
// man _exit
#include
void _exit(int status);
2、exit在退出时,会先做一些清理操作(比如:关闭文件描述符),这样会使输出缓存中的数据被刷新一下;_exit不会做。
如:文件IO中,用到一个行缓存,没有用\0,暂时不会被打印出来的。用return或exit,就会将信息刷到屏幕上/文件中。而用_exit是不会做清理的,在退出时若没有打印出来,就一直不会被打印出来。
三、进程创建
1、fork函数
通过fork函数创建进程。
创建进程也可以叫fork一个进程。
Linux系统中的进程,都是由已有的进程派生出来的,即:父进程创建子进程。除了OS启动时,会创建一个init进程外,其他进程都是通过fork创建的。
vfork:最终也是调用了fork。
fork调用成功后,会派生出子进程;若调用失败,会返回-1。
子进程会继承父进程的几乎所有的数据(包括 数据段、代码段、用户id、主id、创建的文件描述符等),相当于父进程的一个拷贝(整个程序都会拷贝),唯一的区别是pid号不一样。
fork之后,就是2个进程在运行,2个进程是相互独立的。
CPU先调用哪个进程,是不能确定的。
例2:
// 002.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid = 0;
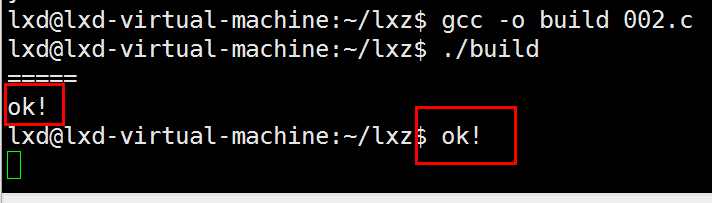
printf("=====\n"); // =====存在于数据段
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
fork之后,会产生2个返回值:若返回值>0,则是父进程;若返回值==0,则是子进程。
例3:
// 003.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid = 0;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
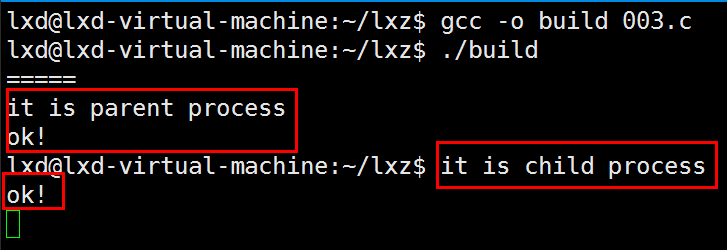
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("it is child process\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
2、进程ID
进程创建后,就会得到一个唯一标识这个进程的ID(进程号)。
include
include
pid_t getpid(void); // 得到当前调用函数的进程的id
pid_t getppid(void); // 得到当前调用函数的进程的父进程的id
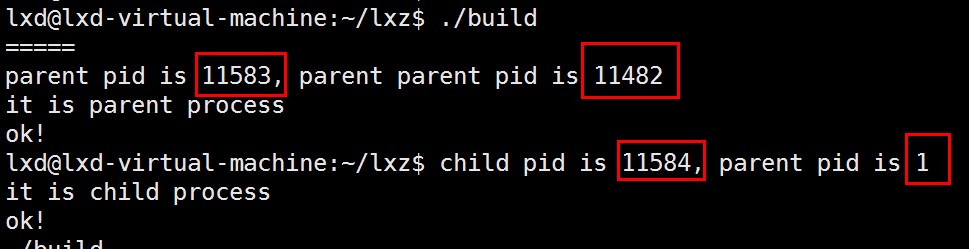
例4:
// 004.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
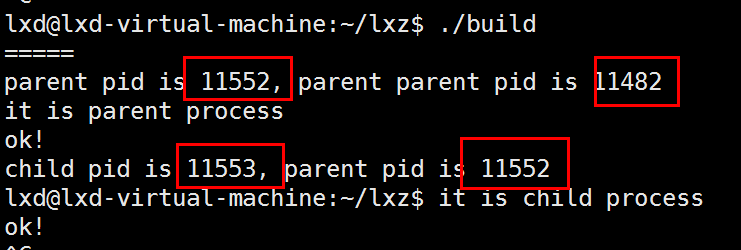
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child pid is %d, parent pid is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is child process\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
printf("parent pid is %d, parent parent pid is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
bash fork得到父进程,父进程fork得到子进程。
四、进程运行时
1、回收子进程
Q:若不想让子进程变为孤儿进程,该如何做?
