IK Analyzer 介绍
IKAnalyzer是一个开源的,基于java语言开发的轻量级的中文分词工具包。从2006年12月推出1.0版开始,IKAnalyzer已经推出了3个大版本。最初,它是以开源项目Luence为应用主体的,结合词典分词和文法分析算法的中文分词组件。新版本的 IKAnalyzer3.0则发展为面向Java的公用分词组件,独立于Lucene项目,同时提供了对Lucene的默认优化实现。
IK Analyzer 2012特性:
- 采用了特有的“正向迭代最细粒度切分算法“,支持细粒度和智能分词两种切分模式;
- 2012版本的智能分词模式支持简单的分词排歧义处理和数量词合并输出。
- 采用了多子处理器分析模式,支持:英文字母、数字、中文词汇等分词处理,兼容韩文、日文字符
- 优化的词典存储,更小的内存占用。支持用户词典扩展定义。特别的,在2012版本,词典支持中文,英文,数字混合词语。
介绍了Ik分词器基本情况之后,接下来分析分析源码。从github上将IK分词器源码下载下来https://github.com/wks/ik-analyzer,这个是官方 ik 分词器的一个fork, 原项目地址为 https://code.google.com/p/ik-analyzer。
-
将工程文件夹打开之后是下图的结构
- pom.xml中项目依赖
org.apache.lucene
lucene-core
${lucene.version}
provided
org.apache.solr
solr-core
${lucene.version}
provided
junit
junit
${junit.version}
test
可以看出,IK分词器实现依赖了lucene及solr,其实solr只是作为Solr分词器工厂实现的依赖,与IK分词器关系不大。
配置文件分析
IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml为IK分词器的配置文件,main2012.dic文件为主词典,quantifier.dic文件为量词词典,stopword.dic文件为停用词词典,ext.dic文件为扩展词词典。
- IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml文件内容如下:
IK Analyzer 扩展配置
ext.dic;
stopword.dic;
源码分析
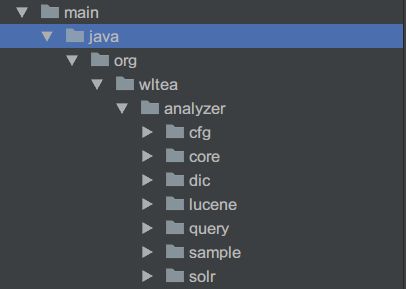
- 目录解释
cfg:配置管理类接口和实现
core:分词器上下文,字符集工具,中文-日韩文子分词器,中文数量词子分词器,IK分词歧义裁决器,IK分词器主类,子分词器接口,英文字符及阿拉伯数字子分词器,IK词元对象,IK分词器专用的Lexem快速排序集合
dic:词典管理类,词典树,词典匹配命中类
lucene:IK分词器的Lucene Analyzer接口实现,IK分词器 Lucene Tokenizer适配器类
query:IK简易查询表达式解析,SWMC算法
sample:IK分词器使用demo
solr:Solr分词器工厂实现
由于今天主题是实现IK分词器访问远程词典的功能实现,故IK具体分词算法今天不分析,只分析新功能实现。
要实现IK分词器远程访问词典,首先要了解IK分词器如何进行分词的。先从一个demo开始。
public Map getParticipleByStr(String content, boolean useSmart) {
Map res=new HashMap<>();
try {
byte[] bt = content.getBytes();// str
InputStream ip = new ByteArrayInputStream(bt);
Reader read = new InputStreamReader(ip);
IKSegmenter iks = new IKSegmenter(read, useSmart);
Lexeme t;
while ((t = iks.next()) != null) {
String tmpKey=t.getLexemeText();
if(res.containsKey(tmpKey)){
Integer val= res.get(tmpKey)+1;
res.replace(tmpKey,val);
}else{
res.put(tmpKey,1);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return res;
}
该方法是根据传入一段文本,根据useSmart值来决定是否启用智能分词。从demo可以看出,真正进行分词的是IKSegmenter iks = new IKSegmenter(read, useSmart);这一行代码。IKSegmenter 类是IK分词器主类,是一个单例类,构造该类的时候有两个参数,一个是传入文本的字节流Reader对象,一个是是否启用智能分词。构造方法如下:
public IKSegmenter(Reader input , boolean useSmart){
this.input = input;
this.cfg = DefaultConfig.getInstance();
this.cfg.setUseSmart(useSmart);
this.init();
}
DefaultConfig类实现了Configuration接口。也是个单例类,类中有获取主词典路径,量词词典路径,本地扩展词典路径,停用词典路径等方法。DefaultConfig构造方法源码如下:
/*
* 初始化配置文件
*/
private DefaultConfig(){
props = new Properties();
InputStream input = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(FILE_NAME);
if(input != null){
try {
props.loadFromXML(input);
} catch (InvalidPropertiesFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IKSegmenter构造方法中有个this.init()方法,该方法代码如下:
private void init(){
//初始化词典单例
Dictionary.initial(this.cfg);
//初始化分词上下文
this.context = new AnalyzeContext(this.cfg);
//加载子分词器