(1)使用sleep()函数:等待多长时间
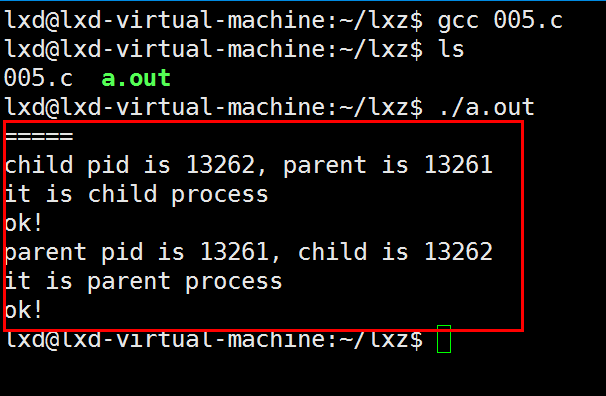
例5:
// 005.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child pid is %d, parent is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is child process\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
sleep(1); // 睡1s,保证子进程先退出,然后再运行父进程
printf("parent pid is %d, child is %d\n", getpid(), pid);
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
(2)使用getchar函数:等待键盘输入
例6:
// 006.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child pid is %d, parent is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is child process\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
getchar(); // 等待键盘输入
printf("parent pid is %d, child is %d\n", getpid(), pid);
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
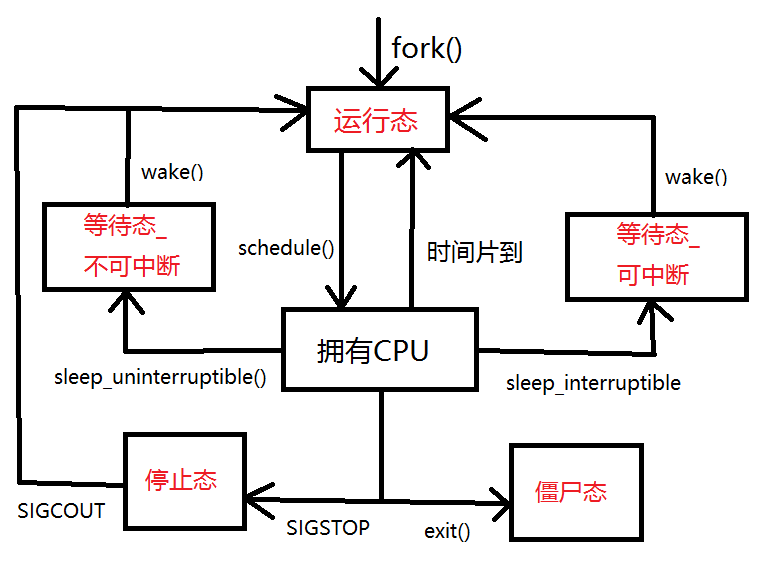
2、进程状态
- 运行态:进程正在运行或在运行队列中等待
- 不可中断等待态:进程必须等待某个事件完成,在等待中不可以被信号或者定时器唤醒
- 可中断等待态:进程等待过程中可以被信号或定时器唤醒
- 停止状态:进程收到信号,如:
SIGSTOP、SIGSTP、SIGIN、SIGOUT - 僵尸态:子进程先于父进程结束,子进程变为僵尸态(子进程虽然结束了,但是资源仍然占用着),父进程需要对子进程资源进行回收即可解除僵尸态(调用wait函数)
3、wait函数
DESCRIPTION
All of these system calls are used to wait for state changes in a child of the calling process, and obtain information about the child whose state has changed. A state change is considered to be: the child terminated; the child was stopped by a signal; or the child was resumed by a signal. In the case of a terminated child, performing a wait allows the system to release the resources associated with the child; if a wait is not performed, then the terminated child remains in a "zombie" state.
If a child has already changed state, then these calls return immediately. Otherwise they block until either a child changes state or a signal handler interrupts the call (assuming that system calls are not automatically restarted using the SA_RESTART flag of sigaction(2)). In the remainder of this page, a child whose state has changed and which has not yet been waited upon by one of these system calls is termed waitable.
// man wait:
#include
#include
pid_t wait(int *status); // 只能等到第一个子进程退出
// 父进程调用wait后,父进程就会阻塞,直到子进程运行结束,wait继续运行,此时父进程就对子进程的资源进行回收
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options); // 可以等待指定的子进程退出
wait() and waitpid()
The wait() system call suspends execution of the calling process until one of its children terminates. The call wait(&status) is equivalent to:
waitpid(-1, &status, 0);
The waitpid() system call suspends execution of the calling process until a child specified by pid argument has changed state. By default, waitpid() waits only for terminated children, but this behavior is modifiable via the options argument.
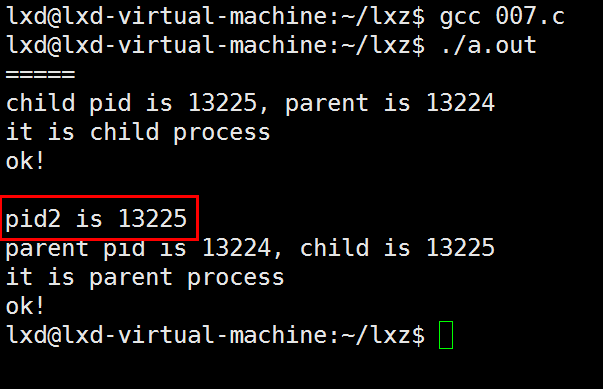
例7:
// 007.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t pid2;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child pid is %d, parent is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is child process\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
getchar();
pid2 = wait(0); // 也可以不用返回值pid2。使用pid2意义不大,因为一旦wait返回,肯定子进程退出了;若wait不返回一直阻塞,说明一直在等待
// wait中是一个指针,此处不关心此指针,写一个0
printf("pid2 is %d\n", pid2);
printf("parent pid is %d, child is %d\n", getpid(), pid);
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
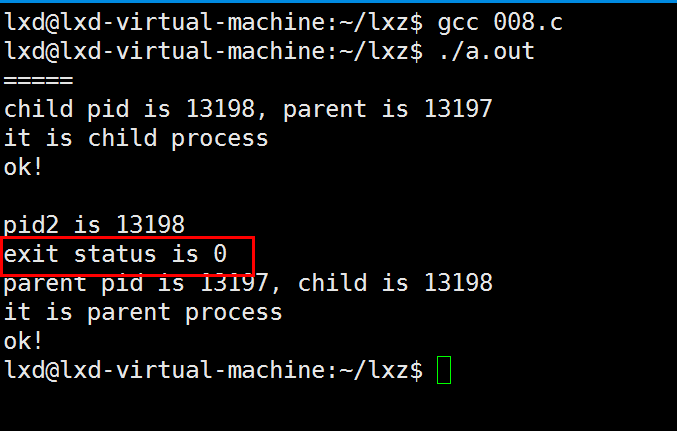
例8:
// 008.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t pid2;
int status;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child pid is %d, parent is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is child process\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
getchar();
pid2 = wait(&status);
printf("pid2 is %d\n", pid2);
printf("exit status is %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
printf("parent pid is %d, child is %d\n", getpid(), pid);
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
五、子进程执行新程序
子进程若是拷贝父进程,是没有意义的;子进程必须执行新程序,才有创建的意义。
方法:使用exec函数族。
// man exec:
execl, execlp, execle, execv, execvp, execvpe - execute a file
#include
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
// const char *path:只读的路径(相对路径/绝对路径)。
// const char *arg:参数,是字符串。它是可执行文件的名字。
// ...:可变参数
// 若无参数,写 NULL;不管有没有参数,最后结尾的必须是 NULL (为了告诉函数,参数到此为止)
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ..., char * const envp[]);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
// 将参数写进一个数组中,因此不需要可变参数。结尾也是NULL。
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
例9:
(1)
// address.c
#include
#include
int a;
int main()
{
int b;
printf("a is %p, b is %p\n", &a, &b);
return 0;
}
(2)
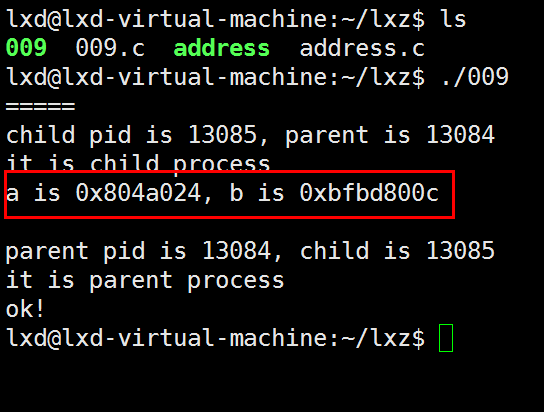
// 009.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t pid2;
int status;
printf("=====\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
printf("child pid is %d, parent is %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
printf("it is child process\n");
execl("./address", "address", NULL);
printf("after execl\n");
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
getchar();
printf("parent pid is %d, child is %d\n", getpid(), pid);
printf("it is parent process\n");
}
printf("ok!\n");
return 0;
}
结果说明:
1)运行009时,在子进程中,把address程序也运行了;
2)没有打印出after execl字符串,也只打印了一个ok!:
当子进程调用execl后,子进程就将代码完全替换成了新程序:
- 子进程的代码段替换成新程序的代码段
- 原有的数据段和堆段还有其他数据都废弃掉,全部更新为新程序的数据段和堆段)
- 唯一保留的是进程ID
并开始执行新程序。
因此,execl后面的代码都不起作用了,因此没有打印出after execl字符串,也只打印了一个ok!。