this.segmenters = this.loadSegmenters();
//加载歧义裁决器
this.arbitrator = new IKArbitrator();
}
故,IkSegment初始化的时候要初始化词典Dictionary,该类为词典管理类,同样是单例模式,同时该类中有加载各种词典的方法及个别分词算法使用的方法。
- Dictionary构造方法
private Dictionary(Configuration cfg){
this.cfg = cfg;
this.loadMainDict();
this.loadStopWordDict();
this.loadQuantifierDict();
}
通过构造方法可以看出,该类初始化的时候就加载了主词典,停用词典,量词词典。先看一个loadMainDict()方法代码:
private void loadMainDict(){
//建立一个主词典实例
_MainDict = new DictSegment((char)0);
//读取主词典文件
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(cfg.getMainDictionary());
if(is == null){
throw new RuntimeException("Main Dictionary not found!!!");
}
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is , "UTF-8"), 512);
String theWord = null;
do {
theWord = br.readLine();
if (theWord != null && !"".equals(theWord.trim())) {
_MainDict.fillSegment(theWord.trim().toLowerCase().toCharArray());
}
} while (theWord != null);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
System.err.println("Main Dictionary loading exception.");
ioe.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
is = null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//加载扩展词典
this.loadExtDict();
}
通过InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(cfg.getMainDictionary());可以看出,加载的词典文件必须存放于类根目录才行,即工程resources文件夹下,这样的功能也限制了词典的动态扩展性。
如何实现远程访问扩展词典?
- 首先在IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml文件中添加远程访问词典路径,要发送http请求访问。
IK Analyzer 扩展配置
ext.dic
stopword.dic
http://192.168.70.33:8080/tag.dic
- 在DefaultConfig类中添加获取远程访问词典路径的方法
private final static String REMOTE_EXT_DICT = "remote_ext_dict";
private final static String REMOTE_EXT_STOP = "remote_ext_stopwords";
/**
* 获取远程扩展词典配置路径
*
* @return List<String>
*/
public List getRemoteExtDictionarys() {
List remoteExtDictFiles = new ArrayList(2);
String remoteExtDictCfg = props.getProperty(REMOTE_EXT_DICT);
if (remoteExtDictCfg != null) {
String[] filePaths = remoteExtDictCfg.split(";");
for (String filePath : filePaths) {
if (filePath != null && !"".equals(filePath.trim())) {
remoteExtDictFiles.add(filePath);
}
}
}
return remoteExtDictFiles;
}
/**
* 获取远程停用词典配置路径
* @return List<String>
*/
public List getRemoteExtStopWordDictionarys() {
List remoteExtStopWordDictFiles = new ArrayList(2);
String remoteExtStopWordDictCfg = props.getProperty(REMOTE_EXT_STOP);
if (remoteExtStopWordDictCfg != null) {
String[] filePaths = remoteExtStopWordDictCfg.split(";");
for (String filePath : filePaths) {
if (filePath != null && !"".equals(filePath.trim())) {
remoteExtStopWordDictFiles.add(filePath);
}
}
}
return remoteExtStopWordDictFiles;
}
- 在Dictionary初始化initial(Configuration cfg)方法中添加一个定时发送head请求的单线程的线程池
private static ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
/**
* 词典初始化
* 由于IK Analyzer的词典采用Dictionary类的静态方法进行词典初始化
* 只有当Dictionary类被实际调用时,才会开始载入词典,
* 这将延长首次分词操作的时间
* 该方法提供了一个在应用加载阶段就初始化字典的手段
*
* @return Dictionary
* @param cfg a {@link Configuration} object.
*/
public static Dictionary initial(Configuration cfg){
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Dictionary.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Dictionary(cfg);
singleton.loadMainDict();
singleton.loadQuantifierDict();
singleton.loadStopWordDict();
if(cfg.isEnableRemoteDict()){
// 建立监控线程
for (String location : cfg.getRemoteExtDictionarys()) {
// 10毫秒是初始延迟可以修改的 60是间隔时间 单位毫秒
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Monitor(location), 0, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
for (String location : cfg.getRemoteExtStopWordDictionarys()) {
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Monitor(location), 0, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
该定时执行的线程池内有个Monitor类,该类实现了Runnable接口,同时该类有个远程访问的路径,线程池会定时访问该路径,如果head请求返回的内容有变化就设置last_modified和eTags,如果没变化,则不做任何动作。代码如下:
public class Monitor implements Runnable {
private static CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
/*
* 上次更改时间
*/
private String last_modified;
/*
* 资源属性
*/
private String eTags;
/*
* 请求地址
*/
private String location;
public Monitor(String location) {
this.location = location;
this.last_modified = null;
this.eTags = null;
}
/**
* 监控流程:
* ①向词库服务器发送Head请求
* ②从响应中获取Last-Modify、ETags字段值,判断是否变化
* ③如果未变化,休眠1min,返回第①步
* ④如果有变化,重新加载词典
* ⑤休眠1min,返回第①步
*/
public void run() {
//超时设置
RequestConfig rc = RequestConfig.custom().setConnectionRequestTimeout(10*1000)
.setConnectTimeout(10*1000).setSocketTimeout(15*1000).build();
HttpHead head = new HttpHead(location);
head.setConfig(rc);
//设置请求头
if (last_modified != null) {
head.setHeader("If-Modified-Since", last_modified);
}
if (eTags != null) {
head.setHeader("If-None-Match", eTags);
}
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
response = httpclient.execute(head);
//返回200 才做操作
if(response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()==200){
if (((response.getLastHeader("Last-Modified")!=null) && !response.getLastHeader("Last-Modified").getValue().equalsIgnoreCase(last_modified))
||((response.getLastHeader("ETag")!=null) && !response.getLastHeader("ETag").getValue().equalsIgnoreCase(eTags))) {
// 远程词库有更新,需要重新加载词典,并修改last_modified,eTags
Dictionary.getSingleton().reLoadMainDict();
last_modified = response.getLastHeader("Last-Modified")==null?null:response.getLastHeader("Last-Modified").getValue();
eTags = response.getLastHeader("ETag")==null?null:response.getLastHeader("ETag").getValue();
}
}else if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()==304) {
//没有修改,不做操作
//noop
}else{
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
try {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
为什么会发送Head请求?因为head请求并不返回消息体,特别适用在优先的速度和带宽下来检查资源的有效性,检查超链接的有效性,检查请求资源是否被修改。
4.将远程扩展词典文件置于tomca/webapps/ROOT文件夹下面,启动远程tomcat。
5.启用新IK分词器
功能实现!
实现代码github地址:https://github.com/tandormocha/MyIKAnalyzer